This Draft Registration Statement has not been filed publicly with the Securities and Exchange Commission and all information contained herein remains confidential.
As confidentially submitted to the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 26, 2013.
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 20-F/A
Amendment No. 4
| R | REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR (g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| Or | |
| £ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 For the fiscal year ended_____________________________________________________ |
| Or | |
| £ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| Or | |
| £ | SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File No. ______-______
Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., an Israeli Limited Company
(Translation of the Registrant’s name into English)
Israel
(Jurisdiction of incorporation)
10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, P.O. Box 7537, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel
(Address of principal executive offices)
Motti Farbstein
Chief Operating and Financial Officer
Tel: +972 (3) 924-1114
Fax: +972 (3) 924-9378
motti@canfite.co.il
10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, P.O. Box 7537, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel
(Name, Telephone, E-mail and/or Facsimile number and Address of Company Contact Person)
Copies of communications to:
| Robert L. Grossman, Esq. | Ronen Kantor, Adv. |
| Greenberg Traurig, P.A. | Kantor & Co. Law Offices |
| 333 Avenue of the Americas | 12 Abba Hillel Silver Rd. |
| (333 S.E. 2nd Avenue) | Ramat Gan, Israel 52506 |
| Miami, Florida 33131 | Tel: 972-3-6133371 |
| Tel: (305) 579-0500 | Fax: 972-3-6133372 |
| Fax: (305) 961-5756 |
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
None
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
American Depositary Shares, each representing 2 Ordinary Shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share
(Title of Class)
Ordinary Shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share*
(Title of Class)
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act:
None
* Not for trading, but only in connection with the registration of the American Depositary Shares.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Yes ¨ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such a shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ¨ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one): Large accelerated filer ¨ Accelerated filer ¨ Non-accelerated filer x
Indicate by check
mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
| U.S. GAAP ¨ | International Financial Reporting Standards | Other ¨ |
| as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board x |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the Registrant has elected to follow: Item 17 ¨ Item 18 ¨
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No ¨
(APPLICABLE ONLY TO ISSUERS INVOLVED IN BANKRUPTCY PROCEEDINGS DURING THE PAST FIVE YEARS)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed all documents and reports required to be filed by Sections 12, 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 subsequent to the distribution of securities under a plan confirmed by a court. Yes ¨ No ¨
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| PART I | 8 |
| ITEM 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisers. | 8 |
| ITEM 2. Offer Statistics and Expected Timetable. | 9 |
| ITEM 3. Key Information. | 9 |
| ITEM 4. Information on the Company | 31 |
| ITEM 4A. Unresolved Staff Comments | 73 |
| ITEM 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects | 73 |
| ITEM 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees | 86 |
| ITEM 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions | 102 |
| ITEM 8. Financial Information | 103 |
| ITEM 9. The Offer and Listing | 104 |
| ITEM 10. Additional Information | 105 |
| ITEM 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | 124 |
| ITEM 12. Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities | 124 |
| PART II | 132 |
| ITEM 13. Defaults, Dividend Arrearages and Delinquencies | 132 |
| ITEM 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds | 132 |
| ITEM 15. Controls and Procedures | 132 |
| ITEM 16. [RESERVED] | 132 |
| ITEM 16A. Audit Committee Financial Expert | 132 |
| ITEM 16B. Code of Ethics | 132 |
| ITEM 16C. Principal Accountant Fees and Services | 132 |
| ITEM 16D. Exemptions from the Listing Standards for Audit Committees | 133 |
| ITEM 16E. Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers | 133 |
| ITEM 16F. Change in Registrant’s Certifying Accountant | 133 |
| ITEM 16G. Corporate Governance | 133 |
| ITEM 16H. Mine Safety Disclosure | 133 |
| PART III | 133 |
| ITEM 17. Financial Statements | 133 |
| ITEM 18. Financial Statements | 133 |
| ITEM 19. Exhibits | 134 |
| 3 |
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Registration Statement on Form 20-F contains forward-looking statements, about our expectations, beliefs or intentions regarding, among other things, our product development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations, strategies or prospects. In addition, from time to time, we or our representatives have made or may make forward-looking statements, orally or in writing. Forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking words such as “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “may,” “should” or “anticipate” or their negatives or other variations of these words or other comparable words or by the fact that these statements do not relate strictly to historical or current matters. These forward-looking statements may be included in, but are not limited to, various filings made by us with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC, press releases or oral statements made by or with the approval of one of our authorized executive officers. Forward-looking statements relate to anticipated or expected events, activities, trends or results as of the date they are made. Because forward-looking statements relate to matters that have not yet occurred, these statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from any future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Many factors could cause our actual activities or results to differ materially from the activities and results anticipated in forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to, the factors summarized below.
This Registration Statement on Form 20-F identifies important factors which could cause our actual results to differ materially from those indicated by the forward-looking statements, particularly those set forth under the heading “Risk Factors.” The factors that could affect our actual results include the following:
| · | we have a limited operating history and we do not expect to become profitable in the near future; |
| · | we have not yet commercialized any products or technologies, and we may never become profitable; |
| · | our product candidates are at various stages of clinical and preclinical development and may never be commercialized; |
| · | we might be unable to develop product candidates that will achieve commercial success in a timely and cost-effective manner, or ever; |
| · | we may be forced to abandon development of certain products altogether, which will significantly impair our ability to generate product revenues; |
| · | it is highly likely that we will need to raise additional capital to meet our business requirements in the future, and such capital raising may be costly or difficult to obtain and will dilute current shareholders’ ownership interests; |
| · | if we fail to obtain necessary funds for our operations, we will be unable to maintain and improve our patented or licensed technology, and we will be unable to develop and commercialize our products and technologies; |
| · | our current pipeline is based on our platform technology utilizing the Gi protein associated A3 adenosine receptor, or A3AR, as a potent therapeutic target and currently includes three molecules, the CF101, CF102 and CF602 product candidates, of which CF101 is the most advanced. Failure to develop these molecules will have a material adverse effect on the Company; |
| · | clinical trials are very expensive, time-consuming and difficult to design and implement, and, as a result, we may suffer delays or suspensions in future trials which would have a material adverse effect on our ability to generate revenues; |
| 4 |
| · | if we acquire or license additional technology or product candidates, we may incur a number of costs, may have integration difficulties and may experience other risks that could harm our business and results of operations; |
| · | the manufacture of our product candidates is a straight forward chemical synthesis process, however, if one of our materials suppliers encounters problems manufacturing our products, our business could suffer; |
| · | we do not currently have sales, marketing or distribution capabilities or experience, and we are unable to effectively sell, market or distribute our product candidates now and we do not expect to be able to do so in the future. The failure to enter into agreements with third parties that are capable of performing these functions would have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations; |
| · | we will to some extent rely on third parties to implement our manufacturing and supply strategies. Failure of these third parties in any respect could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition; |
| · | we depend on key members of our management and consultants and will need to add and retain additional leading experts. Failure to retain our management and consulting team and add additional leading experts could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition; |
| · | under current U.S. and Israeli law, we may not be able to enforce employees’ covenants not to compete and therefore may be unable to prevent our competitors from benefiting from the expertise of some of our former employees; |
| · | we face significant competition and continuous technological change, and developments by competitors may render our products or technologies obsolete or non-competitive. If we cannot successfully compete with new or existing products, our marketing and sales will suffer and we may not ever be profitable; |
| · | we may suffer losses from product liability claims if our product candidates cause harm to patients; |
| · | our product candidates will remain subject to ongoing regulatory requirements even if they receive marketing approval, and if we fail to comply with these requirements, we could lose these approvals, and the sales of any approved commercial products could be suspended; |
| · | we may not be able to successfully grow and expand our business. Failure to manage our growth effectively will have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition; |
| · | we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth. These difficulties could increase our losses; |
| · | if we are unable to obtain adequate insurance, our financial condition could be adversely affected in the event of uninsured or inadequately insured loss or damage. Our ability to effectively recruit and retain qualified officers and directors could also be adversely affected if we experience difficulty in obtaining adequate directors’ and officers’ liability insurance; |
| · | if we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or detect fraud. Consequently, investors could lose confidence in our financial reporting and this may decrease the trading price of our stock; |
| · | potential political, economic and military instability in the State of Israel, where key members of our senior management and our research and development facilities are located, may adversely affect our results of operations; |
| 5 |
| · | recent disruptions in the financial markets and economic conditions could affect our ability to raise capital and could disrupt or delay the performance of our third-party contractors and suppliers; |
| · | as an “emerging growth company” under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, or JOBS Act, we are permitted to, and intend to, rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements; |
| · | we license from the U.S. National Institutes of Health, or the NIH, and Leiden University of the Netherlands, or Leiden University, intellectual property which protects certain small molecules which target the A3AR, in furtherance of our platform technology, and we could lose our rights to these licenses if a dispute with the NIH or Leiden University arises or if we fail to comply with the financial and other terms of the licenses; |
| · | the failure to obtain or maintain patents, licensing agreements, including our current licensing agreements, and other intellectual property could impact our ability to compete effectively; |
| · | costly litigation may be necessary to protect our intellectual property rights and we may be subject to claims alleging the violation of the intellectual property rights of others; |
| · | we rely on confidentiality agreements that could be breached and may be difficult to enforce, which could result in third parties using our intellectual property to compete against us; |
| · | international patent protection is particularly uncertain, and if we are involved in opposition proceedings in foreign countries, we may have to expend substantial sums and management resource; |
| · | we may be unable to protect the intellectual property rights of the third parties from whom we license certain of our intellectual property or with whom we have entered into other strategic relationships; |
| · | we are subject to government regulations and we may experience delays in obtaining required regulatory approvals in the United States to market our proposed product candidates; |
| · | we expect the healthcare industry to face increased limitations with respect to reimbursement as a result of healthcare reform, which could adversely affect third-party coverage of our products and how much or under what circumstances healthcare providers will prescribe or administer our products; |
| · | we are subject to federal anti-kickback laws and regulations. Our failure to comply with these laws and regulations could have adverse consequences to us; |
| · | we may be a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes in 2013 or in any subsequent year. There may be negative tax consequences for U.S. taxpayers that are holders of our ordinary shares or our American Depositary Shares, or ADSs; |
| · | the market price of our ordinary shares is, and the market price of our ADSs will be, subject to fluctuation, which could result in substantial losses by our investors; |
| · | substantial sales of our ordinary shares or ADSs either on the TASE or on the NYSE MKT, as applicable, may cause the market price of our ordinary shares or ADSs to decline; |
| · | raising additional capital by issuing securities may cause dilution to existing shareholders; |
| · | our ADS holders are not shareholders and do not have shareholder rights; |
| · | our ordinary shares and our ADSs will be traded on different markets and this may result in price variations; |
| 6 |
| · | our ADSs have a limited prior trading history in the United States, and an active market may not develop, which may limit the ability of our investors to sell our ADSs in the United States; |
| · | we will incur significant additional increased costs as a result of the listing of our ADSs for trading on the NYSE MKT, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives as well as to compliance with ongoing U.S. and Israeli reporting requirements; |
| · | as a foreign private issuer, we are permitted to follow certain home country corporate governance practices instead of applicable SEC and NYSE MKT requirements, which may result in less protection than is accorded to investors under rules applicable to domestic issuers; |
| · | if we are unable to satisfy the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act as they apply to a foreign private issuer that is listing on a U.S. exchange for the first time, or our internal controls over financial reporting are not effective, the reliability of our financial statements may be questioned and our share price and ADS price may suffer; |
| · | we conduct our operations in Israel and therefore our results may be adversely affected by political, economic and military instability in Israel and its region; |
| · | our operations may be disrupted as a result of the obligation of Israeli citizens to perform military service; |
| · | because a certain portion of our expenses is incurred in currencies other than the NIS, our results of operations may be harmed by currency fluctuations and inflation; |
| · | provisions of Israeli law may delay, prevent or otherwise impede a merger with, or an acquisition of, our Company, which could prevent a change of control, even when the terms of such a transaction are favorable to us and our shareholders; |
| · | it may be difficult to enforce a U.S. judgment against us and our officers and directors named in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F in Israel or the United States, or to serve process on our officers and directors; and |
| · | your rights and responsibilities as a shareholder will be governed by Israeli law which may differ in some respects from the rights and responsibilities of shareholders of U.S. companies. |
The risk factors included in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F are not necessarily all of the important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in any of our forward-looking statements. Given these uncertainties, readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements.
All forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf speak only as of the date of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F and are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements included in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. We undertake no obligations to update or revise forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances that arise after the date made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. In evaluating forward-looking statements, you should consider these risks and uncertainties.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
Market data and certain industry data and forecasts used throughout this Registration Statement on Form 20-F were obtained from internal company surveys, market research, consultant surveys, publicly available information, reports of governmental agencies and industry publications and surveys. Industry surveys, publications, consultant surveys and forecasts generally state that the information contained therein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but that the accuracy and completeness of such information is not guaranteed. We have not independently verified any of the data from third-party sources, nor have we ascertained the underlying economic assumptions relied upon therein. Similarly, internal surveys, industry forecasts and market research, which we believe to be reliable based upon our management’s knowledge of the industry, have not been independently verified. Forecasts are particularly likely to be inaccurate, especially over long periods of time. In addition, we do not necessarily know what assumptions regarding general economic growth were used in preparing the forecasts we cite. Statements as to our market position are based on the most currently available data. While we are not aware of any misstatements regarding the industry data presented in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F, our estimates involve risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed under the heading “Risk Factors” in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
The Company effected a reverse share split with respect to its ordinary shares on May 12, 2013. The impact of such reverse share split on the Company, its shareholders and the information contained in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F is reflected in this amendment to this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
| 7 |
PART I
ITEM 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisers.
A. Directors and Senior Management.
The following table lists the members of our Board of Directors. The business address for all directors is 10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, P.O. Box 7537, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel. Avigdor Kaplan, our former Chairman of the Board, was not re-elected to the Board of Directors at the annual shareholders meeting held on May 2, 2013. On May 30, 2013, Ilan Cohn was appointed as the new Chairman of the Board.
| Name | Position(s) | |
| Ilan Cohn, Ph.D. | Chairman of the Board | |
| Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. | Chief Executive Officer, Director | |
| Liora Lev | Director, Audit Committee, Balance Sheet Committee and Compensation Committee member | |
| Guy Regev | Director | |
| Avraham Sartani, M.D. | Director | |
| Yechezkel Barenholz, Ph.D. | Director, Audit Committee, Balance Sheet Committee and Compensation Committee member | |
| Gil Oren | Director, Audit Committee, Balance Sheet Committee and Compensation Committee member |
The following table lists our executive officers. The business address for all executive officers is 10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, P.O. Box 7537, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel.
| Name | Position(s) | |
| Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. | Chief Executive Officer, Director | |
| Motti Farbstein | Chief Operating and Financial Officer | |
| Barak Singer | Vice President, Business Development |
B. Advisers.
Not applicable.
| 8 |
C. Auditors.
Our auditor since our inception in 1994 has been Kost Forer Gabbay & Kasierer, an independent registered public accounting firm and member firm of Ernst & Young Global Limited. Kost Forer Gabbay & Kasierer audited our consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, and for the three years ended December 31, 2012. The address of Kost Forer Gabbay & Kasierer is 3 Aminadav St., Tel-Aviv 67067, Israel.
ITEM 2. Offer Statistics and Expected Timetable.
Not applicable.
ITEM 3. Key Information.
A. Selected Financial Data.
The following table sets forth our selected consolidated financial data for the periods ended and as of the dates indicated. The following selected consolidated financial data for our company should be read in conjunction with the financial information, “Item 5. Operational and Financial Review and Prospects” and other information provided elsewhere in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F and our consolidated financial statements and related notes. The selected consolidated financial data in this section is not intended to replace the consolidated financial statements and is qualified in its entirety thereby. In the opinion of our management, our unaudited consolidated financial statements contain all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of our financial position, results of operations and cash flows as of and for the periods indicated therein.
We derived the selected consolidated financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
Our consolidated financial statements included in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F were prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and reported in Israeli New Shekels, or NIS.
| Consolidated Statements Of | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operations Data: | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NIS | Convenience translation to US $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues | 5,481 | 3,299 | 2,644 | 1,785 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development, expenses net | 25,621 | 13,841 | 9,993 | 12,969 | 13,160 | 3,525 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 7,308 | 5,994 | 6,005 | 7,081 | 9,272 | 2,484 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income | (88 | ) | (42 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating loss | 27,448 | 16,536 | 13,354 | 18,177 | 22,390 | 5,998 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other expense – due to M&A | - | - | - | 11,496 | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial expenses | 723 | 36 | 356 | 232 | 27 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Financial income | 2,103 | 847 | 897 | 1,669 | 541 | 145 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes on income | 548 | 263 | 235 | 191 | 11 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | 26,616 | 15,988 | 13,048 | 28,427 | 21,887 | 5,863 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | - | - | - | (92 | ) | (7 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss | 26,616 | 15,988 | 13,048 | 28,335 | 21,880 | 5,861 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss per ordinary share | 3.50 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 2.73 | 2.07 | 0.55 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Number of ordinary shares used in computing loss per ordinary share | 7,684,410 | 8,130,135 | 8,687,311 | 9,352,990 | 10,050,927 | 10,050,927 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 9 |
| Consolidated Balance | As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sheet Data: | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands NIS) | (in thousands NIS) | (in thousands NIS) | (in thousands NIS) | (in thousands NIS) | (in US $ thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 19,963 | 18,991 | 17,506 | 14,622 | 4,278 | 1,146 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other receivables | 870 | 448 | 550 | 3,760 | 1,672 | 448 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed assets | 1,029 | 662 | 490 | 278 | 159 | 42 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 21,862 | 20,101 | 18,546 | 18,660 | 6,109 | 1,636 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 7,068 | 6,615 | 5,474 | 6,133 | 8,754 | 2,345 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 14,794 | 13,486 | 13,072 | 12,527 | (2,645 | ) | (709 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
We report our financial statements in NIS. This Registration Statement on Form 20-F contains conversions of NIS amounts into U.S. dollars at specific rates solely for the convenience of the reader. Unless otherwise noted, for the purposes of annual financial data, all conversions from NIS to U.S. dollars and from U.S. dollars to NIS were made at a rate of 3.733 NIS to $1.00 U.S. dollar, the daily representative rates in effect as of December 31, 2012. No representation is made that the NIS amounts referred to in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F could have been or could be converted into U.S. dollars at any particular rate or at all.
The following table sets forth information regarding the exchange rates of U.S. dollars per Israeli New Shekels for the periods indicated. Average rates are calculated by using the daily representative rates as reported by the Bank of Israel on the last day of each month during the periods presented.
| NIS per U.S. $ | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | High | Low | Average | Period End | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 4.084 | 3.700 | 3.858 | 3.733 | ||||||||||||
| 2011 | 3.821 | 3.363 | 3.579 | 3.821 | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 3.894 | 3.549 | 3.732 | 3.549 | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 4.256 | 3.690 | 3.923 | 3.775 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 4.022 | 3.230 | 3.586 | 3.802 | ||||||||||||
| NIS per U.S. $ | ||||||||||||||||
| Month Ended | High | Low | Average | Period End | ||||||||||||
| June 2013 | 3.687 | 3.594 | 3.630 | 3.618 | ||||||||||||
| May 2013 | 3.707 | 3.556 | 3.629 | 3.683 | ||||||||||||
| April 2013 | 3.633 | 3.592 | 3.620 | 3.594 | ||||||||||||
| March 2013 | 3.733 | 3.637 | 3.692 | 3.648 | ||||||||||||
| February 2013 | 3.733 | 3.663 | 3.693 | 3.708 | ||||||||||||
| January 2013 | 3.791 | 3.714 | 3.739 | 3.728 | ||||||||||||
B. Capitalization and Indebtedness.
The following table sets forth our consolidated capitalization as of December 31, 2012. This table should be read in conjunction with “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
| As of December 31, 2012 | ||||||||
| (NIS in thousands) | (U.S.$ in thousands)(1) | |||||||
| Warrants | 1,279 | 343 | ||||||
| Liability for employees benefits | 68 | 18 | ||||||
| Shareholders’ equity: | ||||||||
| Ordinary shares | 2,734 | 732 | ||||||
| Share premium | 233,754 | 62,618 | ||||||
| Capital reserve for share-based payment transactions | 15,279 | 4,093 | ||||||
| Options exercisable into shares (series 9) | 669 | 179 | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation reserve | 84 | 23 | ||||||
| Treasury shares | (5,805 | ) | (1,555 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated loss | (251,359 | ) | (67,334 | ) | ||||
| Minority interests | 1,999 | 535 | ||||||
| Total capitalization (debt and equity) | (1,298 | ) | (348 | ) | ||||
| (1) | Calculated using the exchange rate reported by the Bank of Israel for December 31, 2012 at the rate of one U.S. dollar per NIS 3.733. |
C. Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds.
Not applicable.
| 10 |
D. Risk Factors
Risks Related to Our Company and Our Business
We have a limited operating history and we do not expect to become profitable in the near future.
We are a development stage biopharmaceutical company with a limited operating history. We are not profitable and have incurred losses since our inception. We have not generated any revenue since our inception other than income derived from out-licensing agreements, and we continue to incur research and development and general and administrative expenses related to our operations. As of December 31, 2012, the Company had an accumulated loss of NIS 252,404,000. We expect to continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future, and these losses will likely increase as we:
| · | initiate and manage pre-clinical development and clinical trials for our current and new product candidates; |
| · | seek regulatory approvals for our product candidates; |
| · | implement internal systems and infrastructures; |
| · | seek to license in additional technologies to develop; |
| · | hire management and other personnel; and |
| · | move towards commercialization. |
If our product candidates fail in clinical trials or do not gain regulatory clearance or approval, or if our product candidates do not achieve market acceptance, we may never become profitable. Even if we achieve profitability in the future, we may not be able to sustain profitability in subsequent periods. Accordingly, it is difficult to evaluate our business prospects. Moreover, our prospects must be considered in light of the risks and uncertainties encountered by an early-stage company and in highly regulated and competitive markets, such as the biopharmaceutical market, where regulatory approval and market acceptance of our products are uncertain. There can be no assurance that our efforts will ultimately be successful or result in revenues or profits.
We have not yet commercialized any products or technologies, and we may never become profitable.
We have not yet commercialized any products or technologies, and we may never be able to do so. We do not know when or if we will complete any of our product development efforts, obtain regulatory approval for any product candidates incorporating our technologies or successfully commercialize any approved products. Even if we are successful in developing products that are approved for marketing, we will not be successful unless these products gain market acceptance for appropriate indications at favorable reimbursement rates. The degree of market acceptance of these products will depend on a number of factors, including:
| · | the timing of regulatory approvals in the countries, and for the uses, we seek; |
| · | the competitive environment; |
| · | the establishment and demonstration in the medical community of the safety and clinical efficacy of our products and their potential advantages over existing therapeutic products; |
| · | the Company’s ability to enter into strategic agreements with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with strong marketing and sales capabilities; |
| · | the adequacy and success of distribution, sales and marketing efforts; and |
| 11 |
| · | the pricing and reimbursement policies of government and third-party payors, such as insurance companies, health maintenance organizations and other plan administrators. |
Physicians, patients, thirty-party payors or the medical community in general may be unwilling to accept, utilize or recommend, and in the case of third-party payors, cover any of our products or products incorporating our technologies. As a result, we are unable to predict the extent of future losses or the time required to achieve profitability, if at all. Even if we successfully develop one or more products that incorporate our technologies, we may not become profitable.
Our product candidates are at various stages of clinical and preclinical development and may never be commercialized.
Our product candidates are at various stages of clinical development and may never be commercialized. The progress and results of any future pre-clinical testing or future clinical trials are uncertain, and the failure of our product candidates to receive regulatory approvals will have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition to the extent we are unable to commercialize any products. None of our product candidates has received regulatory approval for commercial sale. In addition, we face the risks of failure inherent in developing therapeutic products. Our product candidates are not expected to be commercially available for several years, if at all.
In addition, our product candidates must satisfy rigorous standards of safety and efficacy before they can be approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or the FDA, and foreign regulatory authorities for commercial use. The FDA and foreign regulatory authorities have full discretion over this approval process. We will need to conduct significant additional research, involving testing in animals and in humans, before we can file applications for product approval. Typically, in the pharmaceutical industry, there is a high rate of attrition for product candidates in pre-clinical testing and clinical trials. Also, satisfying regulatory requirements typically takes many years, is dependent upon the type, complexity and novelty of the product and requires the expenditure of substantial resources. Success in pre-clinical testing and early clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful. For example, a number of companies in the pharmaceutical industry, including biotechnology companies, have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials, even after promising results in earlier trials. In addition, delays or rejections may be encountered based upon additional government regulation, including any changes in FDA policy, during the process of product development, clinical trials and regulatory reviews.
In order to receive FDA approval or approval from foreign regulatory authorities to market a product candidate or to distribute our products, we must demonstrate through pre-clinical testing and through human clinical trials that the product candidate is safe and effective for its intended uses (e.g., treatment of a specific condition in a specific way subject to contradictions and other limitations). Even if we comply with all FDA requests, the FDA may ultimately reject one or more of our new drug applications, or NDA, or grant approval for a narrowly intended use that is not commercially feasible. We might not obtain regulatory approval for our drug candidates in a timely manner, if at all. Failure to obtain FDA approval of any of our drug candidates in a timely manner or at all will severely undermine our business by reducing the number of salable products and, therefore, corresponding product revenues.
We might be unable to develop product candidates that will achieve commercial success in a timely and cost-effective manner, or ever.
Even if regulatory authorities approve our product candidates, they may not be commercially successful. Our product candidates may not be commercially successful because government agencies and other third-party payors may not cover the product or the coverage may be too limited to be commercially successful; physicians and others may not use or recommend our products, even following regulatory approval. A product approval, assuming one issues, may limit the uses for which the product may be distributed thereby adversely affecting the commercial viability of the product. Third parties may develop superior products or have proprietary rights that preclude us from marketing our products. We also expect that at least some of our product candidates will be expensive, if approved. Patient acceptance of and demand for any product candidates for which we obtain regulatory approval or license will depend largely on many factors, including but not limited to the extent, if any, of reimbursement of costs by government agencies and other third-party payors, pricing, the effectiveness of our marketing and distribution efforts, the safety and effectiveness of alternative products, and the prevalence and severity of side effects associated with our products. If physicians, government agencies and other third-party payors do not accept our products, we will not be able to generate significant revenue.
| 12 |
We may be forced to abandon development of certain products altogether, which will significantly impair our ability to generate product revenues.
Upon the completion of any clinical trial, the results might not support the claims sought by us. Further, success in pre-clinical testing and early clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful, and the results of later clinical trials may not replicate the results of prior clinical trials and pre-clinical testing. The clinical trial process may fail to demonstrate that our product candidates are safe for humans and effective for indicated uses. Any such failure may cause us to abandon a product candidate and may delay development of other product candidates. Any delay in, or termination or suspension of, our clinical trials will delay the requisite filings with the FDA and, ultimately, our ability to commercialize our product candidates and generate product revenues. If the clinical trials do not support our product claims, the completion of development of such product candidates may be significantly delayed or abandoned, which will significantly impair our ability to generate product revenues and will materially adversely affect our results of operations.
It is highly likely that we will need to raise additional capital to meet our business requirements in the future, and such capital raising may be costly or difficult to obtain and will dilute current shareholders’ ownership interests.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including the progress and results of our clinical trials, the duration and cost of discovery and preclinical development, and laboratory testing and clinical trials for our product candidates, the timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates, the number and development requirements of other product candidates that we pursue, and the costs of activities, such as product marketing, sales, and distribution. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development and commercialization of our product candidates, we are unable to estimate the amounts of increased capital outlays and operating expenditures associated with our anticipated clinical trials. It is highly likely that we will need to raise additional funds through public or private debt or equity financings to meet various objectives including, but not limited to:
| · | funding laboratory testing, clinical and pre clinical trials; |
| · | research and development of new products; |
| · | pursuing growth opportunities, including more rapid expansion; |
| · | acquiring and/or licensing complementary products; |
| · | making capital improvements to improve our infrastructure; |
| · | hiring qualified management and key employees; |
| · | responding to competitive pressures; |
| · | complying with regulatory and registration requirements; and |
| · | maintaining compliance with applicable laws. |
Any additional capital raised through the sale of equity or equity-linked securities may dilute our current shareholders’ ownership in us and could also result in a decrease in the market price of our ordinary shares. The terms of those securities issued by us in future capital transactions may be more favorable to new investors and may include the issuance of warrants or other derivative securities, which may have a further dilutive effect.
Furthermore, any debt or equity financing that we may need may not be available on terms favorable to us, or at all. If we obtain funding through a strategic collaboration or licensing arrangement, we may be required to relinquish our rights to certain of our technologies, products or marketing territories. If we are unable to obtain required additional capital, we may have to curtail our growth plans or cut back on existing business, and we may not be able to continue operating if we do not generate sufficient revenues from operations needed to stay in business.
| 13 |
We may incur substantial costs in pursuing future capital financing, including investment banking fees, legal fees, accounting fees, securities law compliance fees, printing and distribution expenses and other costs. We may also be required to recognize non-cash expenses in connection with certain securities we issue, such as convertible notes and warrants, which may adversely impact our financial condition.
If we fail to obtain necessary funds for our operations, we will be unable to maintain and improve our patented or licensed technology, and we will be unable to develop and commercialize our products and technologies.
Our present and future capital requirements depend on many factors, including:
| · | the level of research and development investment required to develop our product candidates, and maintain and improve our patented or licensed technology position; |
| · | the costs of obtaining or manufacturing product candidates for research and development and testing; |
| · | the results of preclinical and clinical testing, which can be unpredictable in product candidate development; |
| · | changes in product candidate development plans needed to address any difficulties that may arise in manufacturing, preclinical activities or clinical studies; |
| · | our ability and willingness to enter into new agreements with strategic partners and the terms of these agreements; |
| · | our success rate in preclinical and clinical efforts associated with milestones and royalties; |
| · | the costs of investigating patents that might block us from developing potential product candidates; |
| · | the costs of recruiting and retaining qualified personnel; |
| · | the time and costs involved in obtaining regulatory approvals; |
| · | the number of product candidates we pursue; |
| · | our revenues, if any; |
| · | the costs of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights; and |
| · | our need or decision to acquire or license complementary technologies or new platform or product candidate targets. |
If we are unable to obtain the funds necessary for our operations, we will be unable to maintain and improve our patented technology, and we will be unable to develop and commercialize our products and technologies, which would materially and adversely affect our business, liquidity and results of operations.
| 14 |
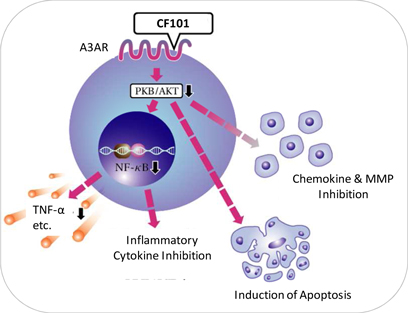
Our current pipeline is based on our platform technology utilizing the Gi protein associated A3 adenosine receptor, or A3AR, as a potent therapeutic target and currently includes three molecules, the CF101, CF102 and CF602 product candidates, of which CF 101 is the most advanced. Failure to develop these molecules will have a material adverse effect on the Company.
Our current pipeline is based on a platform technology where we target the A3AR with highly selective ligands, or small signal triggering molecules that bind to specific cell surface receptors, such as the A3AR, including CF101, CF102 and CF602, currently developed for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic disorders. A3ARs are structures found in cell surfaces that record and transfer messages from small molecules or ligands, such as CF101, CF102 and CF602 to the rest of the cell. CF101 is the most advanced of our drug candidates. As such, we are currently dependent on only three molecules for our potential commercial success, and any safety or efficacy concerns related to such molecules would have a significant impact on our business. Failure to develop our drug candidates, in whole or in part, will have a material adverse effect on the Company.
Clinical trials are very expensive, time-consuming and difficult to design and implement, and, as a result, we may suffer delays or suspensions in future trials which would have a material adverse effect on our ability to generate revenues.
Human clinical trials are very expensive and difficult to design and implement, in part because they are subject to rigorous regulatory requirements. Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA, may preclude clinical trials from proceeding. Additionally, the clinical trial process is time-consuming, failure can occur at any stage of the trials, and we may encounter problems that cause us to abandon or repeat clinical trials. The commencement and completion of clinical trials may be delayed by several factors, including:
| · | unforeseen safety issues; |
| · | determination of dosing issues; |
| · | lack of effectiveness or efficacy during clinical trials; |
| · | failure of third party suppliers to perform final manufacturing steps for the drug substance; |
| · | slower than expected rates of patient recruitment and enrollment; |
| · | lack of healthy volunteers and patients to conduct trials; |
| · | inability to monitor patients adequately during or after treatment; |
| · | failure of third party contract research organizations to properly implement or monitor the clinical trial protocols; |
| · | failure of institutional review boards to approve our clinical trial protocols; |
| · | inability or unwillingness of medical investigators and institutional review boards to follow our clinical trial protocols; and |
| · | lack of sufficient funding to finance the clinical trials. |
We have experienced the risks involved with conducting clinical trials, including but not limited to, increased expense and delay. For example, two Phase IIb studies in rheumatoid arthritis, or RA, utilizing CF101 in combination with methotrexate, a generic drug commonly used for treating RA patients, or MTX, failed to reach their primary end points. The Company believes that this may have been due to low A3AR expression in the subpopulation of RA patients that did not respond well to treatment with MTX. Because of their low A3AR expression, such patients also did not respond well to treatment with CF101. The Company was not aware of this when it designed the studies. As such, the Company must now conduct tests of CF101 as a standalone therapy in patients with A3AR expression levels above a certain threshold.
In addition, we or regulatory authorities may suspend our clinical trials at any time if it appears that we are exposing participants to unacceptable health risks or if the regulatory authorities find deficiencies in our regulatory submissions or the conduct of these trials. Any suspension of clinical trials will delay possible regulatory approval, if any, and adversely impact our ability to develop products and generate revenue.
If we acquire or license additional technology or product candidates, we may incur a number of costs, may have integration difficulties and may experience other risks that could harm our business and results of operations.
We may acquire and license additional product candidates and technologies. Any product candidate or technology we license from others or acquire will likely require additional development efforts prior to commercial sale, including extensive pre-clinical or clinical testing, or both, and approval by the FDA and applicable foreign regulatory authorities, if any. All product candidates are prone to risks of failure inherent in pharmaceutical product development, including the possibility that the product candidate or product developed based on licensed technology will not be shown to be sufficiently safe and effective for approval by regulatory authorities. In addition, we cannot assure you that any product candidate that we develop based on acquired or licensed technology that is granted regulatory approval will be manufactured or produced economically, successfully commercialized or widely accepted in the marketplace. Moreover, integrating any newly acquired product candidates could be expensive and time-consuming. If we cannot effectively manage these aspects of our business strategy, our business may not succeed.
| 15 |
The manufacture of our product candidates is a chemical synthesis process and if one of our materials suppliers encounters problems manufacturing our products, our business could suffer.
The FDA and foreign regulators require manufacturers to register manufacturing facilities. The FDA and foreign regulators also inspect these facilities to confirm compliance with requirements that the FDA or foreign regulators establish. We do not intend to engage in the manufacture of our products other than for pre-clinical and clinical studies, but we or our materials suppliers may face manufacturing or quality control problems causing product production and shipment delays or a situation where we or the supplier may not be able to maintain compliance with the FDA’s or foreign regulators’ requirements necessary to continue manufacturing our drug substance. Drug manufacturers are subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA, the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency, or DEA, and corresponding foreign regulators to ensure strict compliance with requirements and other governmental regulations and corresponding foreign standards. Any failure to comply with DEA requirements or FDA or foreign regulatory requirements could adversely affect our clinical research activities and our ability to market and develop our product candidates.
We do not currently have sales, marketing or distribution capabilities or experience, and we are unable to effectively sell, market or distribute our product candidates now and we do not expect to be able to do so in the future. The failure to enter into agreements with third parties that are capable of performing these functions would have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We do not currently have and we do not expect to develop sales, marketing and distribution capabilities. If we are unable to enter into agreements with third parties to perform these functions, we will not be able to successfully market any of our platforms or product candidates. In order to successfully market any of our platform or product candidates, we must make arrangements with third parties to perform these services.
As we do not intend to develop a marketing and sales force with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities, we will be unable to market any of our product candidates directly. To promote any of our potential products through third parties, we will have to locate acceptable third parties for these functions and enter into agreements with them on acceptable terms, and we may not be able to do so. Any third-party arrangements we are able to enter into may result in lower revenues than we could achieve by directly marketing and selling our potential products. In addition, to the extent that we depend on third parties for marketing and distribution, any revenues we receive will depend upon the efforts of such third parties, as well as the terms of our agreements with such third parties, which cannot be predicted in most cases at this time. As a result, we might not be able to market and sell our products in the United States or overseas, which would have a material adverse effect on us.
We will to some extent rely on third parties to implement our manufacturing and supply strategies. Failure of these third parties in any respect could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If our current and future manufacturing and supply strategies are unsuccessful, then we may be unable to conduct and complete any future pre-clinical or clinical trials or commercialize our product candidates in a timely manner, if at all. Completion of any potential future pre-clinical or clinical trials and commercialization of our product candidates will require access to, or development of, facilities to manufacture a sufficient supply of our product candidates. We do not have the resources, facilities or experience to manufacture our product candidates for commercial purposes on our own and do not intend to develop or acquire facilities for the manufacture of product candidates for commercial purposes in the foreseeable future. We may rely on contract manufacturers to produce sufficient quantities of our product candidates necessary for any pre-clinical or clinical testing we undertake in the future. Such contract manufacturers may be the sole source of production and they may have limited experience at manufacturing, formulating, analyzing, filling and finishing our types of product candidates.
We also intend to rely on third parties to supply the requisite materials needed for the manufacturing of our active pharmaceutical ingredients, or API. There may be a limited supply of these requisite materials. We might not be able to enter into agreements that provide us assurance of availability of such components in the future from any supplier. Our potential suppliers may not be able to adequately supply us with the components necessary to successfully conduct our pre-clinical and clinical trials or to commercialize our product candidates. If we cannot acquire an acceptable supply of the requisite materials to produce our product candidates, we will not be able to complete pre-clinical and clinical trials and will not be able to market or commercialize our product candidates
| 16 |
We depend on key members of our management and key consultants and will need to add and retain additional leading experts. Failure to retain our management and consulting team and add additional leading experts could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
We are highly dependent on our executive officers and other key management and technical personnel. Our failure to retain our Chief Executive Officer, Pnina Fishman, Ph.D., who has developed much of the technology we utilize today, or any other key management and technical personnel, could have a material adverse effect on our future operations. Our success is also dependent on our ability to attract, retain and motivate highly trained technical, and management personnel, among others, to continue the development and commercialization of our current and future products. We presently maintain a life insurance policy on our Chief Executive Officer, Pnina Fishman.
Our success also depends on our ability to attract, retain and motivate personnel required for the development, maintenance and expansion of our activities. There can be no assurance that we will be able to retain our existing personnel or attract additional qualified employees or consultants. The loss of key personnel or the inability to hire and retain additional qualified personnel in the future could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operation.
Under current U.S. and Israeli law, we may not be able to enforce employees’ covenants not to compete and therefore may be unable to prevent our competitors from benefiting from the expertise of some of our former employees.
We have entered into non-competition agreements with our key employees, in most cases within the framework of their employment agreements. These agreements prohibit our key employees, if they cease working for us, from competing directly with us or working for our competitors for a limited period. Under applicable U.S. and Israeli law, we may be unable to enforce these agreements. If we cannot enforce our non-competition agreements with our employees, then we may be unable to prevent our competitors from benefiting from the expertise of our former employees, which could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and ability to capitalize on our proprietary information.
We face significant competition and continuous technological change, and developments by competitors may render our products or technologies obsolete or non-competitive. If we cannot successfully compete with new or existing products, our marketing and sales will suffer and we may not ever be profitable.
We will compete against fully integrated pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and smaller companies that are collaborating with larger pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, government agencies and other public and private research organizations. In addition, many of these competitors, either alone or together with their collaborative partners, operate larger research and development programs than we do, and have substantially greater financial resources than we do, as well as significantly greater experience in:
| · | developing drugs; |
| · | undertaking pre-clinical testing and human clinical trials; |
| · | obtaining FDA, addressing various regulatory matters and other regulatory approvals of drugs; |
| · | formulating and manufacturing drugs; and |
| · | launching, marketing and selling drugs. |
If our competitors develop and commercialize products faster than we do, or develop and commercialize products that are superior to our product candidates, our commercial opportunities will be reduced or eliminated. The extent to which any of our product candidates achieve market acceptance will depend on competitive factors, many of which are beyond our control. Competition in the biotechnology and biopharmaceutical industry is intense and has been accentuated by the rapid pace of technology development. Our competitors include large integrated pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies that currently have drug and target discovery efforts, universities, and public and private research institutions. Almost all of these entities have substantially greater research and development capabilities and financial, scientific, manufacturing, marketing and sales resources than we do. These organizations also compete with us to:
| · | attract parties for acquisitions, joint ventures or other collaborations; |
| · | license proprietary technology that is competitive with the technology we are developing; |
| · | attract funding; and |
| · | attract and hire scientific talent and other qualified personnel. |
Our competitors may succeed in developing and commercializing products earlier and obtaining regulatory approvals from the FDA more rapidly than we do. Our competitors may also develop products or technologies that are superior to those we are developing, and render our product candidates or technologies obsolete or non-competitive. If we cannot successfully compete with new or existing products, our marketing and sales will suffer and we may not ever be profitable.
Our competitors currently include companies with marketed products and/or an advanced research and development pipeline. The major competitors in the arthritis and psoriasis therapeutic field include Abbott Laboratories, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Astellas, Eli Lilly and more. The competitive landscape in the ophthalmic therapeutics field includes Novartis/Alcon, Allergan, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Merck (which acquired Inspire Pharmaceuticals), Santen (which acquired Novagali), Bausch & Lomb (which acquired ISTA Pharmaceuticals and is currently being acquired by Valeant), GlaxoSmithKline, or GSK, Sanofi-Aventis (which acquired Fovea) and more. Competitors in the HCC field include companies such as Onyx, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Arqule and more. Competitors in the HCV field include companies such as Merck, Vertex, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which acquired Inhibitex), Gilead Sciences (which acquired Pharmasset), Achillion, Idenix, Valeant, Human Genome Sciences, Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Idenix, Johnson & Johnson, Presidio, Medivir, Celgene, Enanta, GSK and more. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—Competition”.
Moreover, several companies have reported the commencement of research projects related to the A3AR. Such companies include CV Therapeutics Inc. (which was acquired by Gilead), King Pharmaceuticals R&D Inv. (which was acquired by Merck), Hoechst Marion Roussel Inc., Novo Nordisk A/S and Inotek Pharmaceuticals. However, we are not aware if such projects are ongoing or have been completed and, to the best of our knowledge, there is no approved drug currently on the market which is similar to our A3AR agonists, nor are we aware of any allosteric modulator in the A3AR product pipeline similar to our allosteric modulator with respect to chemical profile and mechanism of action.
| 17 |
We may suffer losses from product liability claims if our product candidates cause harm to patients.
Any of our product candidates could cause adverse events. These adverse events may not be observed in clinical trials, but may nonetheless occur in the future. If any of these adverse events occur, they may render our product candidates ineffective or harmful in some patients, and our sales would suffer, materially adversely affecting our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, potential adverse events caused by our product candidates could lead to product liability lawsuits. If product liability lawsuits are successfully brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit the marketing and commercialization of our product candidates. Our business exposes us to potential product liability risks, which are inherent in the testing, manufacturing, marketing and sale of pharmaceutical products. We may not be able to avoid product liability claims. Product liability insurance for the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries is generally expensive, if available at all. If, at any time, we are unable to obtain sufficient insurance coverage on reasonable terms or to otherwise protect against potential product liability claims, we may be unable to clinically test, market or commercialize our product candidates. A successful product liability claim brought against us in excess of our insurance coverage, if any, may cause us to incur substantial liabilities, and, as a result, our business, liquidity and results of operations would be materially adversely affected.
Although data from a pooled analysis of 730 patients (527 CF101, 203 placebo) indicates that CF101 is safe and well tolerated at doses up to 4.0 mg administered twice daily for up to 12 weeks, there were incidences (albeit less than or equal to five percent (5%)) of adverse events in five completed and fully analyzed trials in inflammatory disease. Such adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, constipation, common and viral syndromes (such as, tonsillitis, otitis and respiratory and urinary tract infections), myalgia, arthralgia, dizziness, headache, palpitations and pruritus. We observed an even lower incidence (less than or equal to two percent (2%)) of serious adverse events, including pancytopenia (although extensive evaluation suggests that such adverse event was associated with an inadvertent overdose of MTX), exacerbation of chronic obstructive lung disease and exacerbation of Parkinson’s Disease. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the placebo group in such studies had a higher incidence of overall adverse events than any CF101 dose group and a higher incidence of drug-related adverse events than any CF101 dose group (with the exception of the 1.0 mg group).
Our product candidates will remain subject to ongoing regulatory requirements even if they receive marketing approval, and if we fail to comply with these requirements, we could lose these approvals, and the sales of any approved commercial products could be suspended.
Even if we receive regulatory approval to market a particular product candidate, the product will remain subject to extensive regulatory requirements, including requirements relating to manufacturing, labeling, packaging, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion, distribution and recordkeeping. Even if regulatory approval of a product is granted, the approval may be subject to limitations on the uses for which the product may be marketed or the conditions of approval, or may contain requirements for costly post-marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of the product, which could negatively impact us or our collaboration partners by reducing revenues or increasing expenses, and cause the approved product candidate not to be commercially viable. In addition, as clinical experience with a drug expands after approval, typically because it is used by a greater number and more diverse group of patients after approval than during clinical trials, side effects and other problems may be observed after approval that were not seen or anticipated during pre-approval clinical trials or other studies. Any adverse effects observed after the approval and marketing of a product candidate could result in limitations on the use of or withdrawal of any approved products from the marketplace. Absence of long-term safety data may also limit the approved uses of our products, if any. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements of the FDA and other applicable U.S. and foreign regulatory authorities, or previously unknown problems with any approved commercial products, manufacturers or manufacturing processes are discovered, we could be subject to administrative or judicially imposed sanctions or other setbacks, including the following:
| · | Restrictions on the products, manufacturers or manufacturing process; |
| · | Warning letters; |
| · | Civil or criminal penalties, fines and injunctions; |
| · | Product seizures or detentions; |
| · | Import or export bans or restrictions; |
| · | Voluntary or mandatory product recalls and related publicity requirements; |
| · | Suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals; |
| · | Total or partial suspension of production, and |
| · | Refusal to approve pending applications for marketing approval of new products or supplements to approved applications. |
| 18 |
If we or our collaborators are slow to adapt, or are unable to adapt, to changes in existing regulatory requirements or adoption of new regulatory requirements or policies, marketing approval for our product candidates may be lost or cease to be achievable, resulting in decreased revenue from milestones, product sales or royalties, which would have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We may not be able to successfully grow and expand our business. Failure to manage our growth effectively will have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may not be able to successfully grow and expand. Successful implementation of our business plan will require management of growth, which will result in an increase in the level of responsibility for management personnel. To manage growth effectively, we will be required to continue to implement and improve our operating and financial systems and controls to expand, train and manage our employee base. The management, systems and controls currently in place or to be implemented may not be adequate for such growth, and the steps taken to hire personnel and to improve such systems and controls might not be sufficient. If we are unable to manage our growth effectively, it will have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may encounter difficulties in managing our growth. These difficulties could increase our losses.
We may experience rapid and substantial growth in order to achieve our operating plans, which will place a strain on our human and capital resources. If we are unable to manage this growth effectively, our losses could materially increase. Our ability to manage our operations and growth effectively requires us to continue to expend funds to enhance our operational, financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures and to attract and retain sufficient numbers of talented employees. If we are unable to scale up and implement improvements to our control systems in an efficient or timely manner, or if we encounter deficiencies in existing systems and controls, then we will not be able to make available the products required to successfully commercialize our technology. Failure to attract and retain sufficient numbers of talented employees will further strain our human resources and could impede our growth or result in ineffective growth.
If we are unable to obtain adequate insurance, our financial condition could be adversely affected in the event of uninsured or inadequately insured loss or damage. Our ability to effectively recruit and retain qualified officers and directors could also be adversely affected if we experience difficulty in obtaining adequate directors’ and officers’ liability insurance.
We may not be able to obtain insurance policies on terms affordable to us that would adequately insure our business and property against damage, loss or claims by third parties. To the extent our business or property suffers any damages, losses or claims by third parties, which are not covered or adequately covered by insurance, our financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
We may be unable to maintain sufficient insurance as a public company to cover liability claims made against our officers and directors. If we are unable to adequately insure our officers and directors, we may not be able to retain or recruit qualified officers and directors to manage the Company.
If we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or detect fraud. Consequently, investors could lose confidence in our financial reporting and this may decrease the trading price of our stock.
We must maintain effective internal controls to provide reliable financial reports and detect fraud. Our failure to properly maintain an effective system of internal controls could harm our operating results and cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information. In addition, such failure may cause us to suffer violations of the U.S. federal securities laws or applicable Israeli law to the extent we are unable to maintain effective internal controls. Any such loss of confidence or violations would have a negative effect on the trading price of our stock.
| 19 |
Potential political, economic and military instability in the State of Israel, where key members of our senior management and our research and development facilities are located, may adversely affect our results of operations.
We maintain office and research and development facilities in the State of Israel. Political, economic and military conditions in Israel may directly affect our ability to conduct business. Since the State of Israel was established in 1948, a number of armed conflicts have occurred between Israel and its Arab neighbors. Any hostilities involving Israel or the interruption or curtailment of trade between Israel and its present trading partners, or a significant downturn in the economic or financial condition of Israel, could affect adversely our operations. Ongoing and revived hostilities or other Israeli political or economic factors could harm our operations and product development and cause our revenues to fail to develop or decrease if we have already begun sales.
Recent disruptions in the financial markets and economic conditions could affect our ability to raise capital and could disrupt or delay the performance of our third-party contractors and suppliers.
In past years, the U.S. and global economies have taken a dramatic downturn as the result of the deterioration in the credit markets and related financial crisis as well as a variety of other factors including, among other things, extreme volatility in security prices, severely diminished liquidity and credit availability, ratings downgrades of certain investments and declining valuations of others. The U.S. and certain foreign governments have recently taken unprecedented actions in an attempt to address and rectify these extreme market and economic conditions by providing liquidity and stability to the financial markets. If the actions taken by these governments are not successful, the continued economic decline may cause a significant impact on our ability to raise capital, if needed, on a timely basis and on acceptable terms or at all. In addition, we rely and intend to rely on third-parties, including our clinical research organizations, third-party manufacturers and second source suppliers, and certain other important vendors and consultants. As a result of the current volatile and unpredictable global economic situation, there may be a disruption or delay in the performance of our third-party contractors and suppliers. If such third-parties are unable to satisfy their contractual commitments to us, our business could be severely adversely affected.
As an “emerging growth company” under the JOBS Act, we are permitted to, and intend to, rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements.
As an “emerging growth company” under the JOBS Act, we are permitted to, and intend to, rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements. We are an emerging growth company until the earliest of: (i) the last day of the fiscal year during which we had total annual gross revenues of $1 billion or more, (ii) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common stock pursuant to an effective registration statement, (iii) the date on which we have, during the previous three-year period, issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt or (iv) the date on which we are deemed a “large accelerated issuer” as defined in Regulation S-K of the Securities Act. For so long as we remain an emerging growth company, we will not be required to:
| · | have an auditor report on our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act; |
| · | comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, or the PCAOB, regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (auditor discussion and analysis); |
| · | submit certain executive compensation matters to shareholders advisory votes pursuant to the “say on frequency” and “say on pay” provisions (requiring a non-binding shareholder vote to approve compensation of certain executive officers) and the “say on golden parachute” provisions (requiring a non-binding shareholder vote to approve golden parachute arrangements for certain executive officers in connection with mergers and certain other business combinations) of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010; and |
| · | include detailed compensation discussion and analysis in our filings under the Exchange Act, and instead may provide a reduced level of disclosure concerning executive compensation. |
Although we intend to rely on the exemptions provided in the JOBS Act, the exact implications of the JOBS Act for us are still subject to interpretations and guidance by the SEC and other regulatory agencies. In addition, as our business grows, we may no longer satisfy the conditions of an emerging growth company. We are currently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to these new rules and we cannot assure you that we will be able to take advantage of all of the benefits from the JOBS Act.
In addition, as an “emerging growth company,” we may elect under the JOBS Act to delay adoption of new or revised accounting pronouncements applicable to public companies until such pronouncements are made applicable to private companies. Therefore, our financial statements may not be comparable to those of companies that comply with standards that are otherwise applicable to public companies.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
We license from the NIH and Leiden University intellectual property which protects certain small molecules which target the A3AR, in furtherance of our platform technology, and we could lose our rights to these licenses if a dispute with the NIH or Leiden University arises or if we fail to comply with the financial and other terms of the licenses.
We have licensed intellectual property from the NIH and Leiden University pursuant to license agreements, or the License Agreements, relating to molecules which target the A3AR. The License Agreements impose certain payment, reporting, confidentiality and other obligations on us. In the event that we were to breach any of the obligations and fail to cure, the NIH and Leiden University would have the right to terminate the respective License Agreement. In addition, the NIH and Leiden University each have the right to terminate the respective License Agreement upon our bankruptcy, insolvency, or receivership. Further, the NIH retains a paid-up, worldwide license to practice the licensed inventions for government purposes and may require us to grant sublicenses when necessary to fulfill health or safety needs and retains “march-in” rights, i.e., the right to terminate the license, if, among other things, the invention is needed for a public use such as addressing a public health crisis or the licensee or sublicensee fails to take within a reasonable time to take effective steps to achieve practical application of the licensed invention. If any dispute arises with respect to our arrangements with the NIH and Leiden University, such dispute may disrupt our operations and would likely have a material adverse impact on us if resolved in a manner that is unfavorable to our Company. All of our current product candidates are partly based on the intellectual property licensed under the License Agreements, and if the License Agreements were terminated, it would have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects and results of operations.
The failure to obtain or maintain patents, licensing agreements, including our current licensing agreements, and other intellectual property could impact our ability to compete effectively.
To compete effectively, we need to develop and maintain a proprietary position with regard to our own technologies, intellectual property, licensing agreements, product candidates and business. Legal standards relating to the validity and scope of claims in the biotechnology and biopharmaceutical fields are still evolving. Therefore, the degree of future protection for our proprietary rights in our core technologies and any products that might be made using these technologies is also uncertain. The risks and uncertainties that we face with respect to our patents and other proprietary rights include the following:
| 20 |
| · | while the patents we license have been issued, the pending patent applications we have filed may not result in issued patents or may take longer than we expect to result in issued patents; |
| · | we may be subject to interference proceedings; |
| · | we may be subject to opposition proceedings in foreign countries; |
| · | any patents that are issued may not provide meaningful protection; |
| · | we may not be able to develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; |
| · | other companies may challenge patents licensed or issued to us or our customers; |
| · | other companies may independently develop similar or alternative technologies, or duplicate our technologies; |
| · | other companies may design around technologies we have licensed or developed; and |
| · | enforcement of patents is complex, uncertain and expensive. |
We cannot be certain that patents will be issued as a result of any of our pending applications, and we cannot be certain that any of our issued patents, whether issued pursuant to our pending applications or licensed from the NIH and Leiden University, will give us adequate protection from competing products. For example, issued patents, including the patents licensed from the NIH and Leiden University, may be circumvented or challenged, declared invalid or unenforceable, or narrowed in scope. In addition, since publication of discoveries in the scientific or patent literature often lags behind actual discoveries, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make our inventions or to file patent applications covering those inventions.
Moreover, the composition of matter patents pertaining to CF101 and CF102 that the Company licensed from the NIH will expire on July 13, 2014 in Europe and on June 30, 2015 in the United States. As of June 30, 2015, the License Agreement with the NIH will terminate. We do not expect that we will be able to submit an NDA seeking approval of CF101 or CF102 prior to the composition of matter patents’ respective expiration dates. However, because CF101 and CF102 each may be a new chemical entity, or NCE, following approval of an NDA, we, if we are the first applicant to obtain NDA approval, may be entitled to five years of data and market exclusivity in the United States with respect to such NCEs. Analogous data and market exclusivity provisions, of varying duration, may be available in Europe and other foreign jurisdictions. The Company also has rights under its pharmaceutical use issued patents with respect to CF101 and CF102, which provide patent exclusivity within the Company’s field of activity until the mid- to late-2020s. While the Company believes that it may be able to protect its exclusivity in its field of activity through such use patent portfolio and such period of exclusivity, the lack of composition of matter patent protection may diminish the Company’s ability to maintain a proprietary position for its intended uses of CF101 and CF102. Moreover, the Company cannot be certain that it will be the first applicant to obtain an FDA approval for any indication of CF101 and it cannot be certain that it will be entitled to NCE exclusivity. Such diminution of its proprietary position could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation and financial condition.
It is also possible that others may obtain issued patents that could prevent us from commercializing our products or require us to obtain licenses requiring the payment of significant fees or royalties in order to enable us to conduct our business. As to those patents that we have licensed, our rights depend on maintaining our obligations to the licensor under the applicable license agreement, and we may be unable to do so.
In addition to patents and patent applications, we depend upon trade secrets and proprietary know-how to protect our proprietary technology. We require our employees, consultants, advisors and collaborators to enter into confidentiality agreements that prohibit the disclosure of confidential information to any other parties. We require our employees and consultants to disclose and assign to us their ideas, developments, discoveries and inventions. These agreements may not, however, provide adequate protection for our trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use or disclosure.
Costly litigation may be necessary to protect our intellectual property rights and we may be subject to claims alleging the violation of the intellectual property rights of others.
We may face significant expense and liability as a result of litigation or other proceedings relating to patents and other intellectual property rights of others. In the event that another party has also filed a patent application or been issued a patent relating to an invention or technology claimed by us in pending applications, we may be required to participate in an interference proceeding declared by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office to determine priority of invention, which could result in substantial uncertainties and costs for us, even if the eventual outcome were favorable to us. We, or our licensors, also could be required to participate in interference proceedings involving issued patents and pending applications of another entity. An adverse outcome in an interference proceeding could require us to cease using the technology or to license rights from prevailing third parties.
The cost to us of any patent litigation or other proceeding relating to our licensed patents or patent applications, even if resolved in our favor, could be substantial. Our ability to enforce our patent protection could be limited by our financial resources, and may be subject to lengthy delays. If we are unable to effectively enforce our proprietary rights, or if we are found to infringe the rights of others, we may be in breach of our License Agreement.
| 21 |
A third party may claim that we are using inventions claimed by their patents and may go to court to stop us from engaging in our normal operations and activities, such as research, development and the sale of any future products. Such lawsuits are expensive and would consume time and other resources. There is a risk that the court will decide that we are infringing the third party’s patents and will order us to stop the activities claimed by the patents, redesign our products or processes to avoid infringement or obtain licenses (which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms). In addition, there is a risk that a court will order us to pay the other party damages for having infringed their patents.
Moreover, there is no guarantee that any prevailing patent owner would offer us a license so that we could continue to engage in activities claimed by the patent, or that such a license, if made available to us, could be acquired on commercially acceptable terms. In addition, third parties may, in the future, assert other intellectual property infringement claims against us with respect to our product candidates, technologies or other matters.
We rely on confidentiality agreements that could be breached and may be difficult to enforce, which could result in third parties using our intellectual property to compete against us.
Although we believe that we take reasonable steps to protect our intellectual property, including the use of agreements relating to the non-disclosure of confidential information to third parties, as well as agreements that purport to require the disclosure and assignment to us of the rights to the ideas, developments, discoveries and inventions of our employees and consultants while we employ them, the agreements can be difficult and costly to enforce. Although we seek to obtain these types of agreements from our contractors, consultants, advisors and research collaborators, to the extent that employees and consultants utilize or independently develop intellectual property in connection with any of our projects, disputes may arise as to the intellectual property rights associated with our products. If a dispute arises, a court may determine that the right belongs to a third party. In addition, enforcement of our rights can be costly and unpredictable. We also rely on trade secrets and proprietary know-how that we seek to protect in part by confidentiality agreements with our employees, contractors, consultants, advisors or others. Despite the protective measures we employ, we still face the risk that:
| · | these agreements may be breached; |
| · | these agreements may not provide adequate remedies for the applicable type of breach; |
| · | our trade secrets or proprietary know-how will otherwise become known; or |
| · | our competitors will independently develop similar technology or proprietary information. |
International patent protection is particularly uncertain, and if we are involved in opposition proceedings in foreign countries, we may have to expend substantial sums and management resources.
Patent law outside the United States is in some cases different than in the United States and is currently undergoing review and revision in many countries. Further, the laws of some foreign countries may not protect our intellectual property rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. For example, certain countries do not grant patent claims that are directed to the treatment of humans. We may participate in opposition proceedings to determine the validity of our foreign patents or our competitors’ foreign patents, which could result in substantial costs and diversion of our efforts.
Although most jurisdictions in which Can-Fite has applied for, intends to apply for, or has been issued patents have patent protection laws similar to those of the United States, some of them do not. For example, the Company expects to do business in Brazil and India in the future. However, the Brazilian drug regulatory agency, ENVISA, has the authority to nullify patents on the basis of its perceived public interest and the Indian patent law does not allow patent protection for new uses of pharmaceuticals (many of the Company’s current patent applications are of such nature). Additionally, due to uncertainty in patent protection law, the Company has not filed applications in many countries where significant markets exist, including Indonesia, Pakistan, Russia, African countries and Taiwan.
We may be unable to protect the intellectual property rights of the third parties from whom we license certain of our intellectual property or with whom we have entered into other strategic relationships.
Certain of our intellectual property rights are currently licensed from the NIH and Leiden University, and, in the future, we intend to continue to license intellectual property from the NIH and Leiden University and/or other universities and/or strategic partners. Such third parties may determine not to protect the intellectual property rights that we license from them and we may be unable defend such intellectual property rights on our own or we may have to undertake costly litigation to defend the intellectual property rights of such third parties. There can be no assurances that we will continue to have proprietary rights to any of the intellectual property that we license from such third parties or otherwise have the right to use through similar strategic relationships. Any loss or limitations on use with respect to our right to use such intellectual property licensed from third parties or otherwise obtained from third parties with whom we have entered into strategic relationships could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
| 22 |
Risks Related to Our Industry
We are subject to government regulations and we may experience delays in obtaining required regulatory approvals in the United States to market our proposed product candidates.
Various aspects of our operations are subject to federal, state or local laws, rules and regulations, any of which may change from time to time. Costs arising out of any regulatory developments could be time-consuming and expensive and could divert management resources and attention and, consequently, could adversely affect our business operations and financial performance.
Delays in regulatory approval, limitations in regulatory approval and withdrawals of regulatory approval may have a material adverse effect on the Company. If we experience significant delays in testing or receiving approvals or sign-offs to conduct clinical trials, our product development costs, or our ability to license product candidates, will increase. If the FDA grants regulatory approval to market a product, this approval will be limited to those disease states and conditions for which the product has demonstrated, through clinical trials, to be safe and effective. Any product approvals that we receive in the future could also include significant restrictions on the use or marketing of our products. Product approvals, if granted, can be withdrawn for failure to comply with regulatory requirements or upon the occurrence of adverse events following commercial introduction of the products. Failure to comply with applicable FDA or other applicable regulatory requirements may result in criminal prosecution, civil penalties, recall or seizure of products, total or partial suspension of production or injunction, as well as other regulatory action against our product candidates or us. If approval is withdrawn for a product, or if a product were seized or recalled, we would be unable to sell or license that product and our revenues would suffer. In addition, outside the United States, our ability to market any of our potential products is contingent upon receiving market application authorizations from the appropriate regulatory authorities and these foreign regulatory approval processes include all of the risks associated with the FDA approval process described above.
| 23 |
We expect the healthcare industry to face increased limitations on reimbursement as a result of healthcare reform, which could adversely affect third-party coverage of our products and how much or under what circumstances healthcare providers will prescribe or administer our products.
In both the United States and other countries, sales of our products will depend in part upon the availability of reimbursement from third-party payors, which include governmental authorities, managed care organizations and other private health insurers. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price and examining the cost effectiveness of medical products and services.
Increasing expenditures for healthcare have been the subject of considerable public attention in the United States. Both private and government entities are seeking ways to reduce or contain healthcare costs. Numerous proposals that would effect changes in the U.S. healthcare system have been introduced or proposed in Congress and in some state legislatures, including reducing reimbursement for prescription products and reducing the levels at which consumers and healthcare providers are reimbursed for purchases of pharmaceutical products.
In 2010, Congress enacted and the President signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended, which will significantly expand access to health care coverage but may lead to reduction in reimbursement for supplies, including pharmaceuticals, and services. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, is in the process of issuing regulations to implement the new law which will affect Medicare, Medicaid and other third-party payors. Medicare, which is the single largest third-party payment program and which is administered by CMS, covers prescription drugs in one of two ways. Medicare part B covers outpatient prescription drugs that are administered by physicians and Medicare part D covers other outpatient prescription drugs, but through private insurers. Medicaid, a health insurance program for the poor, is funded jointly by CMS and the states, but is administered by the states; states are authorized to cover outpatient prescription drugs, but that coverage is subject to caps and to substantial rebates.
Although we cannot predict the full effect on our business of the implementation of existing legislation, including the Affordable Care Act or the enactment of additional legislation, we believe that legislation or regulations that reduce reimbursement for or restrict coverage of our products could adversely affect how much or under what circumstances healthcare providers will prescribe or administer our products. This could materially and adversely affect our business by reducing our ability to generate revenue, raise capital, obtain additional collaborators and market our products. In addition, we believe the increasing emphasis on managed care in the United States has and will continue to put pressure on the price and usage of pharmaceutical products, which may adversely impact product sales.
We are subject to federal anti-kickback laws and regulations. Our failure to comply with these laws and regulations could have adverse consequences to us.
There are extensive U.S. federal and state laws and regulations prohibiting fraud and abuse in the healthcare industry that can result in significant criminal and civil penalties. These federal laws include: the anti-kickback statute, which prohibits certain business practices and relationships, including the payment or receipt of remuneration for the referral of patients whose care will be paid by Medicare or other federal healthcare programs; the physician self-referral prohibition, commonly referred to as the Stark Law; the anti-inducement law, which prohibits providers from offering anything to a Medicare or Medicaid beneficiary to induce that beneficiary to use items or services covered by either program; the False Claims Act, which prohibits any person from knowingly presenting or causing to be presented false or fraudulent claims for payment by the federal government, including the Medicare and Medicaid programs; and the Civil Monetary Penalties Law, which authorizes the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to impose civil penalties administratively for fraudulent or abusive acts.
Sanctions for violating these federal laws include criminal and civil penalties that range from punitive sanctions, damage assessments, money penalties, imprisonment, denial of Medicare and Medicaid payments, or exclusion from the Medicare and Medicaid programs, or both, and debarment. As federal and state budget pressures continue, federal and state administrative agencies may also continue to escalate investigation and enforcement efforts to root out waste and to control fraud and abuse in governmental healthcare programs. Private enforcement of healthcare fraud has also increased, due in large part to amendments to the civil False Claims Act in 1986 that were designed to encourage private persons to sue on behalf of the government. A violation of any of these federal and state fraud and abuse laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and financial condition. An investigation into the use by physicians of any of our products once commercialized may dissuade physicians from either purchasing or using them, and could have a material adverse effect on our ability to commercialize those products.
| 24 |
Risks Related to our Ordinary Shares and ADSs
We may be a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes in 2013 or in any subsequent year. There may be negative tax consequences for U.S. taxpayers that are holders of our ordinary shares or our ADSs.
We will be treated as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes in any taxable year in which either (i) at least 75% of our gross income is “passive income” or (ii) on average at least 50% of our assets by value produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, certain dividends, interest, royalties, rents and gains from commodities and securities transactions and from the sale or exchange of property that gives rise to passive income. Passive income also includes amounts derived by reason of the temporary investment of funds, including those raised in a public offering. In determining whether a non-U.S. corporation is a PFIC, a proportionate share of the income and assets of each corporation in which it owns, directly or indirectly, at least a 25% interest (by value) is taken into account. Although we have not determined whether we will be a PFIC in 2013, or in any subsequent year, our operating results for any such years may cause us to be a PFIC. If we are a PFIC in 2013, or any subsequent year, and a U.S. shareholder does not make an election to treat us as a “qualified electing fund,” or QEF, or make a “mark-to-market” election, then “excess distributions” to a U.S. shareholder, and any gain realized on the sale or other disposition of our ordinary shares or ADSs will be subject to special rules. Under these rules: (i) the excess distribution or gain would be allocated ratably over the U.S. shareholder’s holding period for the ordinary shares (or ADSs, as the case may be); (ii) the amount allocated to the current taxable year and any period prior to the first day of the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income; and (iii) the amount allocated to each of the other taxable years would be subject to tax at the highest rate of tax in effect for the applicable class of taxpayer for that year, and an interest charge for the deemed deferral benefit would be imposed with respect to the resulting tax attributable to each such other taxable year. In addition, if the U.S. Internal Revenue Service determines that we are a PFIC for a year with respect to which we have determined that we were not a PFIC, it may be too late for a U.S. shareholder to make a timely QEF or mark-to-market election. U.S. shareholders who hold our ordinary shares or ADSs during a period when we are a PFIC will be subject to the foregoing rules, even if we cease to be a PFIC in subsequent years, subject to exceptions for U.S. shareholders who made a timely QEF or mark-to-market election. A U.S. shareholder can make a QEF election by completing the relevant portions of and filing IRS Form 8621 in accordance with the instructions thereto. Upon request, we will annually furnish U.S. shareholders with information needed in order to complete IRS Form 8621 (which form would be required to be filed with the IRS on an annual basis by the U.S. shareholder) and to make and maintain a valid QEF election for any year in which we or any of our subsidiaries that we control is a PFIC.
The market price of our ordinary shares is, and the market price of our ADSs will be, subject to fluctuation, which could result in substantial losses by our investors.
The stock market in general and the market price of our ordinary shares on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, or the TASE, in particular, is subject to fluctuation, and changes in our share price may be unrelated to our operating performance. The market price of our ordinary shares on the TASE has fluctuated in the past, and we expect it will continue to do so. It is likely that the market price of our ADSs will likewise be subject to wide fluctuations. The market price of our ordinary shares and ADSs are and will be subject to a number of factors, including:
| · | announcements of technological innovations or new products by us or others; |
| · | announcements by us of significant strategic partnerships, out-licensing, in-licensing, joint ventures, acquisitions or capital commitments; |
| · | expiration or terminations of licenses, research contracts or other collaboration agreements; |
| · | public concern as to the safety of drugs we, our licensees or others develop; |
| 25 |
| · | general market conditions; |
| · | the volatility of market prices for shares of biotechnology companies generally; |
| · | success of research and development projects; |
| · | success in clinical and preclinical studies; |
| · | departure of key personnel; |
| · | developments concerning intellectual property rights or regulatory approvals; |
| · | variations in our and our competitors’ results of operations; |
| · | changes in earnings estimates or recommendations by securities analysts, if our ordinary shares or ADSs are covered by analysts; |
| · | changes in government regulations or patent decisions; |
| · | developments by our licensees; and |
| · | general market conditions and other factors, including factors unrelated to our operating performance. |
These factors and any corresponding price fluctuations may materially and adversely affect the market price of our ordinary shares and ADSs and result in substantial losses by our investors.
Additionally, market prices for securities of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies historically have been very volatile. The market for these securities has from time to time experienced significant price and volume fluctuations for reasons unrelated to the operating performance of any one company. In the past, following periods of market volatility, shareholders have often instituted securities class action litigation. If we were involved in securities litigation, it could have a substantial cost and divert resources and attention of management from our business, even if we are successful. Future sales of our ordinary shares or ADSs could reduce the market price of our ordinary shares and ADSs.
Substantial sales of our ordinary shares or ADSs either on the TASE or on the NYSE MKT, as applicable, may cause the market price of our ordinary shares or ADSs to decline.
All of our outstanding ordinary shares are registered and available for sale in Israel. Sales by us or our securityholders of substantial amounts of our ordinary shares or ADSs, or the perception that these sales may occur in the future, could cause a reduction in the market price of our ordinary shares or ADSs.
The issuance of any additional ordinary shares or ADSs, or any securities that are exercisable for or convertible into our ordinary shares or ADSs, may have an adverse effect on the market price of our ordinary shares or ADSs, as applicable, and will have a dilutive effect on our shareholders.
Raising additional capital by issuing securities may cause dilution to existing shareholders.
We may need to raise substantial future capital to continue to complete clinical development and commercialize our products and product candidates and to conduct the research and development and clinical and regulatory activities necessary to bring our product candidates to market. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| · | the failure to obtain regulatory approval or achieve commercial success of our product candidates, including CF101, CF102 and CF602; |
| · | our success in effecting out-licensing arrangements with third-parties; |
| 26 |
| · | our success in establishing other out-licensing arrangements; |
| · | the success of our licensees in selling products that utilize our technologies; |
| · | the results of our preclinical studies and clinical trials for our earlier stage therapeutic candidates, and any decisions to initiate clinical trials if supported by the preclinical results; |
| · | the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates that progress to clinical trials; |
| · | the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our issued patents and defending intellectual property-related claims; |
| · | the extent to which we acquire or invest in businesses, products or technologies and other strategic relationships; and |
| · | the costs of financing unanticipated working capital requirements and responding to competitive pressures. |
If we raise additional funds through licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our product candidates, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity or convertible debt securities, we will reduce the percentage ownership of our then-existing shareholders, and these securities may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of our existing shareholders. See also “The market price of our ordinary shares is, and the market price of our ADSs will be, subject to fluctuation, which could result in substantial losses by our investors.”
Our ADS holders are not shareholders and do not have shareholder rights.
The Bank of New York Mellon, as Depositary, executes and delivers our ADSs on our behalf. Each ADS is a certificate evidencing a specific number of ordinary shares. Our ADS holders will not be treated as shareholders and do not have the rights of shareholders. The depositary will be the holder of the shares underlying our ADSs. Holders of our ADSs will have ADS holder rights. A deposit agreement among us, the depositary and our ADS holders, and the beneficial owners of ADSs, sets out ADS holder rights as well as the rights and obligations of the depositary. New York law governs the deposit agreement and the ADSs. Our shareholders have shareholder rights. Israeli law and our Articles of Association govern shareholder rights. Our ADS holders do not have the same voting rights as our shareholders. Shareholders are entitled to our notices of general meetings and to attend and vote at our general meetings of shareholders. At a general meeting, every shareholder present (in person or by proxy, attorney or representative) and entitled to vote has one vote. This is subject to any other rights or restrictions which may be attached to any shares. Our ADS holders may instruct the depositary to vote the ordinary shares underlying their ADSs, but only if we ask the depositary to ask for their instructions. If we do not ask the depositary to ask for the instructions, our ADS holders are not entitled to receive our notices of general meeting or instruct the depositary how to vote. Our ADS holders will not be entitled to attend and vote at a general meeting unless they withdraw the ordinary shares from the depository. However, our ADS holders may not know about the meeting enough in advance to withdraw the ordinary shares. If we ask for our ADS holders’ instructions, the depositary will notify our ADS holders of the upcoming vote and arrange to deliver our voting materials and form of notice to them. The depositary will try, as far as is practical, subject to the provisions of the deposit agreement, to vote the shares as our ADS holders instruct. The depositary will not vote or attempt to exercise the right to vote other than in accordance with the instructions of the ADS holders. We cannot assure our ADS holders that they will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that they can instruct the depositary to vote their shares. In addition, there may be other circumstances in which our ADS holders may not be able to exercise voting rights.
Our ADS holders do not have the same rights to receive dividends or other distributions as our shareholders. Subject to any special rights or restrictions attached to a share, the directors may determine that a dividend will be payable on a share and fix the amount, the time for payment and the method for payment (although we have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our ordinary shares and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future). Dividends and other distributions payable to our shareholders with respect to our ordinary shares generally will be payable directly to them. Any dividends or distributions payable with respect to ordinary shares will be paid to the depositary, which has agreed to pay to our ADS holders the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on shares or other deposited securities, after deducting its fees and expenses. Our ADS holders will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of ordinary shares their ADSs represent. In addition, there may be certain circumstances in which the depositary may not pay to our ADS holders amounts distributed by us as a dividend or distribution.
Risks Associated with Potential NYSE MKT Listing of our ADSs
Our ordinary shares and our ADSs will be traded on different markets and this may result in price variations.
Our ordinary shares have traded on the TASE since October 2005 and we intend to apply to have our ADSs listed on the NYSE MKT. Trading in our securities on these markets will take place in different currencies (U.S. dollars on the NYSE MKT and NIS on the TASE), and at different times (resulting from different time zones, different trading days and different public holidays in the United States and Israel). The trading prices of our securities on these two markets may differ due to these and other factors. Any decrease in the price of our securities on one of these markets could cause a decrease in the trading price of our securities on the other market.
Our ADSs have a limited prior trading history in the United States, and an active market may not develop, which may limit the ability of our investors to sell our ADSs in the United States.
There is a limited public market for our ADSs or ordinary shares in the United States on the Over the Counter market, or OTC. Although we intend to apply to have our ADSs listed on the NYSE MKT, an active trading market for our ADSs may never develop or may not be sustained if one develops. If an active market for our ADSs does not develop or is not sustained, it may be difficult to sell your ADSs.
| 27 |
We will incur significant additional increased costs as a result of the listing of our ADSs for trading on the NYSE MKT, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives as well as to compliance with ongoing U.S. and Israeli reporting requirements.
As a public company in the United States, we will incur additional significant accounting, legal and other expenses that we did not incur before the offering. We also anticipate that we will incur costs associated with corporate governance requirements of the SEC and the NYSE MKT Company Guide, as well as requirements under Section 404 and other provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We expect these rules and regulations to increase our legal and financial compliance costs, introduce new costs such as investor relations, stock exchange listing fees and shareholder reporting, and to make some activities more time consuming and costly. The implementation and testing of such processes and systems may require us to hire outside consultants and incur other significant costs. Any future changes in the laws and regulations affecting public companies in the United States and Israel, including Section 404 and other provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the rules and regulations adopted by the SEC and the NYSE MKT Company Guide, as well as applicable Israeli reporting requirements, for so long as they apply to us, will result in increased costs to us as we respond to such changes. These laws, rules and regulations could make it more difficult or more costly for us to obtain certain types of insurance, including director and officer liability insurance, and we may be forced to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. The impact of these requirements could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our Board of Directors, our board committees or as executive officers. Furthermore, until such time as our shareholders may vote to approve our transition from Israeli securities law reporting requirements to U.S. requirements, we will also be required to comply fully with both Israeli and U.S. requirements. The need to comply with both U.S. and Israeli reporting and other securities law requirements will also add to our legal and financial compliance costs and require devotion of additional management resources to reporting and compliance efforts.
As a foreign private issuer, we are permitted to follow certain home country corporate governance practices instead of applicable SEC and NYSE MKT requirements, which may result in less protection than is accorded to investors under rules applicable to domestic issuers.
As a foreign private issuer, we will be permitted to follow certain home country corporate governance practices instead of those otherwise required under the NYSE MKT Company Guide for domestic issuers. For instance, we may follow home country practice in Israel with regard to, among other things, composition and function of the audit committee and other committees of our Board of Directors and certain general corporate governance matters. In addition, in certain instances we will follow our home country law, instead of the NYSE MKT Company Guide, which requires that we obtain shareholder approval for certain dilutive events, such as an issuance that will result in a change of control of the company, certain transactions other than a public offering involving issuances of a 20% or more interest in the company and certain acquisitions of the stock or assets of another company. The Company intends to comply with the director independence requirements of the NYSE MKT Company Guide, including the requirement that a majority of the board of directors be independent, and make the required affirmative determination thereunder upon filing the listing application with the NYSE MKT. We will evaluate the extent to which we will avail ourselves of the other exemptions available to foreign private issuers in connection with the actual listing of our ADSs for trading on the NYSE MKT. Following our home country governance practices as opposed to the requirements that would otherwise apply to a United States company listed on the NYSE MKT may provide less protection than is accorded to investors under the NYSE MKT Company Guide applicable to domestic issuers.
In addition, as a foreign private issuer, we will be exempt from the rules and regulations under the U.S. Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, related to the furnishing and content of proxy statements, and our officers, directors and principal shareholders will be exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, we will not be required under the Exchange Act to file annual, quarterly and current reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as domestic companies whose securities are registered under the Exchange Act.
If we are unable to satisfy the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act as they apply to a foreign private issuer that is listing on a U.S. exchange for the first time, or our internal controls over financial reporting are not effective, the reliability of our financial statements may be questioned and our share price and ADS price may suffer.
We will become subject to the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act if our ADSs are listed on the NYSE MKT. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires companies subject to the reporting requirements of the U.S. securities laws to do a comprehensive evaluation of its and its subsidiaries’ internal controls over financial reporting. To comply with this statute, we will be required to document and test our internal control procedures and our management will be required to assess and issue a report concerning our internal controls over financial reporting. Pursuant to the JOBS Act, we will be classified as an “emerging growth company.” Under the JOBS Act, Emerging Growth Companies are exempt from certain reporting requirements, including the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Under this exemption, our auditor will not be required to attest to and report on management’s assessment of our internal controls over financial reporting during a five-year transition period. We will need to prepare for compliance with Section 404 by strengthening, assessing and testing our system of internal controls to provide the basis for our report. However, the continuous process of strengthening our internal controls and complying with Section 404 is complicated and time-consuming. Furthermore, as our business continues to grow both domestically and internationally, our internal controls will become more complex and will require significantly more resources and attention to ensure our internal controls remain effective overall. During the course of its testing, our management may identify material weaknesses or significant deficiencies, which may not be remedied in a timely manner to meet the deadline imposed by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. If our management cannot favorably assess the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting, or our independent registered public accounting firm identifies material weaknesses in our internal controls, investor confidence in our financial results may weaken, and the market price of our securities may suffer.
| 28 |
Risks Related to our Operations in Israel
We conduct our operations in Israel and therefore our results may be adversely affected by political, economic and military instability in Israel and its region.
Our headquarters, all of our operations and some of our suppliers and third party contractors are located in central Israel and our key employees, officers and most of our directors are residents of Israel. Accordingly, political, economic and military conditions in Israel and the surrounding region may directly affect our business. Since the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, a number of armed conflicts have taken place between Israel and its Arab neighbors. Any hostilities involving Israel or the interruption or curtailment of trade within Israel or between Israel and its trading partners could adversely affect our operations and results of operations and could make it more difficult for us to raise capital. During the winter of 2008, Israel was engaged in an armed conflict with Hamas, a militia group and political party operating in the Gaza Strip, and during the summer of 2006, Israel was engaged in an armed conflict with Hezbollah, a Lebanese Islamist Shiite militia group and political party. These conflicts involved missile strikes against civilian targets in various parts of Israel, and negatively affected business conditions in Israel. Recent political uprisings and social unrest in various countries in the Middle East and North Africa are affecting the political stability of those countries. This instability may lead to deterioration of the political relationships that exist between Israel and these countries, and have raised concerns regarding security in the region and the potential for armed conflict. Any armed conflicts, terrorist activities or political instability in the region could adversely affect business conditions and could harm our results of operations. For example, any major escalation in hostilities in the region could result in a portion of our employees and service providers being called up to perform military duty for an extended period of time. Parties with whom we do business have sometimes declined to travel to Israel during periods of heightened unrest or tension, forcing us to make alternative arrangements when necessary. In addition, the political and security situation in Israel may result in parties with whom we have agreements involving performance in Israel claiming that they are not obligated to perform their commitments under those agreements pursuant to force majeure provisions in such agreements.
Our commercial insurance does not cover losses that may occur as a result of events associated with the security situation in the Middle East. Although the Israeli government currently covers the reinstatement value of direct damages that are caused by terrorist attacks or acts of war, we cannot assure you that this government coverage will be maintained. Any losses or damages incurred by us could have a material adverse effect on our business. Any armed conflicts or political instability in the region would likely negatively affect business conditions and could harm our results of operations.
Further, in the past, the State of Israel and Israeli companies have been subjected to an economic boycott. Several countries still restrict business with the State of Israel and with Israeli companies. These restrictive laws and policies may have an adverse impact on our operating results, financial condition or the expansion of our business.
Our operations may be disrupted as a result of the obligation of Israeli citizens to perform military service.
Many Israeli citizens, including Motti Farbstein, our Chief Operating and Financial Officer, are obligated to perform one month, and in some cases more, of annual military reserve duty until they reach the age of 45 (or older, for reservists with certain occupations) and, in the event of a military conflict, may be called to active duty. In response to increases in terrorist activity, there have been periods of significant call-ups of military reservists. It is possible that there will be military reserve duty call-ups in the future. Our operations could be disrupted by such call-ups, which may include the call-up of Motti Farbstein. Such disruption could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Because a certain portion of our expenses is incurred in currencies other than the NIS, our results of operations may be harmed by currency fluctuations and inflation.
Our reporting and functional currency is the NIS, and we pay a substantial portion of our expenses in NIS. The revenues from our licensing arrangements are payable in U.S. dollars and we expect our revenues from future licensing arrangements to be denominated in U.S. dollars or in Euros. As a result, we are exposed to the currency fluctuation risks relating to the recording of our revenues in NIS. For example, if the NIS strengthens against either the U.S. dollar or the Euro, our reported revenues in NIS may be lower than anticipated. The Israeli rate of inflation has not offset or compounded the effects caused by fluctuations between the NIS and the U.S. dollar or the Euro. To date, we have not engaged in hedging transactions. Although the Israeli rate of inflation has not had a material adverse effect on our financial condition during 2010, 2011, or 2012 to date, we may, in the future, decide to enter into currency hedging transactions to decrease the risk of financial exposure from fluctuations in the exchange rates of the currencies mentioned above in relation to the NIS. These measures, however, may not adequately protect us from material adverse effects.
| 29 |
Provisions of Israeli law may delay, prevent or otherwise impede a merger with, or an acquisition of, our Company, which could prevent a change of control, even when the terms of such a transaction are favorable to us and our shareholders.
Israeli corporate law regulates mergers, requires tender offers for acquisitions of shares above specified thresholds, requires special approvals for transactions involving directors, officers or significant shareholders and regulates other matters that may be relevant to these types of transactions. For example, a merger may not be consummated unless at least 50 days have passed from the date that a merger proposal was filed by each merging company with the Israel Registrar of Companies and at least 30 days from the date that the shareholders of both merging companies approved the merger. In addition, a majority of each class of securities of the target company must approve a merger. Moreover, a full tender offer can only be completed if the acquirer receives at least 95% of the issued share capital; provided that, pursuant to an amendment to the Israeli Companies Law, effective as of May 15, 2011, a majority of the offerees that do not have a personal interest in such tender offer shall have approved the tender offer; except that, if the total votes to reject the tender offer represent less than 2% of the company’s issued and outstanding share capital, in the aggregate, approval by a majority of the offerees that do not have a personal interest in such tender offer is not required to complete the tender offer), and the shareholders, including those who indicated their acceptance of the tender offer, may, at any time within six months following the completion of the tender offer, petition the court to alter the consideration for the acquisition (unless the acquirer stipulated in the tender offer that a shareholder that accepts the offer may not seek appraisal rights).
Furthermore, Israeli tax considerations may make potential transactions unappealing to us or to our shareholders whose country of residence does not have a tax treaty with Israel exempting such shareholders from Israeli tax. For example, Israeli tax law does not recognize tax-free share exchanges to the same extent as U.S. tax law. With respect to mergers, Israeli tax law allows for tax deferral in certain circumstances but makes the deferral contingent on the fulfillment of numerous conditions, including a holding period of two years from the date of the transaction during which sales and dispositions of shares of the participating companies are restricted. Moreover, with respect to certain share swap transactions, the tax deferral is limited in time, and when such time expires, the tax becomes payable even if no actual disposition of the shares has occurred.
These and other similar provisions could delay, prevent or impede an acquisition of us or our merger with another company, even if such an acquisition or merger would be beneficial to us or to our shareholders. See “Item 10. Additional Information — Memorandum and Articles of Association.”
It may be difficult to enforce a U.S. judgment against us and our officers and directors named in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F in Israel or the United States, or to serve process on our officers and directors.
We are incorporated in Israel. All of our executive officers and directors listed in this registration statement on Form 20-F reside outside of the United States, and all of our assets and most of the assets of our executive officers and directors are located outside of the United States. Therefore, a judgment obtained against us or most of our executive officers and all of our directors in the United States, including one based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws, may not be collectible in the United States and may not be enforced by an Israeli court. It also may be difficult for you to effect service of process on these persons in the United States or to assert U.S. securities law claims in original actions instituted in Israel.
| 30 |
Your rights and responsibilities as a shareholder will be governed by Israeli law which may differ in some respects from the rights and responsibilities of shareholders of U.S. companies.
We are incorporated under Israeli law. The rights and responsibilities of the holders of our ordinary shares and ADSs are governed by our Articles of Association and Israeli law. These rights and responsibilities differ in some respects from the rights and responsibilities of shareholders in typical U.S.-based corporations. In particular, a shareholder of an Israeli company has a duty to act in good faith toward the company and other shareholders and to refrain from abusing its power in the company, including, among other things, in voting at the general meeting of shareholders on matters such as amendments to a company’s articles of association, increases in a company’s authorized share capital, mergers and acquisitions and interested party transactions requiring shareholder approval. In addition, a shareholder who knows that it possesses the power to determine the outcome of a shareholder vote or to appoint or prevent the appointment of a director or executive officer in the company has a duty of fairness toward the company. There is limited case law available to assist us in understanding the implications of these provisions that govern shareholders’ actions. These provisions may be interpreted to impose additional obligations and liabilities on holders of our ordinary shares and ADSs that are not typically imposed on shareholders of U.S. corporations.
ITEM 4. Information on the Company
A. History and Development of the Company
Our legal name is Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. and our commercial name is “Can-Fite”. We are a company limited by shares organized under the laws of the State of Israel. Our principal executive offices are located at 10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel. Our telephone number is +972 (3) 924-1114.
We were founded on September 11, 1994 by Pnina Fishman, Ph.D., the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and a director, and Ilan Cohn, Ph.D., the company’s Vice-Chairman of the Board of Directors, under the name Can-Fite Technologies Ltd. On January 7, 2001, we changed our name to Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. We completed our initial public offering in Israel in October 2005 and our ordinary shares are traded on the TASE under the symbol “CFBI”. Our ADSs currently trade in the United States on the OTC under the symbol “CANFY”.
In November 2011, through a series of transactions, we spun-off our activity in the ophthalmic field to OphthaliX, Inc., a Delaware corporation and successor-in-interest to Denali Concrete Management, Inc., a Nevada corporation, or OphthaliX, whose common shares are traded in the United States on OTC under the symbol “OPLI”. In the spin-off transactions, we granted an exclusive license for the use of our CF101 drug candidate in the ophthalmic field to Eye-Fite Ltd., an Israel limited company and a former wholly-owned subsidiary of ours, or Eye-Fite, and transferred our issued and outstanding ordinary shares in Eye-Fite to OphthaliX in exchange for an 86.7% interest in OphthaliX. In connection with the spin-off transactions, OphthaliX completed a series of private placement financing transactions. Following the spin-off transactions and the private placement financing transactions, we hold approximately 82% interest in OphthaliX and OphthaliX continues to develop the CF101 drug candidate for ophthalmic indications. See “Item 10. Additional Information—Material Contracts—OphthaliX Agreements”.
Our capital expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 were NIS 17,000, NIS 81,000 and NIS 107,000, respectively. Our current capital expenditures are made solely within Israel and primarily consist of the acquisition of computers and related communications equipment. Such capital expenditures are financed internally.
We qualify as an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act. For as long as we are deemed an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of specified reduced reporting and other regulatory requirements that are generally unavailable to other public companies. These provisions include:
| · | an exemption from the auditor attestation requirement in the assessment of our internal controls over financial reporting required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002; |
| · | an exemption from the adoption of new or revised financial accounting standards until they would apply to private companies; |
| · | an exemption from compliance with any new requirements adopted by the PCAOB requiring mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report in which the auditor would be required to provide additional information about our audit and our financial statements; and |
| · | reduced disclosure about our executive compensation arrangements. |
We will continue to be deemed an emerging growth company until the earliest of:
| · | the last day of our fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1,000,000,000 (as such amount is indexed for inflation every five years by the SEC to reflect the change in the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, setting the threshold to the nearest $1,000,000) or more; |
| · | the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of our first sale of common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act; |
| · | the date on which we have, during the prior three-year period, issued more than $1,000,000,000 in non-convertible debt; or |
| · | the date on which we are deemed to be a ‘large accelerated filer,” as defined in Regulation S-K under the Securities Act. |
B. Business Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on developing orally bioavailable small molecule therapeutic products for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic diseases. Our platform technology utilizes the Gi protein associated A3AR as a therapeutic target. A3AR is highly expressed in inflammatory and cancer cells, and not significantly expressed in normal cells, suggesting that the receptor could be a unique target for pharmacological intervention. Our pipeline drugs are synthetic, highly specific agonists and allosteric modulators, or ligands or molecules that initiate molecular events when binding with target proteins, targeting the A3AR.
| 31 |
Our product pipeline is based on the research of Dr. Pnina Fishman, who investigated a clinical observation that tumor metastasis can be found in most body tissues, but are rarely found in muscle tissue, which constitutes approximately 60% of human body weight. Dr. Fishman’s research revealed that one reason that striated muscle tissue is resistant to tumor metastasis is that muscle cells release small molecules which bind with high selectivity to the A3AR. As part of her research, Dr. Fishman also discovered that A3ARs have significant expression in tumor and inflammatory cells, whereas normal cells have low or no expression of this receptor. The A3AR agonists and allosteric modulators, currently the company pipeline drugs, bind with high selectivity and affinity to the A3ARs and upon binding to the receptor initiate down-stream signal transduction pathways resulting in apoptosis, or programmed cell death, of tumors and inflammatory cells and to the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are proteins produced by cells that interact with cells of the immune system in order to regulate the body’s response to disease and infection. Overproduction or inappropriate production of certain cytokines by the body can result in disease. We have in-licensed certain patents and patent applications protecting three different A3AR ligands which represent our current pipeline drugs under development and include two synthetic A3AR agonists, CF101 (known generically as IB-MECA) and CF102 (known generically as CI-IB-MECA) from the NIH, and an allosteric modulator at the A3AR, CF602 from Leiden University. In addition, we have out-licensed CF101 for (i) the treatment of autoimmune diseases to Seikagaku Corporation, a Japanese public corporation, or SKK, for the Japanese market, (ii) for the treatment of RA to Kwang Dong Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., a South Korean limited company, or KD, for the Korean market and (iii) for the treatment of ophthalmic diseases to Eye-Fite, a wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX for the global market.
Our drugs, CF101, CF102 and CF602 are being developed to treat several autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic indications. CF101 is in various stages of clinical development for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, or RA; psoriasis and osteoarthritis, or OA. CF101 is also being developed by OphthaliX for the treatment of ophthalmic indications, including keratoconjunctivitis sicca, also known as dry eye syndrome, or DES, glaucoma and uveitis. The CF102 drug candidate is being developed for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, also known as primary liver cancer, or HCC, and for the treatment of the hepatitis C virus, or HCV. CF602 is our second generation allosteric drug candidate for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, which has shown proof of concept in in vitro and in vivo studies. In addition, we recently announced that we are planning to develop CF602 to treat sexual dysfunction. Preclinical studies revealed that our drugs have potential to treat additional inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, oncological diseases and viral diseases, such as the JC virus, a virus that causes a potentially fatal brain disease in persons with an immunodeficiency.
Our pipeline drugs represent a significant market opportunity. For instance, according to Datamonitor, as of 2010, RA market size was approximately $12 billion and was expected to grow to approximately $18 billion by 2020. According to Nature Biotechnology, as of 2010, the market for psoriasis treatments was estimated at approximately $3.3 billion a year. According to GlobalData, the global OA market was $4.4 billion in 2010 and forecast to grow to $5.9 billion by 2018. According to GlobalData, the DES global market size was approximately $1.6 billion in 2012, and was expected to grow to approximately $5.5 billion by 2022, the market for glaucoma drugs was estimated at approximately $3.0 billion and the uveitis therapeutics market is expected to grow from $0.32 billion in 2010 to $1.6 billion by 2017. Additionally, GlobalData recently estimated that the market size for HCC drugs in 2017 will be $1.2 billion. Lastly, according to Renub Research, the market size for treatment of HCV was approximately $6.0 billion in 2011.
We believe that our drugs have certain unique characteristics and advantages over drugs currently available on the market and under development to treat these indications. To date, we have generated our pipeline by in-licensing, researching and developing two synthetic A3AR agonists, CF101 and CF102, and an allosteric modulator, CF602. For example, our technology platform is based on the finding that the A3AR is highly expressed in pathological cells, such as various tumor cell types and inflammatory cells. High A3AR expression levels are also found in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, or PBMCs, of patients with cancer, inflammatory and viral diseases. PBMCs are a critical part of the immune system required to fight infection. We believe that targeting the A3AR with synthetic and highly selective A3AR agonists, such as CF101 and CF102, and allosteric modulators, such as CF602, induces anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. In addition, our human clinical data suggests that the A3AR is a biological marker and that high A3AR expression prior to treatment may be predictive of good patient response to our drug treatment. In fact, as a result of our research we have developed a simple blood assay to test for A3AR expression as a predictive biological marker. We have applied for a patent with respect to the intellectual property related to such assay and are currently utilizing this assay in our ongoing Phase IIb study of CF101 tor the treatment of RA.
Moreover, characteristics of CF101, as exhibited in our clinical studies to date, including its good safety profile, clinical activity, simple and less frequent delivery through oral administration and its low cost of production, position it well against the competition in the autoimmune-inflammatory markets, including the psoriasis and RA markets, where treatments, when available, often include injectable drugs, many of which can be highly toxic, expensive and not always effective. Furthermore, pre-clinical pharmacology studies in different experimental animal models of arthritis revealed that CF101 acts as a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug, or a DMARD, which, when coupled with its good safety profile, make it competitive in the psoriasis, RA and OA markets. Our recent findings also demonstrate that a biological predictive marker can be utilized prior to treatment with CF101, which may allow it to be used as a personalized medicine therapeutic approach for the treatment of RA. CF101 is also well-positioned against some of the competition in the ophthalmic markets, where treatments, when available, often include frequent self-administered eye drops, which may be more difficult than taking pills and may result in less than the full dose of the drug actually entering the eye, have undesirable side effects and do not simultaneously treat the underlying cause and relieve the symptoms associated with the indication. Like CF101, CF102 has a good safety profile, is orally administered and has a low cost of production, which positions it well in the HCC market, where only one drug, Nexavar, has been approved by the FDA.
Nevertheless, other drugs on the market, new drugs under development (including drugs that are in more advanced stages of development in comparison to our drug pipeline) and additional drugs that were originally intended for other purposes, but were found effective for purposes targeted by us, may all be competitive to the current drugs in our pipeline. In fact, some of these drugs are well established and accepted among patients and physicians in their respective markets, are orally bioavailable, can be efficiently produced and marketed, and are relatively safe. None of our product candidates have been approved for sale or marketing and, to date, there have been no commercial sales of any of our product candidates.
| 32 |
Our research further suggests that A3AR affects pathological and normal cells differently. While specific A3AR agonists, such as CF101 and CF102, and allosteric modulators, such as CF602, appear to inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of cancer and inflammatory cells, normal cells are refractory, or unresponsive to the effects of these drugs. To date, the A3AR agonists have had a positive safety profile as a result of this differential effect.
We also seek to obtain technologies that complement and expand our existing technology base by entering into license agreements with academic institutions and biotechnology companies. To date, we have in-licensed intellectual property which protects certain small molecules, such as CF101 and CF102, from the NIH, and CF602 from Leiden University. Under our license agreements we are generally obligated to diligently pursue product development, make development milestone payments, pay royalties on any product sale and make payments upon the grant of sublicense rights. The scope of payments we are required to make under our in-licensing agreements is comprised of various components that are paid commensurate with the progressive development and commercialization of our drug products. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—In-Licensing Agreements”.
In addition to in-licensing, we have also out-licensed one of our molecules to third-parties to capitalize on the experience, capabilities and location of such third-parties. Similar to our obligations under any in-license agreements, pursuant to these out-licensing agreements, our licensees are generally obligated to diligently pursue product development, make up-front payments, make development milestone payments and pay royalties on sales. Accordingly, we expect to fund certain of our future operations through out-licensing arrangements with respect to our product candidates. To date, we have out-licensed CF101 for the treatment of autoimmune diseases for the Japanese market to SKK, and CF101 for the treatment of RA for the Korean market to KD and CF101 for ophthalmic diseases for the global market to OphthaliX. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”.
We are currently: (i) conducting a Phase II/III trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of psoriasis; (ii) conducting a Phase IIb trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of RA; (iii) preparing for a Phase II study with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of OA; (iv) preparing for a Phase II study with respect to the development of CF102 for the treatment of HCC (and as part of this study, we will also test CF102 in patients with both HCC and HCV); and (v) in preclinical work with respect to the development of CF602. OphthaliX is currently: (i) conducting a Phase III trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of DES; (ii) conducting a Phase II trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of glaucoma or related syndromes of ocular hypertension; and (iii) initiating a Phase II study of CF101 for the treatment of uveitis.
Our Strategy
Our strategy is to build a fully integrated biotechnology company that discovers, in-licenses and develops an innovative and effective small molecule drug portfolio of ligands that bind to a specific therapeutic target for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological, ophthalmic diseases and more. We continue to develop and test our existing pipeline, while also testing other indications for our existing drugs and examining, from time to time, the potential of other small molecules that may fit our platform technology of utilizing small molecules to target the A3AR. We generally focus on drugs with global market potential and we seek to create global partnerships to effectively assist us in developing our portfolio and to market our products. Our approach allows us to:
| · | continue to advance our clinical and preclinical pipeline; |
| · | test our products for additional indications which fit our molecules’ mechanism of action; |
| · | identify other small molecule drugs or ligands; |
| · | focus on our therapeutic candidates closest to realizing their potential; and |
| · | avoid dependency on a small number of small molecules and indications. |
Using this approach, we have successfully advanced our therapeutic candidates for a number of indications into various stages of clinical development. Specific elements of our current strategy include the following:
| 33 |
Successful development of our existing portfolio of small molecule orally bioavailable drugs for the treatment of various diseases. We intend to continue to develop our existing portfolio of small molecule orally bioavailable drugs, both for existing targeted diseases, as well as other potential indications. Our drug development will continue to focus on inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic diseases. We will focus most prominently on advancing our product candidates that are in the most advanced stages, i.e., DES, plaque psoriasis and RA (and later posterior uveitis, glaucoma and OA) with respect to CF101, and HCC with respect to CF102.
Use our expertise with our platform technology to evaluate in-licensing opportunities. We continuously seek attractive product candidates and innovative technologies to in-license or acquire. We intend to focus on product candidates that would be synergistic with our A3AR expertise. We believe that by pursuing selective acquisitions of technologies in businesses that complement our own, we will be able to enhance our competitiveness and strengthen our market position. We intend to utilize our expertise in A3AR and our pharmacological expertise to validate new classes of small molecule orally bioavailable drugs. We will then seek to grow our product candidate portfolio by attempting to in-license those various candidates and to develop them for a variety of indications.
Primarily develop products that target major global markets. Our existing product candidates are almost all directed at diseases that have major global markets. Our intent is to continue to develop products that target diseases that affect significant populations using our platform technology. These arrangements will allow us to share the high development cost, minimize the risk of failure and enjoy our partners’ marketing capabilities, while also enabling us to treat a more significant number of persons. We believe that this strategy will increase the likelihood of advancing clinical development and potential commercialization of our product candidates.
Commercialize our therapeutic candidate through out-licensing arrangements. We have entered into two out-licensing arrangements with major pharmaceutical companies in the Far East. We intend to continue to commercialize our products through out-licensing arrangements with third parties who may perform any or all of the following tasks: completing development, securing regulatory approvals, manufacturing, marketing and sales. We do not intend to develop our own manufacturing facilities or sales forces. If appropriate, we may enter into co-development and similar arrangements with respect to any therapeutic candidate with third parties or commercialize a therapeutic candidate ourselves. These arrangements will allow us to share the high development cost, minimize the risk of failure and enjoy our partners’ marketing capabilities. We believe that this strategy will increase the likelihood of advancing clinical development and potential commercialization of our product candidates.
| 34 |
Our Product Pipeline
The table below sets forth our current pipeline of product candidates, including the target indication and status of each.
| Clinical Application/Drug | Pre-Clinical | Phase I | Phase II | Phase III | |
| Autoimmune-Inflammatory | |||||
| Psoriasis – CF101 | |||||
| Rheumatoid Arthritis – CF101 | |||||
| Osteoarthritis – CF101(1) | |||||
| Inflammation and Sexual Dysfunction – CF602 | |||||
| Oncology | |||||
| HCC – CF102(1) (2) | |||||
| Ophthalmology (3) | |||||
| DES – CF101 | |||||
| Glaucoma – CF101 | |||||
| Uveitis – CF101 | |||||
| (1) | In preparatory work to commence a Phase II study. |
| (2) | As part of the HCC study, the Company will study HCC patients with the HCV. |
| (3) | OphthaliX, an 82% owned subsidiary of the Company, develops CF101 for ophthalmic indications. |
CF101
CF101, our lead therapeutic product candidate, is in development for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory diseases, psoriasis, RA and OA, and the ophthalmic diseases, DES, glaucoma and uveitis. In certain of our pharmacological studies, CF101 has also shown potential for development for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. CF101 is a highly-selective, orally bioavailable small molecule synthetic drug, which targets the A3AR. Based on our clinical studies to date, we believe that CF101 has a favorable safety profile and significant anti-inflammatory effects as a result of its capability to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1, and chemokines, or small cytokines, such as MMPs, by signaling key proteins such as NF-кB and PKB/AKT. Overall, these up-stream events result in apoptosis of inflammatory cells. See Figure 1 below. CF101’s anti-inflammatory effect is mediated via the A3AR, which is highly expressed in inflammatory cells.
| 35 |

Figure 1: CF101 anti-inflammatory mechanism of action
Set forth below are general descriptions of the inflammatory and ophthalmic diseases with respect to which CF101 has underwent, is currently undergoing, or is in preparation for clinical trials.
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune hereditary disease that affects the skin. In psoriasis, immune cells move from the dermis to the epidermis, where they stimulate keratinocytes, or skin cells, to proliferate. DNA acts as an inflammatory stimulus to stimulate receptors which produce cytokines, such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, and antimicrobial peptides. These cytokines and antimicrobial peptides signal more inflammatory cells to arrive and produce further inflammation. In other words, psoriasis occurs when the immune system overreacts and mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow gradually and flake off approximately every four weeks. New skin cells grow to replace the outer layers of the skin as they shed. But in psoriasis, new skin cells move rapidly to the surface of the skin in days rather than weeks. They build up and form thick patches called plaques.
There are five types of psoriasis: plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular and erythrodermic. The most common form, plaque psoriasis, is commonly seen as red and white hues of scaly patches appearing on the top first layer of the epidermis, or skin. In plaque psoriasis, skin rapidly accumulates at these sites, which gives it a silvery-white appearance. Plaques frequently occur on the skin of the lower back, elbows and knees, but can affect any area, including the scalp, palms of hands, soles of feet and genitals. The plaques range in size from small to large. In contrast to eczema, psoriasis is more likely to be found on the outer side of the joint. Some patients, though, have no dermatological symptoms.
Psoriasis is a chronic recurring condition that varies in severity from minor localized patches to complete body coverage. Fingernails and toenails are frequently affected, known as psoriatic nail dystrophy, and can be seen as an isolated symptom. Psoriasis can also cause inflammation of the joints, which is known as psoriatic arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: RA, is a chronic, systemic autoimmune-inflammatory disease that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks flexible synovial, or joints, on both sides of the body. This symmetry helps distinguish RA from other types of arthritis, which is the general term for joint inflammation. Although the cause of RA is unknown, autoimmunity plays a pivotal role in both its chronicity and progression. The disease involves abnormal B cell–T cell interaction, which results in the release of cytokines. The cytokines signal the release of inflammatory cells. The inflammatory cells migrate from the blood into the joints and joint-lining tissue. There, the cells produce inflammatory substances that cause irritation, wearing down of cartilage, or the cushioning material at the end of bones, swelling and inflammation of the joint lining, which is caused by excess synovial fluid, the development of pannus, or fibrous tissue, in the joint, and ankylosis, or fusion of the joints. Joint inflammation is characterized by redness, warmth, swelling and pain within the joint. As the cartilage wears down, the space between the bones narrows. If the condition worsens, the bones could rub against each other. As the lining expands due to inflammation from excess fluid, it may erode the adjacent bone, resulting in bone damage. RA can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, membrane around the heart, the membranes of the lungs, and white of the eye, and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue.
| 36 |
Osteoarthritis: OA is a common chronic degenerative joint disease that is characterized by a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage, or the cartilage found on joint surfaces. Although degeneration of joint cartilage is the central feature in OA, the disease is also associated with changes in synovium and subchondral bone metabolism, causing inflammation of the synovial membrane in the involved joints. Synovial inflammation and local concentration of pro-inflammatory mediators seem to be directly involved in the generation of pain in osteoarthritic joints.
OA is related to, but not caused by, aging. As a person ages, the water content of the cartilage decreases, causing the cartilage to be less resilient. When the cartilage is less resilient, it can become susceptible to degradation or exacerbation of existing degeneration. Inflammation of the surrounding joint capsule can also occur, though often mild (compared to what occurs in RA). This can happen as breakdown products from the cartilage are released into the synovial space and the cells lining the joint attempt to remove them. New bone outgrowths, called “spurs” or osteophytes, can form on the margins of the joints. These bone changes, together with the inflammation, can be both painful and debilitating.
Mechanical stress on joints underlies all OA. There are many and varied sources of mechanical stress, including misalignments of bones caused by congenital or pathogenic causes, mechanical injury, obesity, loss of strength in muscles supporting joints and impairment of peripheral nerves, leading to sudden or uncoordinated movements that overstress joints. However, despite the numerous causes of osteoarthritis, the resulting pathology remains the same.
Dry Eye Syndrome: DES is an eye disease caused by eye dryness, which, in turn, is caused by either decreased tear production or increased tear film evaporation. The tear film is comprised of the lower mucous layer which helps the tear film adhere to the eyes, a middle layer of water and an upper oil layer that seals the tear film and prevents evaporation. The tear film keeps the eye moist, creates a smooth surface for light to pass through the eye, nourishes the front of the eye and provides protection from injury and infection. DES is usually caused by aqueous tear deficiency, or inadequate tear production, whereby the lachrymal gland, the gland that secretes the aqueous layer of the tear film, does not produce sufficient tears to keep the entire conjunctiva, or the tissue inside the eyelids that covers the sclera, and cornea covered by a complete layer of tear film. In rare cases, aqueous tear deficiency may be a symptom of collagen vascular diseases, including RA, Wegener’s granulomatosis, an incurable form of vasculitis (the inflammatory destruction of blood vessels), systemic lupus erythematosus, an autoimmune connective tissue disease, Sjögren’s syndrome, an autoimmune process in which patients suffer from mouth and eye dryness, and autoimmune diseases associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. DES can also be caused by abnormal tear composition resulting in rapid evaporation or premature destruction of tears. Additional causes include, but are not limited to, age, use of certain drugs and the use of contact lenses.
DES is characterized by eye irritation symptoms, blurred and fluctuating vision, tear film instability, increased tear osmolarity and ocular surface epithelial disease. DES causes constant ocular discomfort, typically dryness, burning, a sandy-gritty eye irritation and a decrease in visual function. Over an extended period of time, DES can lead to tiny abrasions on the surface of the eyes. In advanced cases, the epithelium undergoes pathologic changes, namely squamous metaplasia, a non-cancerous change of surface-lining cells, and loss of goblet cells, which secrete mucin, which in turn dissolves in water to form mucous. Some severe cases result in thickening of the corneal surface, corneal erosion, epithelial defects, corneal ulceration (sterile and infected), corneal neovascularization, or excessive ingrowth of blood vessels, corneal scarring, corneal thinning, and even corneal perforation. In the most severe cases, DES may result in deterioration of vision.
| 37 |
Glaucoma: Glaucoma is an eye disease in which the optic nerve is damaged. This optic nerve damage involves loss of retinal ganglion cells, or neurons located near the inner surface of the retina, in a characteristic pattern. There are many different subtypes of glaucoma, but they can all be considered to be a type of optic neuropathy. Raised intraocular pressure, or IOP, is the most important and only modifiable risk factor for glaucoma. However, some individuals may have high IOP for years and never develop optic nerve damage. This is known as ocular hypertension. Others may develop optic nerve damage at a relatively low IOP, and, thus, glaucoma. Untreated glaucoma can lead to permanent damage of the optic nerve and resultant visual field loss, which over time can progress to blindness.
Glaucoma can be roughly divided into two main categories, “open angle” and “closed angle” glaucoma. The angle refers to the area between the iris and cornea through which fluid must flow to exit the eye. The difficulty or inability of such fluid to exit the eye causes an acute increase of pressure and pain. Closed angle glaucoma can appear suddenly, is often painful and visual loss can progress quickly. However, the discomfort often leads patients to seek medical attention before permanent damage occurs. Open angle, chronic glaucoma tends to progress at a slower rate and patients may not notice they have lost vision until the disease has progressed significantly.
Uveitis: Uveitis is inflammation of the middle layer of the eye, or the uvea, caused by an immune reaction. Uveitis can be associated with auto-immune inflammatory diseases and various eye infections. Uveitis is a common cause of blindness. The most common form of uveitis is anterior uveitis, which involves inflammation in the front part of the eye. It is often called iritis because it usually only affects the iris, the colored part of the eye. The inflammation may be associated with autoimmune diseases, but most cases occur in healthy people. The disorder may affect only one eye and is most common in young and middle-aged people.
Posterior uveitis affects the back part of the uvea, and involves primarily the choroid, a layer of blood vessels and connective tissue in the middle part of the eye. This type of uveitis is called choroiditis. If the retina is also involved, it is called chorioretinitis. Anterior uveitis affects the front part of the uvea, and involves primarily the iris and the cilliary body. This type of uveitis is called iridocyclitis. These conditions may develop as a result of a body-wide, or systemic, infection or an autoimmune disease. Another form of uveitis is pars planitis. This inflammation affects the narrowed area, or the pars plana, between the iris, or colored part of the eye, and the choroid. Pars planitis usually occurs in young men and is generally not associated with any other disease. However, some evidence suggests it may be linked to Crohn’s disease and, possibly, multiple sclerosis.
Pre-Clinical Studies of CF101
The information below is based on the various studies conducted with CF101, including preclinical studies. All of the studies were conducted by Can-Fite and/or by Can-Fite’s partners or affiliates.
The toxicity of CF101 has been evaluated following 28-day, 90-day, six-month and nine-month good laboratory practice repeated-dose toxicity studies in male and female mice (28-day, 90-day and six-month), dogs (single-dose only), and monkeys (28-day, 90-day and nine-month). Even though the dose of CF101 in these studies was escalated to an exposure that is many folds higher than the dose used in human clinical studies, no toxic side effects were identified.
Effects on cardiovascular parameters were evaluated in conscious instrumented monkeys and anesthetized dogs. These studies demonstrated no significant cardiovascular risk.
Genotoxicity studies were conducted in bacterial and mammalian mutation assays in vitro (i.e., laboratory) and in an in vivo (i.e., animal) mouse micronucleus assay. These studies were all negative, indicating no deleterious action on cellular genetic material.
Reproductive toxicology studies that we completed in mice and rabbits did not reveal evidence of negative effects on male or female fertility. In mouse teratology studies, or studies for abnormalities of physiological developments, craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities were observed at doses greater than 10 mg/kg; however, no such effects were observed at 3 mg/kg. Teratogenicity, or any developmental anomaly in a fetus, was not observed in rabbits given doses (greater than 13 mg/kg) that induced severe maternal toxicity in such rabbits.
| 38 |
Studies of P450 enzymes, or enzymes that participate in the metabolism of drugs, showed that CF101 caused no P450 enzyme inhibition, or increased drug activity, or induction, or reduced drug activity. Studies carried out with radiolabeled (C14) CF101 in rats showed that the drug is excreted essentially unchanged. These studies also showed that the drug is widely distributed in all body parts, except the central nervous system.
Clinical Studies of CF101
The information below is based on the various studies conducted with CF101, including clinical studies in patients with autoimmune-inflammatory and ophthalmic diseases. All of the studies were conducted by Can-Fite and/or by Can-Fite’s partners or affiliates.
Phase I Clinical Studies of CF101
CF101 has been studied comprehensively in normal volunteer trials to assess safety, pharmacokinetic metabolism and food interaction. Two Phase I studies in 40 healthy volunteers, single dose and repeated dose, indicated that CF101 is rapidly absorbed (reaching a maximal concentration within one to two hours) with a half life of eight to nine hours. Some mild adverse events (principally, increased heart rate) were observed at doses higher than single doses of 10.0 mg and twice-daily doses of 5.0 mg. Such increase in heart rate was not accompanied by any change in QT intervals. The drug showed linear kinetics, in that the concentration that results from the dose is proportional to the dose and the rate of elimination of the drug is proportional to the concentration, and low inter-subject variability, meaning that the same dose of the drug does not produce large differences in pharmacological responses in different individuals. A fed-fast Phase I study (with and without food) demonstrated that food causes some attenuation in CF101 absorption; accordingly CF101 is instructed to be given to patients on an empty stomach in our trials. An additional Phase I study of the absorption, metabolism, excretion and mass balance of 4.0 mg (C14) CF101 was conducted in six healthy male subjects and demonstrated that CF101 was generally well-tolerated in this group.
Based on the findings from Phase I clinical studies, 4.0 mg BID, or twice daily, was selected as the upper limit for initial Phase II clinical trials.
Phase II and Phase II/III Clinical Studies of CF101
CF101 has completed five Phase II studies in DES, Psoriasis and RA in approximately 730 patients (527 patients treated with CF101 and 203 patients treated with a placebo) for an aggregate exposure of approximately 150 patient years. These studies indicate that CF101 has a favorable safety profile at doses up to 4.0 mg BID for up to 12 weeks. In these Phase II studies, we did not observe a dose-response relationship between CF101 and adverse events. Moreover, we did not observe any clinically significant changes in vital signs, electrocardiograms, blood chemistry or hematology. CF101 given as a standalone therapy reached the primary endpoint in Phase II clinical studies in DES and psoriasis. In addition, we observed positive data utilizing CF101 as a standalone drug in a Phase IIa clinical study in RA. In this study, we also observed a significant direct correlation between A3AR expression prior to treatment and the patients’ responses to CF101. However, we did not fully attain the primary endpoint in this study as we did not observe a significant difference in responses between CF101 and the placebo (which for this study was 0.1 mg of CF101). Moreover, two Phase IIb studies in RA utilizing CF101 in combination with methotrexate, a generic drug commonly used for treating RA patients, or MTX, also failed to reach the primary endpoints. Based on this data, the Company believes that the failures in the Phase IIb studies in RA may have been due to low A3AR expression in the MTX-treated patients and as such, is currently in the process of testing CF101 as a standalone therapy in patients with A3AR expression levels above a certain threshold. CF101 has been tested in Phase II trials to establish dose and activity (first, orally administered capsules and then tablets in formulations of 1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mg of CF101 BID) in the following clinical settings:
| · | Psoriasis (moderate to severe plaque psoriasis). |
| · | RA; and |
| · | DES (moderate to severe). |
| 39 |
Psoriasis: The rationale for utilizing CF101 to treat psoriasis stems from our pre-clinical pharmacology studies showing that CF101 acts as an anti-inflammatory agent via the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, which plays a major role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. In addition, the A3AR is over-expressed in the tissue and PBMCs of patients with psoriasis.
We completed an exploratory Phase II trial in ten European and Israeli medical centers involving 76 patients. This study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled and included four cohorts of 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mg of CF101 and a placebo for a 12-week period. The study objectives were efficacy and safety of daily doses of CF101 administered orally in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque-type psoriasis and the efficacy endpoints were improvements in both the Psoriasis Area Sensitivity Index score, or PASI score, and the Physicians’ Global Assessment score, or PGA score. We concluded that CF101 met such efficacy endpoints and was safe, well tolerated and effective in ameliorating disease manifestations in these patients. The patient group receiving 2.0 mg CF101 BID showed progressive improvement over the course of the 12-week study in the PGA and PASI scores. Analysis of the mean change from baseline in the PASI score at week 12 revealed a statistically significant difference between the 2.0 mg CF101 BID treated group and the placebo group (P < 0.001 versus baseline and P = 0.031 versus placebo). Analysis of the PGA score revealed that 23.5% of the patients treated with the 2.0 mg CF101 BID achieved a score of 0 or 1, in comparison to 0% in the placebo group (P < 0.05). The study also demonstrated linear improvement in patients in both PASI and PGA. See Figure 2. No drug-related serious adverse events were evident during the study.
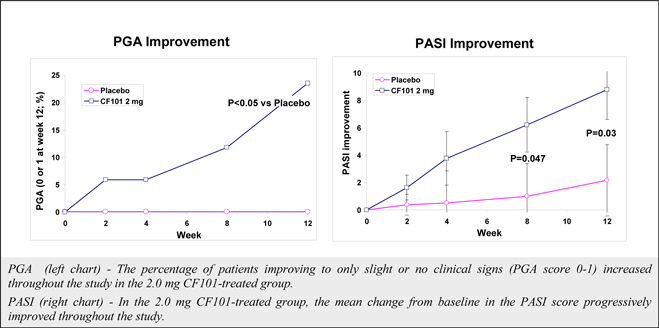
Figure 2: Psoriasis efficacy by PGA and PASI
| 40 |
Set forth below are representative pictures of a patient with plaque-type psoriasis on the upper and lower back treated with 2.0 mg CF101 BID, both baseline and week 12.
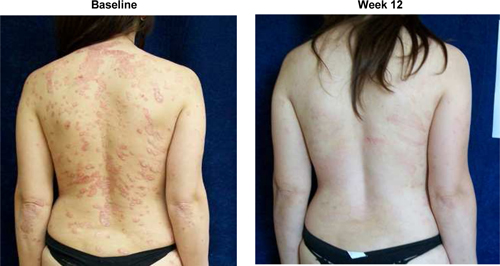
A comparison between baseline and week 12 of a patient treated with 2.0 mg CF 101
In June 2010, the Company obtained FDA approval to conduct a Phase II/III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study of the efficacy and safety of CF101 administered daily orally in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. This clinical trial will include approximately 300 patients that will be treated for a period of six months in the United States, Europe and Israel. Based on a positive safety and efficacy interim analysis of the first 103 patients who completed 24 weeks of treatment in the trial, the Company decided to continue patient enrollment for the second stage of the study. The positive clinical effects of the CF101 2.0 mg BID dose relative to a placebo were observed in a variety of standard psoriasis assessment parameters, including PASI 75 and PGA scores, with the responses accumulating steadily over the 24-week treatment period. See Figure 3. The Company believes that this clinical data corroborates the published Phase II study results described above and confirms the dose selection, while the favorable safety profile of CF101 further supports its development for the systemic treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. To allow the trial to meet its full objectives, the study protocol was amended to extend the CF101 2.0 mg BID and placebo administration for a period of 32 weeks. The studies in the United States will be conducted under an open Investigatory New Drug application, or an IND, which was received by the FDA in 2010.
| 41 |

Figure 3: Psoriasis efficacy by PGA and PASI
Rheumatoid Arthritis: We conducted a Phase IIa blinded to dose study was conducted in 74 patients with RA, randomized to receive CF101 as a monotherapy in one of three doses—0.1 mg, 1.0 mg and 4.0 mg. The primary efficacy endpoint was ACR20 response at week 12, a criteria determined by the American College of Rheumatology that reflects 20% improvement in inflammation parameters. The study data revealed maximal response at the 1.0 mg group, showing 55.6% with ACR20, 33.3% with 50% improvement, or ACR50, and 11.5% with 70% improvement, or ACR70. CF101 administered BID for 12 weeks resulted in improvement in signs and symptoms of RA and was safe and well-tolerated. See Figure 4. Studies conducted in the United States were pursuant to an open IND which was received by the FDA in 2005.
| 42 |
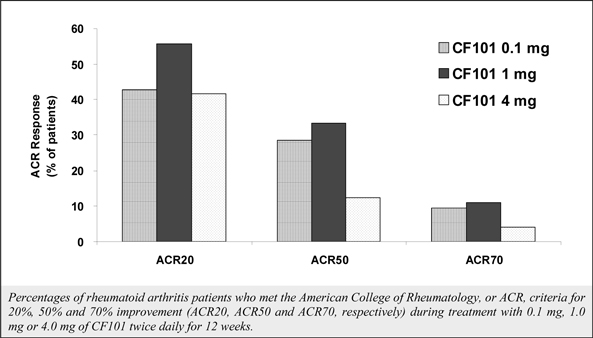
Figure 4: Rheumatoid Arthritis efficacy by ACR
Subsequently, two Phase IIb studies with CF101 in combination with MTX were conducted. The study protocols were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group and dose-finding to determine the safety and efficacy of daily CF101 administered orally when added to weekly MTX in patients with active RA. The objectives of both studies were improvement in ACR20, ACR50, ACR70 and DAS28, or the Disease Activity Score of 28 Joints, and EULAR, or the European League Against Rheumatism, response criteria, as well as a positive safety profile. The trials’ primary endpoints were both ACR20.
The first Phase IIb trial showed that the combined treatment had an excellent safety profile, but no significant ACR20 response was observed between the RA group treated with CF101 and MTX and the group treated with MTX alone (the placebo group). However, the ACR50, ACR70 and the EULAR Good Values in the combined treatment group were higher than those of the MTX placebo group. The study also indicated that the 1.0 mg CF101 dose was the most favorable dose, i.e., the dose yielded the highest ACR50 and EULAR Good Values as compared to the MTX placebo group. The most commonly reported adverse events in this study included nausea, dizziness, headache and common bacterial and viral infections and infestations.
Following a decision of the Company’s Clinical Advisory Board in October 2007, an additional Phase IIb study was initiated. This study was conducted in medical centers in Europe and Israel and included 230 patients who received the drug orally BID (0.1 and 1.0 mg CF101 tablets plus MTX versus a placebo, which was MTX alone) for 12 weeks. On April 30, 2009, the Company published preliminary results of the Phase IIb study, which were later confirmed as the final results, also indicating that the study’s objectives were not achieved. The most commonly reported adverse events in this study included nausea, myalgia and dizziness.
The two Phase IIb studies failed to achieve the primary endpoint of ACR20. A cross study analysis of the three RA clinical studies revealed that in the first Phase IIa study, where CF101 had been administered as a standalone drug, A3AR had been over-expressed in the patients’ PBMCs prior to CF101 treatment, whereas A3AR had not been over-expressed in the Phase IIb patient population. The Company believes, based on the foregoing data, that there may be a direct and statistically significant correlation between A3AR over-expression at baseline and patients’ response to CF101, and that CF101 should be administered as a standalone drug and not in combination with MTX. Furthermore, the correlation between A3AR expression levels prior to treatment and patients’ response to the drug suggest that the A3AR may be a predictive biomarker to be analyzed prior to CF101 treatment. See Figures 5 and 6.
| 43 |
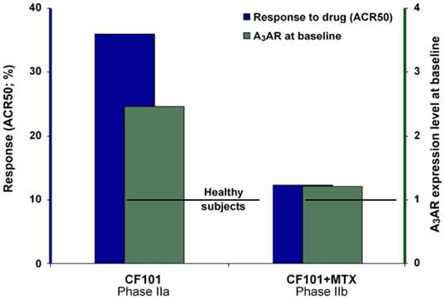
Figure 5: Direct correlation between A3AR at baseline and response to CF101
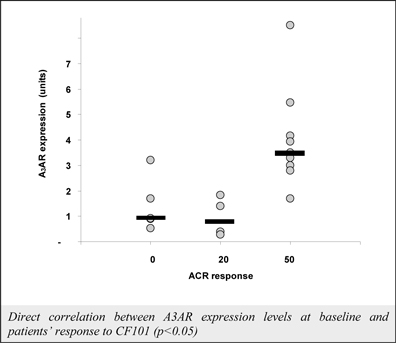
Figure 6: Direct correlation between A3AR at baseline and response to CF101
Based on the results of the two Phase IIb studies, we have determined to conduct an additional Phase IIb clinical study with CF101 as a stand-alone, monotherapy treatment and not in combination with MTX. In June 2010, we received approval from the Israeli Ministry of Health to conduct the Phase IIb trial as a 12-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to determine the safety and efficacy of CF101 administered orally daily in patients with active RA and elevated baseline expression levels of the A3AR in PBMCs. The Company has developed a simple blood assay to test the expression level of this biomarker and has applied for a patent with respect to utilizing the A3AR as a marker to predict patients’ response to the drug. We will only enroll patients with A3AR over-expression at baseline in this study. The trial will include 80 patients, 40 will be treated with CF101 1.0 mg as a standalone and 40 with a placebo. The primary objectives of this study are to determine the efficacy of oral CF101 when administered daily as a standalone treatment for 12 weeks to patients with active RA and elevated baseline expression levels of the A3AR in the patients’ PBMCs, in comparison to a placebo treatment, and to assess the safety of daily oral CF101 under the circumstances of the trial. Top line data from this study are expected in the second half of 2013.
| 44 |
DES: The Company conducted a Phase II study in DES after discovering that patients in the Phase IIa study for RA also experienced improvement in DES symptoms. The study prompted an application for two patents relating to DES and Sjörgen’s Syndrome. We have since successfully completed a Phase II study of CF101 in patients with moderate to severe DES, meeting its primary endpoint and demonstrating the drug’s ability to improve signs of ocular surface inflammation in these patients. The trial was a multicenter, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study with 76 patients (39 CF101 and 37 placebo). Patients were treated orally with either 1.0 mg CF101 pills or matching vehicle-filled placebo pills, BID for 12 weeks, followed by a two-week post-treatment observation. The primary endpoints of the Phase II trial were based on an improvement of more than 25% over baseline at week 12 in one of the following parameters: (i) tear break-up time, or BUT; (ii) superficial punctate keratitis (epithelial staining of the cornea) assessed by fluorescein staining, or FS, results; and (iii) Schirmer tear test 1 results, which are assessed by using paper strips inserted into the eye for several minutes to measure the production of tears. The results of the Phase II trial demonstrated the ability of CF101 to improve signs of ocular surface inflammation of the patients studied. The CF101-treated group experienced a statistically significant increase in the proportion of patients who achieved more than 25% improvement in FS and in the clearance of FS, as compared to the placebo group. Treatment with CF101 resulted in a statistically significant improvement in the mean change from baseline at week 12 of the FS, BUT and tear meniscus height, or TM, in the CF101-treated group. See Figure 7.
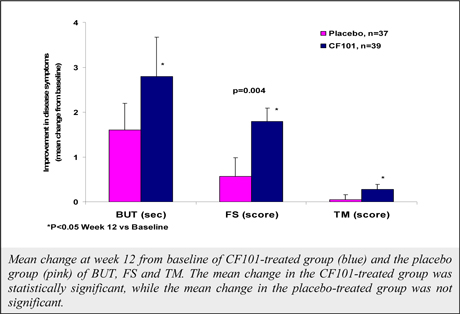
Figure 7: DES efficacy by BUT, FS, and TM
CF101 treatment induced a statistically significant increase in the proportion of patients who achieved greater than 25% improvement in FS and in the clearance of corneal staining between the CF101-treated group and the placebo. See Figure 8.
| 45 |
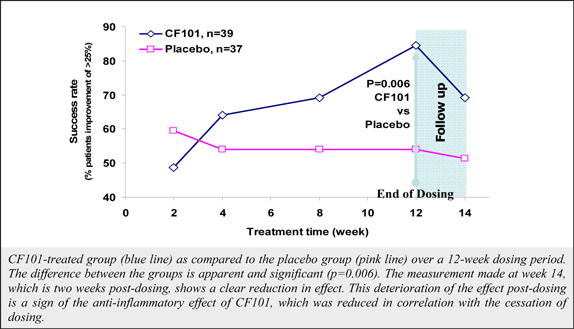
Figure 8: DES efficacy as determined utilizing FS
Patients treated with CF101 1.0 mg BID showed statistically significant FS clearing in almost all sub-segments of the cornea, especially the central cornea or pupil segment. See Figure 9.
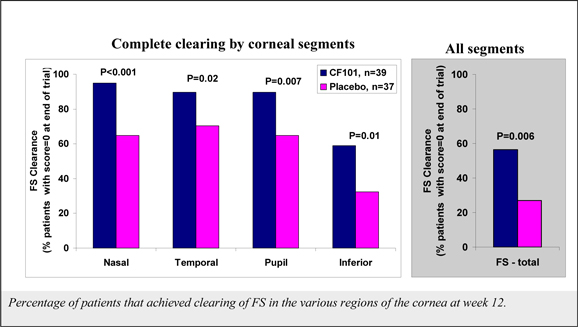
Figure 9: DES efficacy by FS clearing in the different corneal segments
Clinical laboratory safety tests included ophthalmic examinations, IOP measurements, electrocardiographic evaluations, vital sign measurements, and monitoring of adverse events. CF101 was well-tolerated and exhibited an excellent safety profile with no serious adverse events. No clinically significant changes in vital signs, electrocardiograms, blood chemistry or hematology values were observed. However, adverse events resulting in discontinuation of the study were observed in two patients: myalgias and recurrent corneal erosion. The frequency of adverse events was comparable in both treated groups. The most commonly reported adverse events included constipation, headache, palpitations, itching, abdominal pain, arthralgia, myalgia, fatigue and dry mouth.
| 46 |
The study results of the completed Phase II clinical trial for CF101 for the treatment of DES were published in “Ophthalmology,” which is one of the leading journals in the field. The Phase II Complete Study Report, or CSR, demonstrated positive results in patients with moderate to severe DES and also served as the basis for an IND with the FDA for a Phase III trial in the same patient population. The FDA approved the IND in September 2010 and the Phase III trial is currently being conducted by the Company, on behalf of OphthaliX, in the United States, Europe and Israel. The randomized, double-masked phase III clinical trial enrolled 237 patients who will be randomized to receive two doses of CF101 (0.1 and 1.0 mg) and placebo, for a period of 24 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint will be complete clearing of corneal staining. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Clinical Trials of CF101—Phase III Clinical Trials of CF101”. On March 15, 2013, OphthaliX announced that patient enrollment for the study was completed and that the results of this study are expected in the fourth quarter of 2013. OphthaliX plans on initiating an additional Phase III study involving CF101 for the treatment of moderate-to-severe DES after the conclusion of the current study.
Although the Phase II DES trial was not designed to assess the drug effect on IOP, the latter was tested as a safety parameter and at week 12, the CF101-treated group had a 1.1-mmHg, or 6%, decrease from baseline, which was statistically significant (p=0.048) when compared with the placebo. See Figure 10.
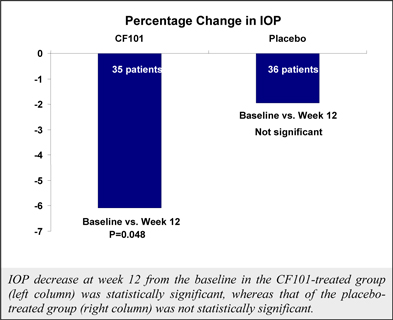
Figure 10: IOP decrease observed in the DES Phase II study
Glaucoma: The Company believes that the statistically significant decrease in IOP in the Phase II trial for DES, although observed in subjects without ocular hypertension, is clinically significant and indicates that CF101 may also have potential as a glaucoma therapy, as the main goal of glaucoma therapy is to reduce IOP. This finding led to a patent application for the use of CF101 for lowering IOP. This result, together with the neuro-protective and anti-inflammatory effects that have been demonstrated in our studies and the studies of others, warrant rapid progression into clinical study in this indication and a Phase II study in patients with glaucoma or related syndromes of ocular hypertension is currently ongoing in Israel and Europe via OphthaliX. This trial is a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of the safety and efficacy of daily CF101 administered orally in subjects with elevated IOP. The objectives of this study are to determine the effects of oral CF101 in lowering IOP when administered BID for 16 weeks in subjects with elevated IOP and the safety of oral CF101 in this subject population. This trial is being performed in two segments. In the first segment, subjects are being randomized to receive either CF101 1.0 mg or a matching placebo, given orally every 12 hours for 16 weeks. OphthaliX is enrolling 44 subjects in the first segment, randomized in a 3:1 ratio to CF101 1.0 mg or to the placebo. At the conclusion of the first segment, a Data Review Committee, or DRC, is to review safety and efficacy data and advise on progression of the trial to the second segment. The second segment, if conducted, will enroll up to approximately 88 subjects in up to three dose groups (CF101 1.0 mg, CF101 2.0 mg or the placebo every 12 hours) randomized in a 3:3:2 ratio. At its discretion, the DRC may also recommend increasing enrollment in the CF101 1.0 mg group or other changes to the protocol design. In May 2010, the Company announced that the Israeli Ministry of Health approved the study protocol. The Company subsequently initiated patient enrollment. The conclusion of the first segment of the study is expected in the second quarter of 2014. The Company has not yet filed an IND for this indication as CF101 for the treatment of glaucoma is not currently being clinically tested in the United States and there are no near-term plans to do so.
| 47 |
Additional Developments with CF101
Uveitis
Pre-clinical pharmacology studies were conducted by the Company in collaboration with the NIH, under a Material Cooperative Research and Development Agreement at its National Eye Institute, a worldwide leader in uveitis research. In January 2008, the Company announced that CF101 had been effective in these studies in inhibiting the development of posterior uveitis in an experimental animal model. On April 9, 2011 OphthaliX announced the completion of preclinical studies, showing that CF101 was effective in treating anterior uveitis in experimental animal models. The efficacy of CF101 in treating both anterior and posterior uveitis in experimental animal models supports further testing of CF101 for the treatment of patients with either anterior or posterior uveitis. The Company, together with the NIH, has applied for a patent for the use of CF101 for the treatment of uveitis. OphthaliX is currently initiating a Phase II study for uveitis and on July 16, 2013, announced the submission of the study protocol for the same. OphthaliX plans to conduct such Phase II study in Europe and Israel and to investigate the efficacy and safety of CF101 in 45 patients with active, sight-threatening, noninfectious intermediate or posterior uveitis, who will be treated with either CF101 or a placebo for a period of six months. The Company has not yet filed an IND for this indication as CF101 for the treatment of uveitis is not currently being clinically tested in the United States and there are no near-term plans to do so.
Osteoarthritis
According to the Arthritis Foundation, OA is the most common arthritic disease. Currently, there is a shortage of effective drugs for treating OA patients. CF101 has induced a significant anti-inflammatory effect in experimental animal models with respect to the treatment of OA and, as such, the Company is currently preparing for a Phase II study. The Company has not yet filed an IND for this indication as CF101 for the treatment of OA is not currently being clinically tested in the United States and there are no near-term plans to do so.
Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that may affect any portion of the gastrointestinal tract, causing a wide variety of symptoms. It primarily causes abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting and weight loss, however, it may also cause complications outside the gastrointestinal tract, such as skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, tiredness and lack of concentration. Pre-clinical pharmacology studies conducted by the Company demonstrated the efficacy of CF101 for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. The Company does not presently have plans for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
CF102
CF102 is our second drug candidate and is under development for the treatment of HCC and HCV. CF102 is also a small, orally bioavailable molecule, and an A3AR agonist, with high affinity and selectivity to the A3AR. In comparison to the expression in adjacent normal liver tissue, the A3AR is over-expressed in tumor tissues of patients with HCC, and the over-expression is also reflected in the patients’ PBMCs. A3AR over-expression in the patients’ tumor cells and PBMCs is attributed to high expression of certain A3AR transcription factors. The binding of CF102 to the A3AR results in down-regulation, or a decrease in the quantity of a cellular component, such as the number of receptors on a cell’s surface, of certain A3AR transcription factors. Our studies have shown that this down-regulation leads to apoptosis of HCC cells. In our pre-clinical and clinical studies, CF102 demonstrated anti-cancer, anti-viral and liver protective effects. As a result, we believe that CF102 can be used to treat a variety of oncological and liver-related diseases and viruses. In February 2012, the FDA granted an orphan drug status for the active moiety, or the part of the drug that is responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of the drug substance, of CF102 for the treatment of HCC. An orphan drug designation is a special designation by the FDA for drug approval and marketing. The special designation is granted to companies that develop a given drug for unique populations and for incurable and relatively rare diseases. The orphan drug designation program provides orphan status to drugs and biologics which are intended for the safe and effective treatment, diagnosis or prevention of rare diseases or disorders that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States. Orphan drug designations have enabled companies to achieve medical breakthroughs that may not have otherwise been achieved due to the economics of drug research and development as this status lessens some of the regulatory burdens, for approval, including statistical requirements for efficacy, safety and stability, in an effort to maintain development momentum. Orphan drug designation also results in additional marketing exclusivity and could result in certain financial incentives.
| 48 |
Set forth below are general descriptions of the diseases with respect to which CF102 has underwent or is currently undergoing clinical trials.
HCC: HCC is an oncological disease characterized by malignant tumors that grow on the surface or inside of the liver. This type of tumor is refractory to chemotherapy and to other anti-cancer agents. HCC, like any other cancer, develops when there is a mutation to the cellular machinery that causes the cell to replicate at a higher rate and/or results in the cell avoiding apoptosis. Chronic infections of Hepatitis B and/or C can aid the development of HCC by repeatedly causing the body’s own immune system to attack the liver cells, some of which are infected by the virus. While this constant cycle of damage followed by repair can lead to mistakes during repair which in turn lead to carcinogenesis, this hypothesis is more applicable, at present, to HCV. Chronic HCV causes HCC through cirrhosis. In chronic Hepatitis B, however, the integration of the virus into infected cells can directly induce a non-cirrhotic liver to develop HCC. Alternatively, repeated consumption of large amounts of ethanol can have a similar effect.
Hepatitis C: HCV is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the Hepatitis C virus. The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years, and chronic liver disease. The virus also increases the chance for HCC development. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop liver failure, liver cancer or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices, or dilated submucosal veins, which can be life-threatening. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact often associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, transfusions, and sexual intercourse.
Pre-Clinical Studies of CF102
The Company conducted several pre-clinical studies, including studies of toxicity. The results indicated that CF102 was well- tolerated with no adverse effects. In these studies, we evaluated the toxicity, stability, metabolism and other safety parameters of CF102 at doses much higher than the doses that we currently administer to humans in our clinical trials of CF102. In pre-clinical pharmacology studies, CF102 inhibited the growth of HCC via the induction of tumor cell apoptosis. In addition, in a collaboration with leading virology labs, we observed that CF102 inhibited viral replication of HCV through the down-regulation of viral proteins. Both of these findings served as a basis to further explore development of this drug for HCC and HCV. Moreover, our pre-clinical studies demonstrated that CF102 acted to stimulate liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy, or removal of a part of the liver, and as such, we applied for a patent for this treatment.
Clinical Studies of CF102
The information discussed below is based on the various studies conducted by Can-Fite with CF102, including clinical studies in patients with oncological and liver-related diseases and viruses.
| 49 |
Phase I Clinical Study
CF102 completed a Phase I double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, ascending single dose trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of orally administered CF102 in healthy volunteers. The study was conducted in the United States under an open IND. CF102 was found to be safe and well-tolerated with a half life time of 12 hours. See Figure 10.
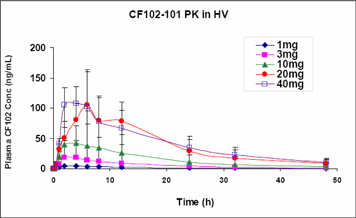
Figure 10. CF102 Pharmacokinetic profile
Phase I/II Clinical Study
CF102 completed two Phase I/II studies in Israel, one in patients with HCC and another in patients with HCV. The HCC Phase I/II study was an open-label, dose-escalation study evaluating the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of orally administered CF102 in patients with advanced HCC. The primary objectives of the study were to determine the safety and tolerability, dose-limiting toxicities, maximum tolerated dose, and recommended Phase II dose of orally administered CF102 in patients with advanced HCC; and to assess the repeat-dose pharmacokinetics behavior of CF102 in those patients. The secondary objectives were to document any observed therapeutic effect of CF102 in patients with HCC and to evaluate the relationship between PBMCs and the A3AR expression at baseline, as a biomarker, and the effects of CF102 in patients with HCC. The study included 18 patients, nine of which were also carriers of HCV. The initial dose of CF102 was 1.0 mg BID, with planned dose escalations in subsequent cohorts to 5.0 and 25.0 mg BID. This Phase I/II study achieved its objectives, showing a good safety profile, or no material differences versus a placebo with respect to observed and patient-indicated side effects, for CF102 and a linear pharmacokinetic drug profile, with no dose-limiting toxicities at any dose level. The median overall survival time for the patients in this study was 7.8 months, which is encouraging data considering that (i) 67% of the patient population in the study had previously progressed on Nexavar, produced by Onyx Pharmaceuticals and Bayer, and that CF102 was a second line therapy for these patients and (ii) 28% of the patient population were Child-Pugh Class B patients (patients classified on the Child Pugh scoring system for chronic liver disease as having significantly impaired liver function) whose overall survival time is usually 3.5 to 5.5 months. Accordingly, we may also consider CF102 as a drug to be developed for this patient sub-population of Child-Pugh Class B patients. CF102 had no adverse effect on routine measures of liver function over a six-month period in 12 patients treated for at least that duration. These findings are consistent with our pre-clinical CF102 data which demonstrated a protective effect on normal liver tissue in an experimental model of liver inflammation. As such, CF102 may potentially be a safer alternative to patients with cirrhosis and/or hepatic impairment. The study also demonstrated a direct relationship between A3AR expression at baseline and patients’ response to CF102, suggesting A3AR as a predictive biological marker. We also observed a decrease in the viral load of seven out of nine patients who were also carriers of HCV. The most commonly reported adverse events included loss of appetite, ascites, nausea, diarrhea, constipation and pain. However, many of these events are expected in a population of patients with advanced HCC. The most frequently reported drug-related adverse events included diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, pain and weakness.
| 50 |
Our second Phase I/II study was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study evaluating the safety, tolerability, biological activity, and pharmacokinetics of orally administered CF102 in 32 subjects with chronic HCV genotype 1. Eligible subjects were assigned in a 3:1 ratio (eight subjects in each cohort) to receive QD or BID treatment (1.0, 5.0 and 25.0 mg of CF102) for 15 days with oral CF102 or with a placebo. Dose escalation occurred in four sequential cohorts. The study’s primary objectives were to determine the safety and tolerability of orally administered CF102 in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1, to assess the effects on HCV load during 15 days of treatment with CF102 and to assess the repeat-dose pharmacokinetic behavior of CF102 under the conditions of this trial. The secondary objective of this trial was to perform an exploratory evaluation of the relationship between A3AR in PBMCs at baseline and the clinical effects of CF102 on the study’s patients. Following the decrease in HCV load that had been observed in HCV patients treated with CF102 in the parallel HCC study and the good safety profile of CF102, the Company received an IRB approval to extend the treatment period of the Phase I/II in patients with HCV to four months with the 1.0 mg dose vs. the placebo. The results of this Phase I/II HCV study demonstrated safety and a linear pharmacokinetic drug profile, however, no significant decrease in the viral load was observed. Notwithstanding, the Company did observe in the parallel HCC study that seven out of the nine patients with both HCC and HCV experienced a decrease in viral load and that these seven patients were treated with higher CF102 dosages than what was administered to the patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 only, and not HCC, possibly explaining the difference in results. The most commonly reported adverse events included loss of appetite, ascites, nausea, diarrhea, constipation and pain. However, many of these events are expected in a population of patients with advanced HCV. The most frequently reported drug-related adverse events included diarrhea, fatigue, loss of appetite, pain and weakness.
We are currently in preparation for a Phase II study in HCC patients. In January 2013, as part of its preparatory work for such study, the Company announced that it believes that the optimal drug dose for the upcoming study is CF102 25.0 mg. This does was found to be the most effective dose out of the three dosages tested (1.0 mg, 5.0 mg and 25.0 mg) in the previous Phase I/II study. The Company filed a patent application protecting such optimal dose of CF102 for HCC. A publication summarizing the results of the Phase I/II study was published in “The Oncologist”, a leading oncology scientific journal. The Company also highlighted that one patient has been treated with CF102 for over three years, and is continuing to be treated, with CF102. Also as part of the Phase II study, we plan to examine the viral load of HCC patients who are also infected with HCV. If we observe a decrease in the viral load in the HCV sub-population during this forthcoming study, we intend to commence a separate Phase II study for the HCV indication.
Additional Developments with CF102
JC Virus
In April 2011, the Company announced that, in laboratory study, CF102 inhibited the reproduction of the JC virus, a type of polyomavirus, which is dormant in approximately 70% to 90% of the world population. However, in patients treated with biological drugs, including monoclonal antibody therapeutics, such as anti-TNFs or anti-CD20, JC virus replication may occur, resulting in development of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, or PML, which is characterized by progressive damage or inflammation of the white matter of the brain and, eventually, death. The ability of CF102 to suppress the JC Virus culture, as indicated in the laboratory study, may indicate that it may be used for the treatment of PML as a combination therapy with biological drugs. As CF102 is already in various stages of clinical development for other indications, its efficacy for this new application may be tested in clinical trials.
CF602
The allosteric modulator, CF602, is the Company’s third drug candidate in its pipeline. CF602 is an orally bioavailable small molecule, which enhances the affinity of the natural ligand, adenosine, to its A3AR. The advantage of this molecule is its capability to target specific areas where adenosine levels are increased. Normal body cells and tissues are refractory to allosteric modulators. This approach complements the basic platform technology of Can-Fite, utilizing the Gi coupled protein A3AR as a potent target in inflammatory diseases. CF602 has demonstrated proof of concept for anti-inflammatory activity in in vitro and in vivo studies performed by the Company. Subject to its financial resources, the Company intends to conduct required pre-clinical studies for this drug candidate. After completion of all pre-clinical testing, the Company intends to file an IND with respect to CF602.
During clinical studies conducted with the Company’s product candidates, other than CF602, patients suffering from sexual dysfunction reported that they returned to normal functioning following the treatment with such drugs. The Company believes that these findings are correlated with the Company’s platform technology, which is the targeting of the A3AR. Adenosine, like nitric oxide, is a potent and short-lived vaso-relaxant that functions via intracellular signaling (in particular, through cAMP) to promote smooth muscle relaxation. Recent studies conducted by others show that adenosine functions to relax the corpus cavernosum and thereby promote penile erection. The Company has filed a patent application in Israel for the treatment of sexual dysfunction utilizing the Company’s drug candidates and is planning to develop CF602 for this indication as it uses the same platform technology and becomes active through the same mechanism as the rest of the Company’s drug candidates. GlobalData valued the erectile dysfunction therapeutic market at $3 billion in 2010, which mainly includes the drugs Viagra, Cialis and Levitra.
| 51 |
In-Licensing Agreements
The following are summary descriptions of certain in-licensing agreements to which we are a party. The descriptions provided below do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the complete agreements, which are attached as exhibits to this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
NIH Agreement
On January 29, 2003, we entered into a license agreement with the NIH, or the NIH Agreement, through the U.S. Public Health Service. Pursuant to the NIH Agreement, we were granted an exclusive license for the use of a family of U.S. and European patents and patent applications relating to CF101, CF102 and other small molecules and for the use, sale, production and distribution of products derived from such patents around the world. Subject to certain conditions, we may sublicense the NIH Agreement. However, the NIH retains a paid-up, worldwide license to practice the licensed inventions for government purposes and may require us to grant sublicenses when necessary to fulfill health or safety needs.
According to the NIH Agreement, we are committed to pay royalties as follows: (i) a $225,000 signing payment; (ii) a minimum non-refundable annual payment of $50,000; (iii) 4% to 5.5% of our total net revenues from sales of licensed products or from conducting tests with respect to CF101, CF102 and the other licensed small molecules worldwide, on a consolidated basis; (iv) individual payments ranging from $25,000 to $500,000 subject to meeting certain drug development milestones, including the initiation of certain clinical trials with respect to the licensed products; and (v) additional payments totaling 20% of all monetary consideration received from sublicensees, except for royalties received on any such sublicensee’s net revenues from sales of the licensed products. As of December 31, 2012, we have paid approximately $925,000 in royalties to the NIH in connection with the NIH Agreement. The Company estimates that it will pay a total of approximately $425,000 in milestone payments to the NIH in connection with the NIH Agreement.
The NIH Agreement sets certain development milestones with which we must comply. On August 4, 2005 and February 4, 2013, amendments were signed with the NIH to extend such milestone dates. The amendments had no effect on the originally determined license terms.
The NIH Agreement will remain in effect until the last patent licensed under the NIH Agreement expires on June 30, 2015, unless it is earlier terminated by one of the parties, according to the NIH Agreement. The termination rights include, but are not limited, our right to terminate upon 60-days’ prior written notice to the NIH, the NIH’s right to terminate if we become insolvent or bankruptcy proceedings are initiated against us, and NIH’s right to terminate upon our default in the performance of any material obligation and our failure to cure such default within 90 days of written notice of such default.
In addition, on January 24, 2006, the Company entered into a cooperative research and development agreement, or CRADA, with the NIH whereby the Company received an option to obtain a license from the NIH for any new group of A3AR agonists to be developed under terms that will be determined between the parties on the date of exercise of such option. In connection with the CRADA and the option granted thereunder, the Company signed a commercial evaluation license agreement with the NIH on April 17, 2007, and selected one molecule, CF502 (or MRS3558) to evaluate. However, at a later stage, the Company decided not to continue the development of CF502, terminated the commercial evaluation license agreement and did not exercise the option granted under the CRADA.
Leiden University Agreements
On November 2, 2009, we entered into a license agreement, or the Leiden University Agreement, with Leiden University. Leiden University is affiliated with the NIH and is the joint owner with the NIH of the patents licensed pursuant to the Leiden University Agreement. The Leiden University Agreement grants an exclusive license for the use of the patents of several compounds, including CF602, that comprise certain allosteric compound drugs, and for the use, sale, production and distribution of products derived from such patents in the territory, i.e., China and certain countries in Europe (Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Holland and England). Subject to certain conditions, we may sublicense the Leiden University Agreement.
| 52 |
Pursuant to the Leiden University Agreement, we are committed to pay royalties as follows: (i) a one-time concession commission of 25,000 Euros; (ii) annual royalties of 10,000 Euros until clinical trials commence; (iii) 2% to 3% of net sales value, as defined in the Leiden University Agreement, received by us; (iv) royalties of up to 850,000 Euros based on certain progress milestones in the clinical stages of the products which are the subject of the patent under the Leiden University Agreement; and (v) if we sublicense the agreement, we will provide Leiden University royalties at a rate of 2-3% of net sales value, as defined in the Leiden University Agreement, and 10% of certain consideration received for granting the sublicense. In the event that we transfer to a transferee the aspect of our business involving the Leiden University Agreement, we must pay to Leiden University an assignment royalty of 10% of the consideration received for the transfer of the agreement. However, a merger, consolidation or any other change in ownership will not be viewed as an assignment of the agreement. In addition, we have agreed to bear all costs associated with the prosecution of the patents and patent applications to which we are granted a license under the Leiden University Agreement. As of December 31, 2012, we have paid approximately 115,000 Euros in royalties to Leiden University in connection with the Leiden University Agreement.
The Leiden University Agreement expires when the last of the patents expires in each country of the territory, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the terms of the Leiden University Agreement. The last of such patents is set to expire on 2027. The termination rights of the parties include, but are not limited to, (i) the non-defaulting party’s right to terminate if the defaulting party does not cure within 90 days of written notice identifying the default and requesting remedy of the same; and (ii) Leiden University’s right to terminate if we become insolvent, have a receiver appointed over our assets or initiate a winding-up.
Out-Licensing Agreements
The following are summary descriptions of certain out-licensing agreements to which we are a party. The descriptions provided below do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the complete agreements, which are attached as exhibits to this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
Seikagaku Agreement
On September 22, 2006, we executed an exclusive license agreement, which was amended in December 2006, with Seikagaku Corporation, a Japanese public corporation, or SKK, for the use, development and marketing of CF101 in Japan with respect to inflammatory indicators, except for ophthalmic disease indicators. The agreement with SKK as amended, or the Seikagaku Agreement, also grants to SKK an exclusive, royalty-free license to use certain of our trademarks, as determined from time to time, in connection with the distribution, marketing, promotion and sale of any products derived from CF101 pursuant to the Seikagaku Agreement. Under the terms of the Seikagaku Agreement, we cannot prevent SKK from making financial, operational or strategic decisions associated with the use, development or marketing of CF101 in Japan.
The Seikagaku Agreement contemplates the creation of a four member joint committee consisting of two members from each party with the purpose of serving as a joint source of experience and knowledge in CF101 development and to facilitate communication and coordination between the parties with respect to such development. The joint committee, among other things specifically identified in the Seikagaku Agreement, provides to the parties opinions, proposals, ideas and updates with respect to the CF101 development processes conducted separately by each party.
Under the Seikagaku Agreement, we are entitled to up-front and milestone payments of up to $19.5 million (of which $2 million is attributable to our participation in certain research and development activities) and at least an additional $1 million in milestone payments if SKK pursues a second indication (the current indication is RA). We will also be entitled to royalties in an amount between 7-12% of annual net sales in Japan subject to certain sales criteria. In accordance with the Seikagaku Agreement, we received an up-front payment of $3.0 million in 2006, a milestone payment of $1.0 million in 2008 and $0.5 million per year from 2007 through 2011 as an annual minimum royalty payment (for an aggregate of $2.5 million). In addition to the amounts above, we will be entitled to additional payments based on sales of raw materials to SKK for the purpose of developing, producing and marketing CF101. If SKK decides to produce the raw materials itself, we will be entitled to $1.0 million and an additional manufacturing royalty payment. Furthermore, we will be entitled to receive additional payments if SKK requests information regarding the results and reports of other clinical and non-clinical studies conducted by us and we will be required to make certain payments to SKK if we request results and reports from their clinical and non-clinical studies. These payments will be calculated based on a percentage of the costs of such clinical and non-clinical studies, as the case may be.
| 53 |
Pursuant to a representative agreement, dated September 22, 2006, we have paid or are committed to pay, 5% of the above amounts actually received as a brokerage commission to Fuji Techno Interface Ltd., the Japanese company that brokered the Seikagaku Agreement. The Seikagaku Agreement is effective until SKK completes all payments required by the agreement, unless it is earlier terminated as a result of a material breach not cured within the specified time frame or as a result of the initiation of bankruptcy or insolvency- related proceedings.
Kwang Dong Agreements
On December 22, 2008, we entered into a license agreement with Kwang Dong Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, a South Korean limited company, or KD, and the Kwang Dong License Agreement, respectively, for the use, development and marketing of CF101 in the Republic of Korea with respect to RA and a purchase agreement, or the Kwang Dong Purchase Agreement, for the purchase of our ordinary shares, with KD. In addition, the Kwang Dong License Agreement grants to KD an exclusive, royalty-free license to use certain of our trademarks, as determined from time to time, in connection with the distribution, marketing, promotion and sale of any products derived from CF101 pursuant to the Kwang Dong License Agreement.
The Kwang Dong License Agreement also provides for the creation of a four member joint committee consisting of two members from each party for the purpose of serving as a joint source of experience and knowledge in CF101 development and to facilitate communication and coordination between the parties with respect to such development. The joint committee will, among other things specifically identified in the Kwang Dong License Agreement, provide to the parties opinions, proposals, ideas and updates with respect to the CF101 development processes conducted separately by each party.
According to the Kwang Dong License Agreement, the Company is entitled to receive or has received the following payments: (i) a non-refundable amount of $300,000 paid within 30 days of the effective date of the agreement; (ii) an amount of up to $1.2 million based on our compliance with certain milestones, including but not limited to, the conclusion of the Phase II clinical trial for CF101 for treating RA and the receipt of various regulatory authorizations; and (iii) annual royalties of 7% of annual net sales of the licensed drug in the Republic of Korea. In addition to the amounts detailed above, we will be entitled to additional payments based on sales of raw materials to KD for the purpose of developing, producing and marketing CF101.
The Kwang Dong License Agreement is effective until KD completes all payments required thereunder, unless it is earlier terminated as a result of a material breach not cured within the specified time frame, the breach by KD of the Kwang Dong Purchase Agreement or the initiation of bankruptcy or insolvency related proceedings.
Pursuant to the Kwang Dong Purchase Agreement, KD purchased 2,382,602 of our ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.01 per share (equivalent to 95,304 of our ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share, after the reverse stock split), representing approximately 1.0 % of our share capital on a fully diluted basis, as of the date of the purchase. The shares were purchased for a premium of 50% on the shares’ average closing price for the ten days preceding December 11, 2008, or a purchase price of NIS 0.455 per share.
After the TASE approved such shares for the listing for trade on January 5, 2009, the shares were allocated to KD and the transaction was finalized in January 2009. As of December 31, 2012, KD had paid us approximately $0.8 million, which represents milestone payments pursuant to the Kwang Dong License Agreement, an advance of certain amounts to become due under the Kwang Dong License Agreement and the purchase price for the shares.
| 54 |
Eye-Fite Agreement
In connection with the spin-off transaction described below in “Item 10. Additional Information—Material Contracts—OphthaliX Agreements”, on November 21, 2011, we entered into a license agreement, or the Eye-Fite Agreement, with Eye-Fite according to which we (i) granted Eye-Fite a sole and exclusive worldwide license for the use of CF101 solely in the field of ophthalmic diseases and patent rights which we received under the NIH Agreement, with respect to CF101 in the field of ophthalmic diseases for research, development, commercialization and marketing throughout the world and (ii) assigned to Eye-Fite our rights, title and interest in and to any and all INDs to CF101 in the ophthalmic field. As consideration for the grant of the license, we received 999 ordinary shares of Eye-Fite, in addition to the one share we already had, which resulted in us owning all of the issued and outstanding shares of Eye-Fite, all of which were transferred to OphthaliX in connection with this transaction. In addition, Eye-Fite must, for the duration of the NIH Agreement, make the following payments to the NIH: (i) a nonrefundable minimum annual royalty of $25,000, (ii) earned royalties of 4.0% to 5.5% on net sales in territories in where such patents exist and (iii) individual payments ranging from $25,000 to $500,000 upon the achievement of various development milestones for each indication. Eye-Fite will also be required to make payments to the NIH of 20% of sublicensing revenues, excluding royalties and net of the required milestone payments. The payments set forth above represent our liabilities to the NIH under to the NIH Agreement, which pursuant to the Eye-Fite Agreement, Eye-Fite is obligated to make to the NIH.
If Eye-Fite fails to make a required payment to the NIH, Can-Fite will be entitled to terminate the license granted to Eye-Fite under the Eye-Fite Agreement upon 30 days’ prior written notice. The Eye-Fite Agreement will remain in effect until the expiration of the last of the patents licensed thereunder, unless earlier terminated by one of the parties in accordance with its terms. Can-Fite may terminate the Eye-Fite Agreement upon customary bankruptcy and insolvency events of Eye-Fite and upon Eye-Fite’s material breach of the Eye-Fite Agreement, upon 30 days’ prior written notice. Eye-Fite may terminate the Eye-Fite Agreement upon three months’ prior written notice for any reason and upon 30 days’ prior written notice for Can-Fite’s material breach of the Eye-Fite Agreement. All inventions resulting from the development and commercialization of CF101 under the Eye-Fite Agreement belong to Can-Fite, whether invented solely by Can-Fite, solely by Eye-Fite or by both entities. However, the Eye-Fite Agreement also grants Eye-Fite an exclusive license to use any such inventions in the field of ophthalmic diseases around the world for no additional consideration.
Total Revenues by Category of Activity and Geographic Markets
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands, U.S. $) | ||||||||||||
| Japan | 500 | 500 | - | |||||||||
| Korea | 200 | - | - | |||||||||
All revenues have been generated from payments received pursuant to our out-licensing agreements with SKK and KD with respect to CF101. See “Item 4—Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”. We expect to generate future revenues through our current and potential future out-licensing arrangements with respect to CF101, as well as through future out-licensing arrangements with respect to our other product candidates, i.e., CF102 and CF602.
Seasonality
Our business and operations are generally not affected by seasonal fluctuations or factors.
Raw Materials and Suppliers
We believe that the raw materials that we require to manufacture CF101, CF102 and CF602 are widely available from numerous suppliers and are generally considered to be generic industrial chemical supplies. We do not rely on a single or unique supplier for the current production of any therapeutic small molecule in our pipeline.
| 55 |
Manufacturing
We are currently manufacturing our API through a leading Chinese contract research organization, or CRO. The relevant suppliers of our drug products are compliant with both current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMP, and current Good Laboratory Practices, or cGLP, and allow us to manufacture drug products for our current clinical trials. We anticipate that we will continue to rely on third parties to produce our drug products for clinical trials and commercialization.
There can be no assurance that our drug candidates, if approved, can be manufactured in sufficient commercial quantities, in compliance with regulatory requirements and at an acceptable cost. We and our contract manufacturers are, and will be, subject to extensive governmental regulation in connection with the manufacture of any pharmaceutical products or medical devices. We and our contract manufacturers must ensure that all of the processes, methods and equipment are compliant with cGMP for drugs on an ongoing basis, as mandated by the FDA and other regulatory authorities, and conduct extensive audits of vendors, contract laboratories and suppliers.
Contract Research Organizations
We outsource certain preclinical and clinical development activities to CROs, which in pre-clinical studies work according to cGMP and cGLP. Our clinical CROs comply with guidelines from the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, which attempt to harmonize the FDA and the European Medicines Agency, or the EMA, regulations and guidelines. We create and implement the drug development plans and, during the preclinical and clinical phases of development, manage the CROs according to the specific requirements of the drug candidate under development.
Marketing and Sales
We do not currently have any marketing or sales capabilities. We intend to license to, or enter into strategic alliances with, larger companies in the pharmaceutical business, which are equipped to market and/or sell our products, if any, through their well-developed marketing capabilities and distribution networks. We intend to out-license some or all of our worldwide patent rights to more than one party to achieve the fullest development, marketing and distribution of any products we develop.
Intellectual Property
Our success depends in part on our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our therapeutic candidates, technology and know-how, to operate without infringing the proprietary rights of others and to prevent others from infringing our proprietary rights. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary position by, among other methods, filing U.S. and foreign patent applications related to our proprietary technology, inventions and improvements that we believe are important to the development of our business. We also rely on trade secrets, know-how and continuing technological innovation to develop and maintain our proprietary position.
Patents
As of August 26, 2013, we owned or exclusively licensed (from the NIH and Leiden University) 15 patent families that, collectively, contain approximately 150 issued patents and pending patent applications in various countries around the world relating to our two clinical candidates, CF101 and CF102, and our preclinical candidate, CF602. Patents related to our drug candidates may provide future competitive advantages by providing exclusivity related to the composition of matter, formulation and method of administration of the applicable compounds and could materially improve their value. The patent positions for our leading drug candidates are described below.
We currently license from the NIH and Leiden University certain intellectual property that is necessary to conduct our business. We currently hold an exclusive license from the NIH to a family of patents that protects certain small molecules that are A3AR agonists, such as CF101 and CF102, and the pharmaceutical use of such molecules. This exclusive license relates to two composition of matter patents that were granted in the United States and Europe (in particular, United Kingdom, France, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Belgium and Luxembourg), the former of which is expected to expire in 2015 and the latter in 2014. We will not be able to extend the foregoing expiration dates and as such, as of June 30, 2015, the license agreement with the NIH will terminate. We do not expect that we will be able to submit an NDA seeking approval of CF101 or CF102 prior to the composition of matter patents’ respective expiration dates. However, because CF101 and CF102 each may be a new chemical entity, or NCE, following approval of an NDA, we, if we are the first applicant to obtain NDA approval, may be entitled to five years of data exclusivity in the United States with respect to such NCEs. Analogous data and market exclusivity provisions, of varying duration, may be available in Europe and other foreign jurisdictions. The Company also has rights under its pharmaceutical use issued patents with respect to CF101 and CF102, which provide patent exclusivity within the Company’s field of activity until the mid- to late-2020s. While the Company believes that it may be able to protect its exclusivity in its field of activity through such use patent portfolio and such period of exclusivity, the lack of composition of matter patent protection may diminish the Company’s ability to maintain a proprietary position for its intended uses of CF101 and CF102. Moreover, the Company cannot be certain that it will be the first applicant to obtain an FDA approval for any indication of CF101 and it cannot be certain that it will be entitled to NCE exclusivity. Such diminution of its proprietary position could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation and financial condition. We also currently hold an exclusive license from the NIH and Leiden University of the Netherlands to a family of patents and patent applications that relate to the allosteric modulators of the A3AR, which includes the allosteric modulator CF602. This exclusive license relates to two patents that were granted in the United States, China and in Europe (validated in, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Holland and England). These granted patents and the patents that may be granted on patent applications of this patent family are set to expire in 2027. We hold the foregoing licenses pursuant to the terms and conditions of certain license agreements.
| 56 |
With respect to our product candidates, we currently own patents and/or have patent applications pending in several countries around the world for the following families of patents:
| · | a family of patents which pertains to the use of substances that bind to the A3AR, including CF101 and CF102; the pharmaceutical uses to which such family relates include the treatment of proliferative diseases, such as cancer, psoriasis and autoimmune diseases. Such patents were granted in the United States, Europe (by the European Patent Office, or the EPO, and validated in Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Holland and the United Kingdom), Australia, Canada, Israel, China, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, Poland, Russia and Hong-Kong. These patents are set to expire in 2020, other than the United States patent that will expire in 2022; |
| · | a family of patents and a patent application which pertain to use of substances that bind to the A3AR for the treatment of viral diseases, such as AIDS and hepatitis, and which inhibit viral replication. Such patents were granted in the United States, in Europe (by the EPO and validated in France, Germany, Italy, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), Australia, China, Israel, Japan, Singapore, Canada and Hong Kong. These patents are set to expire in 2022, other than the United States patent that will expire in 2023. This patent application is pending in Brazil with a filing date of January 1, 2002 and a priority date of January 16, 2001; |
| · | a patent which pertains to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis, in particular RA. This patent was granted in the United States and is set to expire in 2023; |
| · | a family of patents and patent applications which pertain to a method of identifying inflammation, determining its severity, and determining and monitoring the efficacy of the anti-inflammatory treatment by determining the level of A3AR expression in white blood cells as a biological marker for inflammation. These patents were granted in certain countries in Europe (by the EPO and validated in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Switzerland and the United Kingdom), Australia, Israel, Japan and Mexico. These patents are set to expire in 2025. These patent applications are pending in the United States, Canada, China (which was recently approved) and Brazil. Each of the applications has a filing date of November 30, 2005 and a priority date of December 2, 2004; |
| · | a family of patents and patent applications which pertain to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of DES. Such patents were granted in the United States, Australia, Canada, China, South Korea and Mexico. These patents are set to expire in 2026. These patent applications are pending in the United States, EPO (this European application designates all member states of the European Patent Convention – EPC), Brazil, Israel and Japan, each with a filing date of February 1, 2006 and a priority date of January 27, 2007; |
| · | a family of patent applications which pertains to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of reducing IOP. These patent applications are pending in the United States, in the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), Israel, Japan, China, Canada, Australia, Mexico and South Korea, each with a filing date of May 16, 2010 and a priority date of May 17, 2009; |
| · | a family of patent applications which pertains to the use of a specific dose level of CF101 (total daily dose of 4.0 mg) for the treatment of psoriasis. These patent applications are pending in the United States, China, the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), India, Japan and South Korea, each with a filing date of September 6, 2010 and a priority date of September 6, 2009; |
| 57 |
| · | a family of patent applications which pertain to the method for producing CF101. These patent applications are pending in the United States, the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), India, Israel, Japan and China, each with a filing date of March 13, 2008 and a priority date of March 14, 2007; |
| · | a family of patents and patent applications which pertain to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of OA. Such patents were granted in Europe (by the EPO and validated in Austria, Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Holland and the United Kingdom), Australia, Canada, South Korea, China and Mexico. These patents are set to expire in 2026. Patent applications are pending in the United States, Brazil, Israel, India and Japan. These applications have a filing date of November 29, 2006 and a priority date of November 30, 2005; |
| · | a family of patent applications which pertains to the use of A3AR agonists for increasing liver cell division, intended to induce liver regeneration following injury or surgery. These patent applications are pending in the United States, China (which was recently approved and a patent is to be issued), the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), Israel and Japan, each with a filing date of October 22, 2007 and a priority date of October 15, 2007. In addition, we have filed a U.S. provisional patent application which pertains to the use of A3AR agonists for the maintenance of liver function in patients having chronic liver disease. This patent application has a filing date of January 23, 2012 and a priority date of January 23, 2012; |
| · | a family of patents and patent applications which pertain to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of Sjorgen’s syndrome and related diseases. Such patents were granted in the United States and Japan. These patents are set to expire in 2026. The patent application is a European patent application (filed in the EPO and designates all EPC member states) which was recently approved and a patent is to be issued; |
| · | a family of patent application under joint ownership with the NIH and licensed, to the extent of our ownership, to Eye-Fite, which pertain to the use of A3AR agonists for the treatment of uveitis. These patent applications are pending in the United States, Canada, China, the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), Israel, Japan, Mexico, South Korea and the Russian Federation. The patent applications have filing dates of February 27, 2010 and priority dates of March 3, 2010; |
| · | a family of patents and patent applications which pertain to dosage forms comprising CF101 for the treatment of psoriasis. These patent applications are pending in the United States, China, the EPO (this European application designates all EPC member states), Israel, Japan and South Korea. The patent applications have filing dates of September 6, 2010 and priority dates of September 6, 2009; |
| · | a patent application which pertains to the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. This patent application is a PCT application with a filing date of January 23, 2013 and a priority date of January 23, 2012; |
| · | a family of two patent applications which pertain to treatment of sexual dysfunction. This family includes two patent applications in Israel that have have filing dates of August 8, 2012 and November 12, 2012 and a PCT application which was filed on August 8, 2013. |
| 58 |
We believe that our owned and licensed patents provide broad and comprehensive coverage of our technology, and we intend to aggressively enforce our intellectual property rights if necessary to preserve such rights and to gain the benefit of our investment. However, the patent positions of companies like ours are generally uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. Our ability to maintain and solidify our proprietary position for our technology will depend on our success in obtaining effective claims and enforcing those claims once granted. We do not know whether any of our patent applications or those patent applications that we license will result in the issuance of any patents. Our issued patents and those that may issue in the future, or those licensed to us, may be challenged, narrowed, circumvented or found to be invalid or unenforceable, which could limit our ability to stop competitors from marketing related products or the length of term of patent protection that we may have for our products. Neither we nor our licensors can be certain that we were the first to invent the inventions claimed in our owned or licensed patents or patent applications. In addition, our competitors may independently develop similar technologies or duplicate any technology developed by us, and the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with any meaningful competitive advantages against these competitors. Furthermore, because of the extensive time required for development, testing and regulatory review of a potential product, before any of our products can be commercialized, any related patent may expire or remain in force for only a short period following commercialization, thereby reducing any advantage of the patent.
Trade Secrets
We may rely, in some circumstances, on trade secrets to protect our technology. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by confidentiality agreements and assignment of inventions agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, such agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors or others.
Scientific Advisory Board
We seek advice from our Scientific Advisory Board on scientific and medical matters generally. We call for Scientific Advisory Board meetings on an as-needed basis. The following table sets forth certain information with respect to our Scientific Advisory Board members.
| Name | Position/Institutional Affiliation | |
| Nabil Hanna, Ph.D. | Former Chief Science Officer of Biogen-Idec | |
| Kamel Khalili, Ph.D. | Temple University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania |
Clinical Advisory Board
Our Clinical Advisory Board, which consists of three members, a leading U.S.-based rheumatologist, oncologist and dermatologist, plays an active role in consulting the Company with respect to clinical drug development. We call for Clinical Advisory Board meetings on an as-needed basis. The following table sets forth certain information with respect to our Clinical Advisory Board members.
| Name | Position/Institutional Affiliation | |
| Dr. Michael Weinblatt | Head, Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy, Brigham and Women’s Hospital | |
| Dr. Keith Stuart | Chairman, Department of Hematology and Oncology; Professor of Medicine, Tufts University School of Medicine; Lahey Clinic Medical Center | |
| Dr. Jonathan Wilkin | Former Head, Dermatology Division, FDA |
Competition
The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapidly evolving technology, intense competition and a highly risky, costly and lengthy research and development process. Adequate protection of intellectual property, successful product development, adequate funding and retention of skilled, experienced and professional personnel are among the many factors critical to success in the pharmaceutical industry.
| 59 |
Our technology platform is based on the finding that the A3AR is highly expressed in pathological cells, such as various tumor cell types and inflammatory cells. We believe that targeting the A3AR with synthetic and highly selective A3AR agonists, such as CF101 and CF102, and allosteric modulators, such as CF602, induces anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. Currently, our drugs, CF101, CF102 and CF602 are being developed to treat several autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic indications, including but not limited to: psoriasis; RA; OA; DES; glaucoma; uveitis; HCC and HCV. Preclinical studies have also indicated that our drugs have the potential to treat additional inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, oncological diseases and viral disease, such as the JC virus.
Despite the competition, however, we believe that our drugs have unique characteristics and advantages over certain drugs currently available on the market and under development to treat these indications. We believe that our drug pipeline has exhibited a potential for therapeutic success with respect to the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic diseases. We believe that targeting the A3AR with synthetic and highly selective A3AR agonists, such as CF101 and CF102, and allosteric modulators, such as CF602, induces anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects.
The characteristics of CF101, as exhibited in our clinical studies to date, including its good safety profile, clinical activity, simple and less frequent delivery through oral administration and its low cost of production, position it well against the competition in the autoimmune-inflammatory markets, including the psoriasis and RA markets, where treatments, when available, often include injectable drugs, many of which can be highly toxic, expensive and not always effective. Moreover, pre-clinical pharmacology studies in different experimental animal models of arthritis revealed that CF101 acts as a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug, or a DMARD, which, when coupled with its good safety profile, make it competitive in the psoriasis, RA and OA markets. Our recent findings also demonstrate that a biological predictive marker can be utilized prior to treatment with CF101, which may allow it to be used as a personalized medicine therapeutic approach for the treatment of RA. CF101 is also well-positioned against some of the competition in the ophthalmic markets, where treatments, when available, often include frequent self-administered eye drops, which may be more difficult than taking pills and may result in less than the full dose of the drug actually entering the eye, have undesirable side effects and do not simultaneously treat the underlying cause and relieve the symptoms associated with the indication. Like CF101, CF102 has a good safety profile, is orally administered and has a low cost of production, which positions it well in the HCC market, where only one drug, Nexavar, has been approved by the FDA.
In addition, our human clinical data suggests that A3AR may be a biological marker in that high A3AR expression prior to treatment has been predictive of good patient response to our drug treatment. In fact, as a result of our research we have developed a simple blood assay to test for A3AR expression as a predictive biological marker. We have applied for a patent with respect to the intellectual property related to such assay and are currently utilizing this assay in our ongoing Phase IIb study of CF101 tor the treatment of RA.
On the other hand, other drugs on the market, new drugs under development (including drugs that are in more advanced stages of development in comparison to our drug pipeline) and additional drugs that were originally intended for other purposes, but were found effective for purposes targeted by us, may all be competitive to the current drugs in our pipeline. In fact, some of these drugs are well established and accepted among patients and physicians in their respective markets, are orally bioavailable, can be efficiently produced and marketed, and are relatively safe. Moreover, other companies of various sizes engage in activities similar to ours. Most, if not all, of our competitors have substantially greater financial and other resources available to them. Competitors include companies with marketed products and/or an advanced research and development pipeline. The major competitors in the arthritis and psoriasis therapeutic field include Abbott Laboratories, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen, Roche, Pfizer, Novartis, Astellas, Eli Lilly and more. The competitive landscape in the ophthalmic therapeutics field includes Novartis/Alcon, Allergan, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Merck (which acquired Inspire Pharmaceuticals), Santen (which acquired Novagali), Bausch & Lomb (which acquired ISTA Pharmaceuticals and is currently being acquired by Valeant), GlaxoSmithKline, or GSK, Sanofi-Aventis (which acquired Fovea) and more. Competitors in the HCC field include companies such as Onyx, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbott Laboratories, Eli Lilly, Arqule and more. Competitors in the HCV field include companies such as Merck, Vertex, Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb (which acquired Inhibitex), Gilead Sciences (which acquired Pharmasset), Achillion, Idenix, Valeant, Human Genome Sciences, Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Idenix, Johnson & Johnson, Presidio, Medivir, Celgene, Enanta, GSK and more.
| 60 |
Moreover, several companies have reported the commencement of research projects related to the A3AR. Such companies include CV Therapeutics Inc. (which was acquired by Gilead), King Pharmaceuticals R&D Inv. (which was acquired by Merck), Hoechst Marion Roussel Inc., Novo Nordisk A/S and Inotek Pharmaceuticals. However, we are not aware if such projects are ongoing or have been completed and, to the best of our knowledge, there is no approved drug currently on the market which is similar to our A3AR agonists, nor are we aware of any allosteric modulator in the A3AR product pipeline similar to our allosteric modulator with respect to chemical profile and mechanism of action.
CF101 for the Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune hereditary skin disease that, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation, attacks 2% to 3% of the world population. According to Nature Biotechnology, the current market for psoriasis treatment is estimated at about $3.3 billion a year.
The current common treatments for psoriasis include topical and systemic drugs, steroids, immunosuppressive drugs such as Cyclosporine A by Novartis, MTX and biological drugs. Biological drugs, such as Enbrel by Amgen and Pfizer, Amevive by Astellas and Ustakinumab by Centocor, a division of Johnson & Johnson, have significant side effects, are expensive and patients are often not responsive. Many of the current RA drugs on the market or in development are also used for the treatment of psoriasis. See “—CF101 for the Treatment of RA.” In addition, several therapies are in advanced clinical development for psoriasis and many others are in Phase II or earlier stages of development.
CF101 for the Treatment of RA
According to the Arthritis Foundation, RA is a severe disease that attacks approximately 1.0% of the U.S. population, mainly women and, in particular, postmenopausal women. As of 2010, Datamonitor estimated that the global RA market size was approximately $12 billion, and expected it to grow to $18 billion by 2020.
Many drugs are used to treat RA, including DMARDs. These include MTX, plaquenil, sulfasalazine and leflunomide, all of which are small molecule drugs with mild effectiveness. MTX is the most commonly administered DMARD for RA. It is a generic chemotherapeutic agent marketed by several manufacturers that is administered orally. Due to its relatively toxic nature, however, MTX may result in severe side effects.
The second class of DMARD includes biological drugs, such as Enbrel by Amgen Inc. (which contains the active ingredient Etanercept), Remicade by Centocor, a division of Johnson & Johnson (which contains the active ingredient Infliximab) and Humira by Abbott Laboratories (which contains the active ingredient Adalimumab). These drugs are usually administered in combination with MTX and are more effective in combination, but may have severe side effects, including lymphoma. Biological drugs are administered through injection, are generally expensive and there is no biomarker to predict the response, if any. Steroidal drugs are also used to reduce the general activity of the immune system and for pain relief. In addition, the FDA recently approved Pfizer’s Xeljanz (tofacitinib) small molecule drug, which is the first JAK inhibitor drug, or a drug that inhibits the effect of one or more of the enzymes in the janus kinase family, or a family enzymes that transfer cytokine-mediated signals, to treat RA. Moreover, several therapies, including biological drugs and small molecule drugs, are in advanced clinical development for RA, while others are in Phase II or earlier stages of development.
CF101 for the Treatment of OA
According to the Arthritis Foundation, OA is the most common arthritic disease. GlobalData estimated that the global OA market was $4.4 billion in 2010 and forecasts it to increase to $5.9 billion by 2018. The medications most commonly used to treat OA are symptom-modifying drugs, primarily generics, such as non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors, or COX-2 inhibitors, which directly target the COX-2 enzyme involved with the etiology and pathogenesis of inflammation and pain. There are no disease-modifying OA drugs, or DMOADs, currently approved for OA and the late stage drug pipeline also lacks DMOADs, except Novartis’ SMC021, which hasn’t met its primary end points in a Phase III study.
| 61 |
Current and future competition includes drugs being developed to relieve pain associated with OA and for the treatment of OA. In addition to DMOADs, therapies in development for OA include stem cell therapy, COX-2 inhibitors, cathepsin S inhibitors, or synthetic inhibitors of the cathepsin S protein, opioid receptor agonists, or pain relievers that bind to certain nervous system receptors, anti-nerve growth factor inhibitors, or inhibitors of proteins that promote nerve growth, transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 antagonists, or a pain reliever that binds to certain proteins responsible for heat and pain sensations, COX inhibiting nitric oxide donors, or drugs that act as COX inhibitors while donating nitric oxide and thereby promoting an anti-inflammatory effect, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, or drugs that block certain enzymes thereby preventing the inactivation of certain intracellular messaging, and calcitonin receptor agonists, or drugs that bind to receptors related to functional activity.
CF101 had a significant anti-inflammatory effect in pre-clinical pharmacology studies for OA and is currently in preparation for a Phase II study.
CF101 for the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
According to GlobalData, the Crohn’s disease market was approximately $3.6 billion in 2010 and is expected to grow to approximately $4.4 billion by 2018. According to Datamonitor, in 2009, 890,000 persons were estimated to have Crohn’s disease in the seven major markets (the U.S., Japan, France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the U.K.) and more than half of such patients were estimated to reside in the United States.
Therapies in development for Crohn’s disease include interleukin inhibitors, a drug that inhibits cell growth, enzyme inhibitors, stem cell therapy, integrin antagonists, or drugs that bind to certain receptors that are responsible for the regulation of cell cycle, shape and motility, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, or drugs that inhibit the factor that promotes inflammatory responses, and immunomodulators, or drugs that regulate the immune system.
Although CF101 was effective in the Company’s pre-clinical and pharmacological studies relating to Crohn’s disease, we currently do not have any planned clinical trials with respect to the use of CF101 for the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
CF101 for the Treatment of DES
According to Datamonitor, DES is the most common problem of patients who seek eye care. As of 2010, 49.3 million people in the seven major markets suffered from DES. We believe that the number of people who suffer from DES will increase as the population in each of these countries ages. According to GlobalData, as of 2012, the global DES market size was approximately $1.6 billion and is expected to grow to approximately $5.5 billion by 2022.
The current products available to treat DES include Restasis® and Refresh® by Allergan, and Celluvisc®, Hyalein®, Vismed® and Systane® by Alcon. Restasis® is the only FDA-approved prescription therapy indicated to treat DES and, as such, it dominates the U.S. market with respect to the treatment of DES. Restasis® is not registered in Europe because of its side effects (eye irritation, in particular). There are several artificial tear products, such as Refresh®, available to treat DES, which are used either alone (in mild to moderate cases) or in combination with other treatments (in moderate to severe cases). Eye drops are currently the most common method of treating DES and the most common practice is to have patients self-administer such drops several times daily. Patients may have difficulty complying with this regimen as it may be more difficult than taking pills and may result in less than the full dose of the drug actually entering the eye. In addition to the foregoing, several therapies are in advanced clinical stages of development for DES.
CF101 for the Treatment of Glaucoma
According to Datamonitor, as of 2010, seven million people in the seven major markets suffered from glaucoma. GlobalData estimated that the market for glaucoma drugs was $3.0 billion in 2010. We expect that the number of people who suffer from glaucoma will increase as the population in each of the seven major markets ages.
| 62 |
The main drugs used to treat glaucoma include Xalatan®, Travatan® and Cosopt®. Xalatan® is recommended by the European Glaucoma Society and American Academy of Ophthalmologists as the first choice for the treatment of glaucoma. According to a Pfizer annual report, Xalatan®, which is marketed by Pfizer, is the leading drug used to treat glaucoma, and had global sales of over $1.7 billion in 2010. Sales of Xalatan® decreased to $1.25 billion in 2011 and are expected to continue to decrease likely as a result of the expiration of patents covering Xalatan® during 2011 and the launch of new generic brands. Travatan® was first launched in the United States in 2001 and then Europe and the rest of the world markets in 2002. According to Evaluate Pharma, Travatan®, marketed by Alcon, experienced sales of approximately $600 million in 2010. Travatan® is administered once each day, which ophthalmologists cite as a significant advantage over other drugs used to treat glaucoma. Cosopt® is the oldest combination therapy in the glaucoma market. Due to the expiration of patents covering Cosopt® in 2008, some ophthalmologists have begun to look to other brands or generic drugs in the treatment of glaucoma. Another leading company in this field is Allergan, which markets Lumigan®, Ganfort™, Alphagan®, and Combigan®, with over $1.0 billion in aggregate revenues in 2011. The Pfizer annual report predicts that the glaucoma therapeutics market will witness major revenue depletion over the next few years due to a string of upcoming patent expirations, which started with the expiration of the Xalatan® patent.
Several therapies are in advanced clinical development for glaucoma. In addition, in 2012, the FDA approved tafluprost ophthalmic solution, Zioptan by Merck, the first preservative-free prostaglandin analog ophthalmic solution, or a solution derived from fatty acids, for the treatment of glaucoma.
While several anti-glaucoma drugs exist, the glaucoma therapeutics market has a high level of unmet need, which mainly arises from the lack of approved drugs targeting the disease’s progression. Many therapies approved provide only symptomatic relief. The therapies which are available for the treatment of glaucoma have shown low to moderate efficacy and safety profiles. Accordingly, there is a significant need for drugs that reduce IOP. In addition, part of the pathogenesis of glaucoma is damage to the optic nerve, so drugs that, in addition to lowering IOP, have a neuroprotective effect, would also satisfy an unmet need. Based on its toxicological profile, we believe that CF101 has the potential to have fewer side effects than existing drugs for the treatment of glaucoma. At the same time, CF101 offers the potential to act as a neuroprotective agent that prevents the death of retinal cells, as well as the potential to lower IOP. We also believe that CF101 will offer less frequent administration than most existing therapies.
CF101 for the Treatment of Uveitis
According to Data Monitor, uveitis is estimated as the fifth or sixth leading cause of blindness in the United States. The incidence of uveitis worldwide varies from 14 to 52.4 per 100,000 people, while the overall prevalence around the world is reported as 0.73%. We estimate that there are approximately one million uveitis patients around the world. According to GlobalData, in 2010, the uveitis market was $0.32 billion and is estimated to reach $1.6 billion by 2017. The current treatments for uveitis include corticosteroids, anti-metabolites, T-cell inhibitors, alkylating agents and biological drugs, which often involve serious adverse side effects and lack of efficacy. Accordingly, we believe that a need exists for drugs used in the treatment of uveitis that are less toxic and more effective. There are currently several therapies in advance clinical development for anterior and posterior uveitis.
Former pre-clinical pharmacology studies conducted in collaboration with a research group from the NIH demonstrated that CF101 is effective in suppressing ocular inflammation in the experimental murine, or mouse or related rodent, model of uveitis. OphthaliX is continuing to conduct further pharmacological studies and on July 16, 2013 announced the submission of a protocol for the Phase II study of uveitis. OphthaliX plans to conduct such Phase II study in Europe and Israel and to investigate the efficacy and safety of CF101 in 45 patients with active, sight-threatening, noninfectious intermediate or posterior uveitis, who will be treated with either CF101 or a placebo for a period of six months. To date, CF101 has been found to be effective in inhibiting the development of posterior and anterior uveitis and has a favorable safety profile in experimental animal models.
CF102 for the Treatment of HCC
According to the American Cancer Society, HCC is the sixth most common form of cancer, the most common form of liver cancer in adults and the third most common cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, particularly in Asia. According to the American Cancer Society, more than 700,000 people are diagnosed with liver cancer each year throughout the world and more than 600,000 persons die from liver cancer each year. Nexavar is the only approved drug for HCC and prolongs patient survival time by only a few months. GlobalData recently estimated that in 2017, the HCC market will be $1.2 billion. However, Global Industry Analysts predicts that the market for HCC drugs will increase to approximately $2.0 billion by 2015.
| 63 |
Currently, there is no vaccine for HCC. Several therapies are in advanced clinical development for HCC. Some drugs under development act as a single agent and some act in combination with Nexavar. Moreover, some are first line treatments while others are second line treatments. In addition, many existing approaches are used in the treatment of unresectable liver cancer, including alcohol injection, radiofrequency ablation, chemoembolization, cryoablation and radiation therapy.
CF102 for the Treatment of HCV
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the CDC, approximately 3.2 million people in the United States have chronic HCV, a viral disease that causes inflammation of the liver that can lead to diminished liver function or liver failure. Most people with HCV have no symptoms of the disease until liver damage occurs, which may take several years. Also according to the CDC, approximately 75% to 85% of persons carrying the HCV will develop a chronic disease, such as liver cancer, liver failure or death. According to Renub Research, the market for HCV drugs is approximately $6.0 billion and is expected to double by 2015. The market is driven, to a large extent, by the recent approval for marketing, during 2011, of two new protease inhibitor drugs: Telaprevir (Incivek) by Vertex and Boceprevir (Victrelis) by Merck, both of which are delivered orally as a pill and are used in combination with interferon and ribavirin therapy.
Currently, there is no vaccine for HCV. Prior to the recent approval of Telaprevir and Boceprevir, the available treatment was a combination of interferon injections and ribavarin pills. According to the CDC, less than 50% of patients respond to this therapy and after some time, patients may develop a resistance to the combination. In addition, these drugs may cause severe side effects. Drugs currently approved for the treatment of HCV include interferon-alpha-based products, ribavirin-based products and protease inhibitors.
There are also several companies that specialize in the development of HCV therapies. The HCV therapies currently in development in multiple classes include protease inhibitors, polymerase inhibitors (nucleoside and non-nucleoside), NS5A inhibitors, toll-like receptor inhibitors and cyclophilin inhibitors.
In our studies of CF102, it has shown a good safety profile and a capability to decrease the viral load in HCV patients that also have HCC. We plan to examine the viral load of HCC patients who are also infected with HCV as part of our next HCC Phase II study.
Insurance
We maintain insurance for our offices and laboratory in Petah-Tikva, Israel. Our insurance program covers approximately $0.375 million of equipment and lease improvements against risk of loss, excluding damage from inventory theft. In addition, we maintain the following insurance: employer liability with coverage of approximately $5.0 million; third party liability with coverage of approximately $0.750 million; fire peril coverage of approximately $0.725 million; natural disaster coverage of approximately $1.1 million; all risk coverage of approximately $0.02 million for electronic equipment and machinery insurance for laboratory refrigerators; and directors’ and officers’ liability with coverage of $2.0 million per claim and $10.0 million in the aggregate.
We also maintain worldwide product and clinical trial liability insurance with coverage of approximately $3 million with respect to the CF101 and CF102 drugs used in clinical trials. We also procure additional insurance for each specific clinical trial which covers a certain number of trial participants and which varies based on the particular clinical trial. Certain of such policies are based on the Declaration of Helsinki, which is a set of ethical principles regarding human experimentation developed for the medical community by the World Medical Association, and certain protocols of the Israeli Ministry of Health.
We procure cargo marine coverage when we ship substances for our clinical studies. Such insurance is custom-fit to the special requirements of the applicable shipment, such as temperature and/or climate sensitivity. If required, we insure the substances to the extent they are stored in central depots and at clinical sites.
| 64 |
We believe that our insurance policies are adequate and customary for a business of our kind. However, because of the nature of our business, we cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain insurance on a commercially reasonable basis or at all, or that any future claims will not exceed our insurance coverage.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to various environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing air emissions, water and wastewater discharges, noise emissions, the use, management and disposal of hazardous, radioactive and biological materials and wastes and the cleanup of contaminated sites. We believe that our business, operations and facilities are being operated in compliance in all material respects with applicable environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Our laboratory personnel have ongoing communication with the Israeli Ministry of Environmental Protection in order to verify compliance with relevant instructions and regulations. In addition, all of our laboratory personnel participate in instruction on the proper handling of chemicals, including hazardous substances before commencing employment, and during the course of their employment, with us. In addition, all information with respect to any chemical substance that we use is filed and stored as a Material Safety Data Sheet, as required by applicable environmental regulations. Based on information currently available to us, we do not expect environmental costs and contingencies to have a material adverse effect on us. The operation of our facilities, however, entails risks in these areas. Significant expenditures could be required in the future if we are required to comply with new or more stringent environmental or health and safety laws, regulations or requirements. See “Business — Government Regulation and Funding — Israel Ministry of Environment — Toxin Permit.”
Government Regulation and Funding
We operate in a highly controlled regulatory environment. Stringent regulations establish requirements relating to analytical, toxicological and clinical standards and protocols in respect of the testing of pharmaceuticals. Regulations also cover research, development, manufacturing and reporting procedures, both pre- and post-approval. In many markets, especially in Europe, marketing and pricing strategies are subject to national legislation or administrative practices that include requirements to demonstrate not only the quality, safety and efficacy of a new product, but also its cost-effectiveness relating to other treatment options. Failure to comply with regulations can result in stringent sanctions, including product recalls, withdrawal of approvals, seizure of products and criminal prosecution.
Before obtaining regulatory approvals for the commercial sale of our product candidates, we or our licensees must demonstrate through preclinical studies and clinical trials that our product candidates are safe and effective. Historically, the results from preclinical studies and early clinical trials often have not accurately predicted results of later clinical trials. In addition, a number of pharmaceutical products have shown promising results in clinical trials but subsequently failed to establish sufficient safety and efficacy results to obtain necessary regulatory approvals. We have incurred and will continue to incur substantial expense for, and devote a significant amount of time to, preclinical studies and clinical trials. Many factors can delay the commencement and rate of completion of clinical trials, including the inability to recruit patients at the expected rate, the inability to follow patients adequately after treatment, the failure to manufacture sufficient quantities of materials used for clinical trials, and the emergence of unforeseen safety issues and governmental and regulatory delays. If a product candidate fails to demonstrate safety and efficacy in clinical trials, this failure may delay development of other product candidates and hinder our ability to conduct related preclinical studies and clinical trials. Additionally, as a result of these failures, we may also be unable to find additional licensees or obtain additional financing.
Governmental authorities in all major markets require that a new pharmaceutical product be approved or exempted from approval before it is marketed, and have established high standards for technical appraisal, which can result in an expensive and lengthy approval process. The time to obtain approval varies by country and some products are never approved. The lengthy process of conducting clinical trials, seeking approval and the subsequent compliance with applicable statutes and regulations, if approval is obtained, are very costly and require the expenditure of substantial resources.
A summary of the U.S., EU and Israeli regulatory processes follow below.
| 65 |
United States
In the United States, the Public Health Service Act and the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as amended, and the regulations promulgated thereunder, and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the safety and effectiveness standards for our products and the raw materials and components used in the production of, testing, manufacture, labeling, storage, record keeping, approval, advertising and promotion of our products on a product-by-product basis.
Preclinical tests include in vitro and in vivo evaluation of the product candidate, its chemistry, formulation and stability, and animal studies to assess potential safety and efficacy. Certain preclinical tests must be conducted in compliance with good laboratory practice regulations. Violations of these regulations can, in some cases, lead to invalidation of the studies, requiring them to be replicated. After laboratory analysis and preclinical testing, we intend to file an IND with the FDA to begin human testing. Typically, a manufacturer conducts a three-phase human clinical testing program which itself is subject to numerous laws and regulatory requirements, including adequate monitoring, reporting, record keeping and informed consent. In Phase I, small clinical trials are conducted to determine the safety and proper dose ranges of our product candidates. In Phase II, clinical trials are conducted to assess safety and gain preliminary evidence of the efficacy of our product candidates. In Phase III, clinical trials are conducted to provide sufficient data for the statistically valid evidence of safety and efficacy. The time and expense required for us to perform this clinical testing can vary and is substantial. We cannot be certain that we will successfully complete Phase I, Phase II or Phase III testing of our product candidates within any specific time period, if at all. Furthermore, the FDA, the Institutional Review Board responsible for approving and monitoring the clinical trials at a given site, the Data Safety Monitoring Board, where one is used, or the Company may suspend the clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that subjects or patients are exposed to unacceptable health risk.
If the clinical data from these clinical trials (Phases I, II and III) are deemed to support the safety and effectiveness of the candidate product for its intended use, then the Company may proceed to seek to file with the FDA, a New Drug Application, or NDA, seeking approval to market a new drug for one or more specified intended uses. The Company has not completed its clinical trials for any candidate product for any intended use and therefore, the Company cannot ascertain whether the clinical data will support and justify filing an NDA. Nevertheless, if and when the Company is able to ascertain that the clinical data supports and justifies filing an NDA, the Company intends to make such appropriate filings for all indications for which it is testing its product candidates, including, but not limited to, DES, psoriasis, RA and HCC.
The purpose of the NDA is to provide the FDA with sufficient information so that it can assess whether it ought to approve the candidate product for marketing for specific intended uses. The fact that the FDA has designated a drug as an orphan drug for a particular intended use does not mean that the drug has been approved for marketing. Only after an NDA has been approved by the FDA is marketing appropriate. A request for orphan drug status must filed before the NDA is filed. The orphan drug designation, though, provides certain benefits, including a seven-year period of market exclusivity subject to certain exceptions. In February 2012, the FDA granted an orphan drug status for the active moiety, or the part of the drug that is responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of the drug substance, of CF102 for the treatment of HCC. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—B. Business Overview—CF102”.
The NDA normally contains, among other things, sections describing the chemistry, manufacturing, and controls, non-clinical pharmacology and toxicology, human pharmacokinetics and bioavailability, microbiology, the results of the clinical trials, and the proposed labeling which contains, among other things, the intended uses of the candidate product.
We cannot take any action to market any new drug or biologic product in the United States until our appropriate marketing application has been approved by the FDA. The FDA has substantial discretion over the approval process and may disagree with our interpretation of the data submitted. The process may be significantly extended by requests for additional information or clarification regarding information already provided. As part of this review, the FDA may refer the application to an appropriate advisory committee, typically a panel of clinicians. Satisfaction of these and other regulatory requirements typically takes several years, and the actual time required may vary substantially based upon the type, complexity and novelty of the product. Government regulation may delay or prevent marketing of potential products for a considerable period of time and impose costly procedures on our activities. We cannot be certain that the FDA or other regulatory agencies will approve any of our products on a timely basis, if at all. Success in preclinical or early stage clinical trials does not assure success in later-stage clinical trials. Even if a product receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific indications or uses and these limitations may adversely affect the commercial viability of the product. Delays in obtaining, or failures to obtain regulatory approvals, would have a material adverse effect on our business.
Even after we obtain FDA approval, we may be required to conduct further clinical trials (i.e., Phase IV trials) and provide additional data on safety and effectiveness. We are also required to gain separate approval for the use of an approved product as a treatment for indications other than those initially approved. In addition, side effects or adverse events that are reported during clinical trials can delay, impede or prevent marketing approval. Similarly, adverse events that are reported after marketing approval can result in additional limitations being placed on the product’s use and, potentially, withdrawal of the product from the market. Any adverse event, either before or after marketing approval, can result in product liability claims against us.
In addition to regulating and auditing human clinical trials, the FDA regulates and inspects equipment, facilities, laboratories and processes used in the manufacturing and testing of such products prior to providing approval to market a product. If after receiving FDA approval, we make a material change in manufacturing equipment, location or process, additional regulatory review may be required. We also must adhere to cGMP regulations and product-specific regulations enforced by the FDA through its facilities inspection program. The FDA also conducts regular, periodic visits to re-inspect our equipment, facilities, laboratories and processes following the initial approval. If, as a result of these inspections, the FDA determines that our equipment, facilities, laboratories or processes do not comply with applicable FDA regulations and conditions of product approval, the FDA may seek civil, criminal or administrative sanctions and/or remedies against us, including the suspension of our manufacturing operations.
| 66 |
We have currently received no approvals to market our products from the FDA or other foreign regulators.
We are also subject to various federal, state and international laws pertaining to health care “fraud and abuse,” including anti-kickback laws and false claims laws. The federal Anti-kickback law, which governs federal healthcare programs (e.g., Medicare, Medicaid), makes it illegal to solicit, offer, receive or pay any remuneration in exchange for, or to induce, the referral of business, including the purchase or prescription of a particular drug. Many states have similar laws that are not restricted to federal healthcare programs. Federal and state false claims laws prohibit anyone from knowingly and willingly presenting, or causing to be presented for payment to third party payers (including Medicare and Medicaid), claims for reimbursement, including claims for the sale of drugs or services, that are false or fraudulent, claims for items or services not provided as claimed, or claims for medically unnecessary items or services. If the government or a whistleblower were to allege that we violated these laws there could be a material adverse effect on us, including our stock price. Even an unsuccessful challenge could cause adverse publicity and be costly to respond to, which could have a materially adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. A finding of liability under these laws can have significant adverse financial implications for the Company and can result in payment of large penalties and possible exclusion from federal healthcare programs. We will consult counsel concerning the potential application of these and other laws to our business and our sales, marketing and other activities and will make good faith efforts to comply with them. However, given their broad reach and the increasing attention given by law enforcement authorities, we cannot assure you that some of our activities will not be challenged or deemed to violate some of these laws.
European Economic Area
Although we are not currently seeking regulatory approval in the EU, we or our licensees may do so in the future. As such, a summary of the EU regulatory processes follows below.
A medicinal product may only be placed on the market in the European Economic Area, or EEA, composed of the 27 EU member states, plus Norway, Iceland and Lichtenstein, when a marketing authorization has been issued by the competent authority of a member state pursuant to Directive 2001/83/EC (as recently amended by Directive 2004/27/EC), or an authorization has been granted under the centralized procedure in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 726/2004 or its predecessor, Regulation 2309/93. There are essentially three community procedures created under prevailing European pharmaceutical legislation that, if successfully completed, allow an applicant to place a medicinal product on the market in the EEA.
Centralized Procedure
Regulation 726/2004/EC now governs the centralized procedure when a marketing authorization is granted by the European Commission, acting in its capacity as the European Licensing Authority on the advice of the EMA. That authorization is valid throughout the entire community and directly or (as to Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein) indirectly allows the applicant to place the product on the market in all member states of the EEA. The EMA is the administrative body responsible for coordinating the existing scientific resources available in the member states for evaluation, supervision and pharmacovigilance of medicinal products. Certain medicinal products, as described in the Annex to Regulation 726/2004, must be authorized centrally. These are products that are developed by means of a biotechnological process in accordance with Paragraph 1 to the Annex to the Regulation. Medicinal products for human use containing a new active substance for which the therapeutic indication is the treatment of acquired immune deficiency syndrome, or AIDS, cancer, neurodegenerative disorder or diabetes must also be authorized centrally. Starting on May 20, 2008, the mandatory centralized procedure was extended to autoimmune diseases and other immune dysfunctions and viral diseases. Finally, all medicinal products that are designated as orphan medicinal products pursuant to Regulation 141/2000 must be authorized under the centralized procedure. An applicant may also opt for assessment through the centralized procedure if it can show that the medicinal product constitutes a significant therapeutic, scientific or technical innovation or that the granting of authorization centrally is in the interests of patients at the community level. For each application submitted to the EMA for scientific assessment, the EMA is required to ensure that the opinion of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, or CHMP, is given within 210 days after receipt of a valid application. This 210 days period does not include the time that the applicant to answer any questions raised during the application procedure, the so-called ‘clock stop’ period. If the opinion is positive, the EMEA is required to send the opinion to the European Commission, which is responsible for preparing the draft decision granting a marketing authorization. This draft decision may differ from the CHMP opinion, stating reasons for diverging for the CHMP opinion. The draft decision is sent to the applicant and the member states, after which the European Commission takes a final decision. If the initial opinion of the CHMP is negative, the applicant is afforded an opportunity to seek a re-examination of the opinion. The CHMP is required to re-examine its opinion within 60 days following receipt of the request by the applicant. All CHMP refusals and the reasons for refusal are made public on the EMA website. Without a centralized marketing authorization it is prohibited to place a medicinal product that must be authorized centrally on the market in the EU.
| 67 |
Mutual Recognition and Decentralized Procedures
With the exception of products that are authorized centrally, the competent authorities of the member states are responsible for granting marketing authorizations for medicinal products placed on their national markets. If the applicant for a marketing authorization intends to market the same medicinal product in more than one member state, the applicant may seek an authorization progressively in the community under the mutual recognition or decentralized procedure. Mutual recognition is used if the medicinal product has already been authorized in a member state. In this case, the holder of this marketing authorization requests the member state where the authorization has been granted to act as reference member state by preparing an updated assessment report that is then used to facilitate mutual recognition of the existing authorization in the other member states in which approval is sought (the so-called concerned member state(s)). The reference member state must prepare an updated assessment report within 90 days of receipt of a valid application. This report together with the approved Summary of Product Characteristics, or SmPC (which sets out the conditions of use of the product), and a labeling and package leaflet are sent to the concerned member states for their consideration. The concerned member states are required to approve the assessment report, the SmPC and the labeling and package leaflet within 90 days of receipt of these documents. The total procedural time is 180 days.
The decentralized procedure is used in cases where the medicinal product has not received a marketing authorization in the EU at the time of application. The applicant requests a member state of its choice to act as reference member state to prepare an assessment report that is then used to facilitate agreement with the concerned member states and the grant of a national marketing authorization in all of these member states. In this procedure, the reference member state must prepare, for consideration by the concerned member states, the draft assessment report, a draft SmPC and a draft of the labeling and package leaflet within 120 days after receipt of a valid application. As in the case of mutual recognition, the concerned member states are required to approve these documents within 90 days of their receipt.
For both mutual recognition and decentralized procedures, if a concerned member state objects to the grant of a marketing authorization on the grounds of a potential serious risk to public health, it may raise a reasoned objection with the reference member state. The points of disagreement are in the first instance referred to the Co-ordination Group on Mutual Recognition and Decentralized Procedures, or CMD, to reach an agreement within 60 days of the communication of the points of disagreement. If member states fail to reach an agreement, then the matter is referred to the EMEA and CHMP for arbitration. The CHMP is required to deliver a reasoned opinion within 60 days of the date on which the matter is referred. The scientific opinion adopted by the CHMP forms the basis for a binding European Commission decision.
Irrespective of whether the medicinal product is assessed centrally, de-centrally or through a process of mutual recognition, the medicinal product must be manufactured in accordance with the principles of good manufacturing practice as set out in Directive 2003/94/EC and Volume 4 of the rules governing medicinal products in the European community. Moreover, community law requires the clinical results in support of clinical safety and efficacy based upon clinical trials conducted in the European community to be in compliance with the requirements of Directive 2001/20/EC, which implements good clinical practice in the conduct of clinical trials on medicinal products for human use. Clinical trials conducted outside the European community and used to support applications for marketing within the EU must have been conducted in a way consistent with the principles set out in Directive 2001/20/EC. The conduct of a clinical trial in the EU requires, pursuant to Directive 2001/20/EC, authorization by the relevant national competent authority where a trial takes place, and an ethics committee to have issued a favorable opinion in relation to the arrangements for the trial. It also requires that the sponsor of the trial, or a person authorized to act on his behalf in relation to the trial, be established in the community.
| 68 |
National Procedure
This procedure is available for medicinal products that do not fall within the scope of mandatory centralized authorization and are intended for use in only on EU member state. Specific procedures and timelines differ between member states, but the duration of the procedure is generally 210 days and based on a risk/efficacy assessment by the competent authority of the member state concerned, followed by determination of SmPC, package leaflet and label text/layout and subsequently grant of the marketing authorization. Marketing authorizations granted on this basis are not mutually recognized by other member states.
There are various types of applications for marketing authorizations:
Full Applications. A full application is one that is made under any of the community procedures described above and “stands alone” in the sense that it contains all of the particulars and information required by Article 8(3) of Directive 2001/83 (as amended) to allow the competent authority to assess the quality, safety and efficacy of the product and in particular the balance between benefit and risk. Article 8(3)(l) in particular refers to the need to present the results of the applicant’s research on (i) pharmaceutical (physical-chemical, biological or microbiological) tests, (ii) preclinical (toxicological and pharmacological) studies and (iii) clinical trials in humans. The nature of these tests, studies and trials is explained in more detail in Annex I to Directive 2001/83/EC. Full applications would be required for products containing new active substances not previously approved by the competent authority, but may also be made for other products.
Abridged Applications. Article 10 of Directive 2001/83/EC contains exemptions from the requirement that the applicant provide the results of its own preclinical and clinical research. There are three regulatory routes for an applicant to seek an exemption from providing such results, namely (i) cross-referral to an innovator’s results without consent of the innovator, (ii) well established use according to published literature and (iii) consent to refer to an existing dossier of research results filed by a previous applicant.
Cross-referral to Innovator’s Data
Articles 10(1) and 10(2)(b) of Directive 2001/83/EC provide the legal basis for an applicant to seek a marketing authorization on the basis that its product is a generic medicinal product (a copy) of a reference medicinal product that has already been authorized, in accordance with community provisions. A reference product is, in principle, an original product granted an authorization on the basis of a full dossier of particulars and information. This is the main exemption used by generic manufacturers for obtaining a marketing authorization for a copy product. The generic applicant is not required to provide the results of preclinical studies and of clinical trials if its product meets the definition of a generic medicinal product and the applicable regulatory results protection period for the results submitted by the innovator has expired. A generic medicinal product is defined as a medicinal product:
| · | having the same qualitative and quantitative composition in active substance as the reference medicinal product; |
| · | having the same pharmaceutical form as the reference medicinal product; and |
| · | whose bioequivalence with the reference medicinal product has been demonstrated by appropriate bioavailability studies. |
Applications in respect of a generic medicinal product cannot be made before the expiry of the protection period. Where the reference product was granted a national marketing authorization pursuant to an application made before October 30, 2005, the protection period is either six years or 10 years, depending upon the election of the particular member state concerned. Where the reference product was granted a marketing authorization centrally, pursuant to an application made before November 20, 2005, the protection period is 10 years. For applications made after these dates, Regulation 726/2004 and amendments to Directive 2001/83/EC provide for a harmonized protection period regardless of the approval route utilized. The harmonized protection period is in total 10 years, including eight years of research data protection and two years of marketing protection. The effect is that the originator’s results can be the subject of a cross-referral application after eight years, but any resulting authorization cannot be exploited for a further two years. The rationale of this procedure is not that the competent authority does not have before it relevant tests and trials upon which to assess the efficacy and safety of the generic product, but that the relevant particulars can, if the research data protection period has expired, be found on the originator’s file and used for assessment of the generic medicinal product. The 10-year protection period can be extended to 11 years where, in the first eight years post-authorization, the holder of the authorization obtains approval for a new indication assessed as offering a significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing products.
| 69 |
If the copy product does not meet the definition of a generic medicinal product or if certain types of changes occur in the active substance(s) or in the therapeutic indications, strength, pharmaceutical form or route of administration in relation to the reference medicinal product, Article 10(3) of Directive 2001/83/EC provides that the results of the appropriate preclinical studies or clinical trials must be provided by the applicant.
Well-established Medicinal Use
Under Article 10a of Directive 2001/83/EC, an applicant may, in substitution for the results of its own preclinical and clinical research, present detailed references to published literature demonstrating that the active substance(s) of a product have a well-established medicinal use within the community with recognized efficacy and an acceptable level of safety. The applicant is entitled to refer to a variety of different types of literature, including reports of clinical trials with the same active substance(s) and epidemiological studies that indicate that the constituent or constituents of the product have an acceptable safety/efficacy profile for a particular indication. However, use of the published literature exemption is restricted by stating that in no circumstances will constituents be treated as having a well-established use if they have been used for less than 10 years from the first systematic and documented use of the substance as a medicinal product in the EU. Even after 10 years’ systematic use, the threshold for well-established medicinal use might not be met. European pharmaceutical law requires the competent authorities to consider among other factors the period over which a substance has been used, the amount of patient use of the substance, the degree of scientific interest in the use of the substance (as reflected in the scientific literature) and the coherence (consistency) of all the scientific assessments made in the literature. For this reason, different substances may reach the threshold for well-established use after different periods, but the minimum period is 10 years. If the applicant seeks approval of an entirely new therapeutic use compared with that to which the published literature refers, additional preclinical and/or clinical results would have to be provided.
Informed Consent
Under Article 10c of Directive 2001/83/EC, following the grant of a marketing authorization the holder of such authorization may consent to a competent authority utilizing the pharmaceutical, preclinical and clinical documentation that it submitted to obtain approval for a medicinal product to assess a subsequent application relating to a medicinal product possessing the same qualitative and quantitative composition with respect to the active substances and the same pharmaceutical form.
Law Relating to Pediatric Research
Regulation (EC) 1901/2006 (as amended by Regulation (EC) 1902/2006) was adopted on December 12, 2006. This Regulation governs the development of medicinal products for human use in order to meet the specific therapeutic needs of the pediatric population. It requires any application for marketing authorization made after July 26, 2008 in respect of a product not authorized in the European Community on January 26, 2007 (the time the Regulation entered into force), to include the results of all studies performed and details of all information collected in compliance with a pediatric investigation plan agreed by the Pediatric Committee of the EMA, unless the product is subject to an agreed waiver or deferral or unless the product is excluded from the scope of Regulation 1902/2006 (generics, hybrid medicinal products, biosimilars, homeopathic and traditional (herbal) medicinal products and medicinal products containing one or more active substances of well-established medicinal use). Waivers can be granted in certain circumstances where pediatric studies are not required or desirable. Deferrals can be granted in certain circumstances where the initiation or completion of pediatric studies should be deferred until appropriate studies in adults have been performed. Moreover, this regulation imposes the same obligation from January 26, 2009 on an applicant seeking approval of a new indication, pharmaceutical form or route of administration for a product already authorized and still protected by a supplementary protection certificate granted under Regulation EC 469/2009 and its precursor (EEC) 1768/92 or by a patent that qualifies for the granting of such a supplementary protection certificate. The pediatric Regulation 1901/2006 also provides, subject to certain conditions, a reward for performing such pediatric studies, regardless of whether the pediatric results provided resulted in the grant of a pediatric indication. This reward comes in the form of an extension of six months to the supplementary protection certificate granted in respect of the product, unless the product is subject to orphan drug designation, in which case the 10-year market exclusivity period for such orphan products is extended to 12 years. If any of the non-centralized procedures for marketing authorization have been used, the six-month extension of the supplementary protection certificate is only granted if the medicinal product is authorized in all member states.
| 70 |
Post-authorization Obligations
In the pre-authorization phase the applicant must provide a detailed pharmacovigilance plan that it intends to implement post-authorization. An authorization to market a medicinal product in the EU carries with it an obligation to comply with many post-authorization organizational and behavioral regulations relating to the marketing and other activities of authorization holders. These include requirements relating to post-authorization efficacy studies, post-authorization safety studies, adverse event reporting and other pharmacovigilance requirements, advertising, packaging and labeling, patient package leaflets, distribution and wholesale dealing. The regulations frequently operate within a criminal law framework and failure to comply with the requirements may not only affect the authorization, but also can lead to financial and other sanctions levied on the company in question and responsible officers. As a result of the currently on-going overhaul of EU pharmacovigilance legislation the financial and organizational burden on market authorization holders will increase significantly, such as the obligation to maintain a pharmacovigilance system master file that applies to all holders of marketing authorizations granted in accordance with Directive 2001/83/EC or Regulation (EC) No 726/2004. Marketing authorization holders must furthermore collect data on adverse events associated with use of the authorized product outside the scope of the authorization. Pharmacovigilance for biological products and medicines with a new active substance will be strengthened by subjecting their authorization to additional monitoring activities. The EU is currently in the process of issuing implementing regulations for the new pharmacovigilance framework.
Any authorization granted by member state authorities, which within three years of its granting is not followed by the actual placing on the market of the authorized product in the authorizing member state ceases to be valid. When an authorized product previously placed on the market in the authorizing member state is no longer actually present on the market for a period of three consecutive years, the authorization for that product shall cease to be valid. The same two three year periods apply to authorizations granted by the European Commission based on the centralized procedure.
Israel
Israel Ministry of the Environment — Toxin Permit
In accordance with the Israeli Dangerous Substance Law — 1993, the Ministry of the Environment may grant a permit in order to use toxic materials. Because we utilize toxic materials in the course of operation of our laboratories, we were required to apply for a permit to use these materials. Our current toxin permit will remain in effect until January 2014.
Other Licenses and Approvals
We have a business license from the municipality of Petah-Tikva for a drug development research laboratory located at our offices in Petah Tikva, Israel. In order to obtain this license, we also received approval from the Petah-Tikva Association of Towns Fire Department. The business license is valid until December 2014. We also have a radioactive materials or products containing radioactive materials license, which is valid until July 25, 2013.
In 2002, we received approval from the National Council on Animal Experiments, approving us as an institution authorized to conduct experiments on animals.
| 71 |
Clinical Testing in Israel
In order to conduct clinical testing on humans in Israel, special authorization must first be obtained from the ethics committee and general manager of the institution in which the clinical studies are scheduled to be conducted, as required under the Guidelines for Clinical Trials in Human Subjects implemented pursuant to the Israeli Public Health Regulations (Clinical Trials in Human Subjects), as amended from time to time, and other applicable legislation. These regulations also require authorization from the Israeli Ministry of Health, except in certain circumstances, and in the case of genetic trials, special fertility trials and similar trials, an additional authorization of the overseeing institutional ethics committee. The institutional ethics committee must, among other things, evaluate the anticipated benefits that are likely to be derived from the project to determine if it justifies the risks and inconvenience to be inflicted on the human subjects, and the committee must ensure that adequate protection exists for the rights and safety of the participants as well as the accuracy of the information gathered in the course of the clinical testing. Since we intend to perform a portion of the clinical studies on certain of our therapeutic candidates in Israel, we will be required to obtain authorization from the ethics committee and general manager of each institution in which we intend to conduct our clinical trials, and in most cases, from the Israeli Ministry of Health.
Other Countries
In addition to regulations in the United States, the EU and Israel, we are subject to a variety of other regulations governing clinical trials and commercial sales and distribution of drugs in other countries. Whether or not our products receive approval from the FDA, approval of such products must be obtained by the comparable regulatory authorities of countries other than the United States before we can commence clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries. The approval process varies from country to country, and the time may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. The requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials and product licensing vary greatly from country to country.
The requirements that we and our collaborators must satisfy to obtain regulatory approval by government agencies in other countries prior to commercialization of our products in such countries can be rigorous, costly and uncertain. In the European countries, Canada and Australia, regulatory requirements and approval processes are similar in principle to those in the United States. Additionally, depending on the type of drug for which approval is sought, there are currently two potential tracks for marketing approval in the European countries: mutual recognition and the centralized procedure. These review mechanisms may ultimately lead to approval in all European Union countries, but each method grants all participating countries some decision-making authority in product approval. Foreign governments also have stringent post-approval requirements including those relating to manufacture, labeling, reporting, record keeping and marketing. Failure to substantially comply with these on-going requirements could lead to government action against the product, the Company and/or its representatives.
Although we are not currently conducting research and development activities in certain Asian countries, including Korea and Japan, certain of our licensees, KD and SKK, are conducting such activities with respect to CF101 in those countries, respectively. Any regulatory approval process that may impact such licensees’ ability to continue their activities or obtain regulatory approval in those countries could impact the revenues we generate from our out-licensing agreements with them.
Related Matters
From time to time, legislation is drafted, introduced and passed in governmental bodies that could significantly change the statutory provisions governing the approval, manufacturing and marketing of products regulated by the FDA or EMEA and other applicable regulatory bodies to which we are subject. In addition, regulations and guidance are often revised or reinterpreted by the national agency in ways that may significantly affect our business and our therapeutic candidates. It is impossible to predict whether such legislative changes will be enacted, whether FDA or EMEA regulations, guidance or interpretations will change, or what the impact of such changes, if any, may be. We may need to adapt our business and therapeutic candidates and products to changes that occur in the future.
| 72 |
Israel Ministry of Health
Israel’s Ministry of Health, which regulates medical testing, has adopted protocols that correspond, generally, to those of the FDA and the European Medicines Agency, making it comparatively straightforward for studies conducted in Israel to satisfy FDA and the European Medicines Agency requirements, thereby enabling medical technologies subjected to clinical trials in Israel to reach U.S. and EU commercial markets in an expedited fashion. Many members of Israel’s medical community have earned international prestige in their chosen fields of expertise and routinely collaborate, teach and lecture at leading medical centers throughout the world. Israel also has free trade agreements with the United States and the European Union.
C. Organizational Structure
Our corporate structure consists of Can-Fite and three subsidiaries, one of which is an indirect subsidiary: Ultratrend Limited, a U.K. limited company, OphthaliX Inc., a Delaware corporation, or OphthaliX, and Eye-Fite Limited, an Israel limited company, or Eye-Fite. Ultratrend Limited is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Can-Fite, but has yet to conduct any significant activity. Can-Fite holds 82% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of OphthaliX and accordingly may appoint all members of the board of directors of OphthaliX. Eye-Fite Limited, a wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX, holds an exclusive license from Can-Fite, pursuant to which OphthaliX develops CF101 for use in the ophthalmic field.
D. Property, Plants and Equipment.
We are headquartered in Petah-Tikva, Israel. We lease one floor in one facility pursuant to a lease agreement with Eshkolit Nihul Nadlan LTD, an Israeli limited company, that pursuant to a verbal agreement, expires on December 31, 2013. The Petah-Tikva headquarters consists of approximately 160 square meters of space with eight parking spaces. Lease payments are approximately NIS 23,853, or $6,000, per month. If our lease is terminated, we do not foresee significant difficulty in leasing another suitable facility. The current facility houses both our administrative, clinical and research operations. The research laboratory consists of approximately 150 square meters and includes a tissue culture laboratory and a molecular biology laboratory.
ITEM 4A. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not Applicable.
ITEM 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects
The information in this section should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes beginning on page F-1 and the related information included elsewhere in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, and reported in NIS. We maintain our accounting books and records in NIS and our functional currency is NIS. Certain amounts presented herein may not sum due to rounding.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on developing orally bioavailable small molecule therapeutic products for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic diseases. Our platform technology utilizes the Gi protein associated A3AR as a therapeutic target. A3AR is highly expressed in inflammatory and cancer cells, and not significantly expressed in normal cells, suggesting that the receptor could be a unique target for pharmacological intervention. Our pipeline drugs are synthetic, highly specific agonists and allosteric modulators, or ligands or molecules that initiate molecular events when binding with target proteins, targeting the A3AR. Our strategy is to build a fully integrated biotechnology company that discovers, in-licenses and develops an innovative and effective small molecule drug portfolio of ligands that bind to a specific therapeutic target for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological, ophthalmic diseases and more. We continue to develop and test our existing pipeline, while also testing other indications for our existing drugs and examining, from time to time, the potential of other small molecules that may fit our platform technology of utilizing small molecules to target the A3AR. We generally focus on drugs with global market potential and we seek to create global partnerships to effectively assist us in developing our portfolio and to market our products.
| 73 |
We have in-licensed three different A3AR ligands which represent our current pipeline drugs under development and include two synthetic A3AR agonists, CF101 (known generically as IB-MECA) and CF102 (known generically as CI-IB-MECA) from the NIH, and an allosteric modulator at the A3AR, CF602 from Leiden University. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—In-Licensing Agreements”. In addition, we have out-licensed CF101 for (i) the treatment of autoimmune diseases to SKK for the Japanese market, (ii) for the treatment of RA to KD for the Korean market and (iii) for the treatment of ophthalmic diseases to Eye-Fite, a wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX for the global market. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”.
Our drugs, CF101, CF102 and CF602 are being developed to treat several autoimmune-inflammatory, oncological and ophthalmic indications. CF101 is in various stages of clinical development for the treatment of autoimmune-inflammatory diseases, including RA, psoriasis, and OA. CF101 is also being developed by OphthaliX for the treatment of ophthalmic indications, including DES, glaucoma and uveitis. The CF102 drug candidate is being developed for the treatment of HCC and for the treatment of HCV. CF602 is our second generation allosteric drug candidate for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, which has shown proof of concept in in vitro and in vivo studies. In addition, we recently announced that we are planning to develop CF602 to treat sexual dysfunction. Preclinical studies revealed that our drugs have potential to treat additional inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, oncological diseases and viral diseases, such as the JC virus.
We are currently: (i) conducting a Phase II/III trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of psoriasis; (ii) conducting a Phase IIb trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of RA; (iii) preparing for a Phase II study with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of OA; (iv) preparing for a Phase II study with respect to the development of CF102 for the treatment of HCC and HCV; and (v) in preclinical work with respect to the development of CF602. OphthaliX is currently: (i) conducting a Phase III trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of DES; (ii) conducting a Phase II trial with respect to the development of CF101 for the treatment of glaucoma or related syndromes of ocular hypertension; and (iii) initiating a Phase II study of CF101 for the treatment of uveitis.
Since inception, we have incurred significant losses in connection with our research and development. At December 31, 2012, we had an accumulated deficit of NIS 252,404,000. Although we have begun to recognize revenues in connection with our out-licensing agreements with SKK, KD and OphthaliX, we may continue to generate losses in connection with the research and development activities relating to our pipeline of drug candidates. Such research and development activities are budgeted to expand over time and will require further resources if we are to be successful. As a result, we may continue to incur operating losses, which may be substantial over the next several years, and we may need to obtain additional funds to further develop or research and development programs.
We have funded our operations primarily through the sale of equity securities (both in private placements and in public offerings on the TASE) and payments received under the licensing arrangements with SKK and KD. We expect to continue to fund our operations over the next several years through our existing cash resources, potential future milestone payments that we expect to receive from our licensees, interest earned on our investments, if any, and additional capital to be raised through public or private equity offerings or debt financings. As of December 31, 2012, we had approximately $1,146,000, or NIS 4,278,000, of cash and cash equivalents based on the exchange rate reported by the Bank of Israel as of December 31, 2012. This does not include an aggregate of NIS 26,498,488 raised on February 5, 2013 through a public offering in which we issued ordinary shares, Series 10 Warrants and Series 11 Warrants.
Revenues
Our revenues to date have been generated primarily from payments under our licensing arrangements with SKK and KD. Under the Seikagaku Agreement, we are entitled to up-front and milestone payments of up to $19.5 million (of which $2 million is attributable to our participation in certain research and development activities) and up to an additional $4 million in milestone payments if SKK pursues a second indication (the current indication is RA). We will also be entitled to royalties in an amount between 7-12% of annual net sales in Japan subject to certain sales criteria. In accordance with the Seikagaku Agreement, we received an up-front payment of $3.0 million in 2006, a milestone payment of $1.0 million in 2008 and $0.5 million per year from 2007 through 2011 as an annual minimum royalty payment (for an aggregate of $2.5 million). Under the Kwang Dong Agreement, we are entitled to up-front and milestone payments of $1.5 million. In accordance with the Kwang Dong Agreement, we received an up-front payment of $0.3 million and a payment of $0.048 million as consideration for KD’s purchase of our ordinary shares in 2009 and a milestone payment of $0.2 million in 2010. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”.
| 74 |
Under the terms of the Seikagaku Agreement and the Kwang Dong Agreement, in addition to the payments mentioned above, we are entitled to certain future development-related milestone payments, subject to the terms and conditions of the respective agreements. See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”. Certain payments we have received from SKK and KD have been subject to a 10% and 5% withholding tax in Japan and Korea, respectively, and certain payments we may receive in the future, if at all, may also be subject to the same withholding tax in Japan and Korea. Receipt of any milestone payment under our out-licensing agreements depends on many factors, some of which are beyond our control. We cannot assure you that we will receive any of these future payments. We expect our revenues for the next several years to be derived primarily from payments under our current out-license agreements and our public capital raising activities, as well as additional collaborations that we may enter into in the future with respect to our drug candidates.
Research and Development
Our research and development expenses consist primarily of salaries and related personnel expenses, fees paid to external service providers, up-front and milestone payments under our license agreements, patent-related legal fees, costs of preclinical studies and clinical trials, drug and laboratory supplies and costs for facilities and equipment. We charge all research and development expenses to operations as they are incurred. We expect our research and development expense to remain our primary expense in the near future as we continue to develop our products. Increases or decreases in research and development expenditures are attributable to the number and/or duration of the pre-clinical and clinical studies that we conduct.
The following table identifies our current major research and development projects:
| Project | Status | Expected or Recent Near Term Milestone | ||
| CF 101 | Ongoing Phase IIb in RA | Study results are expected in the second half of 2013 | ||
| Ongoing Phase II/III in Psoriasis | Patient enrollment is expected to be complete in 2013 | |||
| Ongoing Phase III in DES (via OphthaliX) | Study results are expected in the fourth quarter of 2013 | |||
| Ongoing Phase II in Glaucoma (via OphthaliX) | Conclusion of the first segment is expected in the second quarter of 2014 | |||
| Exploratory Phase II in Uveitis (via OphthaliX) | Study protocol was submitted in July 2013 | |||
| Phase II in OA | Commencement of the study is expected in the second half of 2013 | |||
| CF 102 | Phase II in HCC | Study protocol is expected to be submitted in the second half of 2013. | ||
| CF 602 | Pre-Clinical Stage | Continuing pre-clinical studies and preparations |
We record certain costs for each development project on a “direct cost” basis, as they are recorded to the project for which such costs are incurred. Such costs include, but are not limited to, CRO expenses, drug production for pre-clinical and clinical studies and other pre-clinical and clinical expenses. However, certain other costs, including but not limited to, salary expenses (including salaries for research and development personnel), facilities, depreciation, share-based compensation and other overhead costs are recorded on an “indirect cost” basis, i.e., they are shared among all of our projects and are not recorded to the project for which such costs are incurred. We do not allocate direct salaries to projects due to the fact that our project managers are generally involved in several projects at different stages of development, and the related salary expense is not significant to the overall cost of the applicable projects. In addition, indirect labor costs relating to our support of the research and development process, such as manufacturing, controls, pre-clinical analysis, laboratory testing and initial drug sample production, as well as rent and other administrative overhead costs, are shared by many different projects and have never been considered by management to be of significance in its decision-making process with respect to any specific project. Accordingly, such costs have not been specifically allocated to individual projects.
| 75 |
Set forth below is a summary of the gross direct costs allocated to our main projects on an individual basis, as well as the gross direct costs allocated to our less significant projects on an aggregate basis, for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2011 and 2012; and on an aggregate basis since project inception:
| Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Costs | ||||||||||||||||
| Since | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | Project | |||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | Inception | |||||||||||||
| CF 101 | 60 | 1,117 | 1,987 | 14,074 | ||||||||||||
| CF 102 | 338 | 250 | 15 | 1,120 | ||||||||||||
| CF 602 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Other projects | - | - | - | 1,710 | ||||||||||||
| Total gross direct project costs (1) | 398 | 1,367 | 2,002 | 16,904 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Does not include indirect project costs and overhead, such as payroll and related expenses (including stock-based compensation), facilities, depreciation and impairment of intellectual property, which are included in total research and development expenses in our financial statements. |
A significant portion of our research and development costs have been incurred in connection with our Phase IIb clinical trial of RA.
Under our licensing agreement with Eye-Fite, Eye-Fite is responsible for making payments to our licensor, the NIH, for certain patent rights relating to CF101. See “Item 10. Additional Information — Material Contracts — Out-Licensing Agreements—Eye-Fite Agreement”.
From our inception through December 31, 2012, we have incurred research and development expenses of approximately $49 million. We expect that a large percentage of our research and development expense in the future will be incurred in support of our current and future preclinical and clinical development projects. Due to the inherently unpredictable nature of preclinical and clinical development processes and given the early stage of our preclinical product development projects, we are unable to estimate with any certainty the costs we will incur in the continued development of the product candidates in our pipeline for potential commercialization. Clinical development timelines, the probability of success and development costs can differ materially from expectations. We expect to continue to test our product candidates in preclinical studies for toxicology, safety and efficacy, and to conduct additional clinical trials for each product candidate. If we are not able to enter into an out-licensing arrangement with respect to any product candidate prior to the commencement of later stage clinical trials, we may fund the trials for the product candidates ourselves.
While we are currently focused on advancing each of our product development projects, our future research and development expenses will depend on the clinical success of each product candidate, as well as ongoing assessments of each product candidate’s commercial potential. In addition, we cannot forecast with any degree of certainty which product candidates may be subject to future out-licensing arrangements, when such out-licensing arrangements will be secured, if at all, and to what degree such arrangements would affect our development plans and capital requirements.
As we obtain results from clinical trials, we may elect to discontinue or delay clinical trials for certain product candidates or projects in order to focus our resources on more promising product candidates or projects. Completion of clinical trials by us or our licensees may take several years or more, but the length of time generally varies according to the type, complexity, novelty and intended use of a product candidate.
The cost of clinical trials may vary significantly over the life of a project as a result of differences arising during clinical development, including, among others:
| · | the number of sites included in the clinical trials; |
| · | the length of time required to enroll suitable patients; |
| · | the number of patients that participate in the clinical trials; |
| 76 |
| · | the duration of patient follow-up; |
| · | the development stage of the product candidate; and |
| · | the efficacy and safety profile of the product candidate. |
We expect our research and development expenses to increase in the future from current levels as we continue the advancement of our clinical trials and preclinical product development and to the extent we in-license new product candidates. The lengthy process of completing clinical trials and seeking regulatory approval for our product candidates requires expenditure of substantial resources. Any failure or delay in completing clinical trials, or in obtaining regulatory approvals, could cause a delay in generating product revenue and cause our research and development expenses to increase and, in turn, have a material adverse effect on our operations. Because of the factors set forth above, we are not able to estimate with any certainty when we would recognize any net cash inflows from our projects.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of compensation for employees in executive and operational functions, including accounting, finance, legal, business development, investor relations, information technology and human resources. Other significant general and administration costs include facilities costs, professional fees for outside accounting and legal services, travel costs, insurance premiums and depreciation.
Financial Expense and Income
Financial expense and income consists of interest earned on our cash and cash equivalents; bank fees and other transactional costs; expense or income resulting from fluctuations of the U.S. dollar and other currencies, in which a portion of our assets and liabilities are denominated, against the NIS (our functional currency); and fluctuations in the market value of our warrants which trade on the TASE.
| 77 |
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our accounting policies and their effect on our financial condition and results of operations are more fully described in our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this registration statement. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards, or IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, or IASB, requires management to make estimates and assumptions that in certain circumstances affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, revenues and expenses and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. These estimates are prepared using our best judgment, after considering past and current events and economic conditions. While management believes the factors evaluated provide a meaningful basis for establishing and applying sound accounting policies, management cannot guarantee that the estimates will always be consistent with actual results. In addition, certain information relied upon by us in preparing such estimates includes internally generated financial and operating information, external market information, when available, and when necessary, information obtained from consultations with third party experts. Actual results could differ from these estimates and could have a material adverse effect on our reported results.
We believe that the accounting policies discussed below are critical to our financial results and to the understanding of our past and future performance, as these policies relate to the more significant areas involving management’s estimates and assumptions. We consider an accounting estimate to be critical if: (1) it requires us to make assumptions because information was not available at the time or it included matters that were highly uncertain at the time we were making our estimate; and (2) changes in the estimate could have a material impact on our financial condition or results of operations.
Functional Currency
The presentation currency of our financial statements and our functional currency is the NIS. When the functional currency of an entity in which we own an equity interest, which is referred to as a subsidiary, differs from our functional currency, that subsidiary represents a foreign operation whose financial statements are translated as follows: (i) assets and liabilities are translated at the closing rate at the date of that balance sheet, (ii) income and expenses are translated at average exchange rates for the presented periods and (iii) share capital and capital reserves are translated at the exchange rate prevailing at the date of incurrence. All resulting translation differences are recognized in a separate component in equity, as other comprehensive loss, “adjustments from translation of financial statements.”
For the convenience of the reader, the reported NIS amounts as of December 31, 2012 have been translated into U.S. dollars at the representative rate of exchange on December 31, 2012 (U.S. $1 = NIS 3.733). The U.S. dollar amounts presented should not be construed as representing amounts that are receivable or payable in U.S. dollars or convertible into U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated. The U.S. dollar amounts were rounded to whole numbers of convenience.
Principles of Consolidation
Our financial statements reflect the consolidation of the financial statements of companies that we control based on legal control or effective control. We fully consolidate into our financial statements the results of operations of companies that we control. Legal control exists when we have the power, directly or indirectly, to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity. The effect of potential voting rights that are exercisable at the balance sheet date are considered when assessing whether we have legal control. In addition, we consolidate on the basis of effective control even if we do not have voting control. The determination that effective control exists involves significant judgment.
In evaluating the effective control on our investees we consider the following criteria to determine if effective control exists:
| · | Whether we hold a significant voting interest (but less than half the voting rights); |
| · | Whether there is a wide diversity of public holdings of the remaining shares conferring voting rights; |
| 78 |
| · | Whether in the past we had the majority of the voting power participating in the general meetings of shareholders and, therefore, have in fact had the right to nominate the majority of the board members; |
| · | The absence of a single entity that holds a significant portion of the investee’s shares; |
| · | Our
ability
to establish
policies
and guide
operations
by appointing
the remainder
of the investee’s
senior management;
and | |
| · | Whether the minority shareholders have participation rights or other preferential rights, excluding traditional shareholder protective rights. |
Entities we control are fully consolidated in our financial statements. All significant intercompany balances and transactions are eliminated in consolidation. Non-controlling interests of subsidiaries represent the non-controlling shareholders’ proportionate interest in the comprehensive income (loss) of the subsidiaries and fair value of the net assets or the net identifiable assets upon the acquisition of the subsidiaries.
Fair Value Measurements
The fair value of assets and liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in financial statements is determined according to the following hierarchy:
| · | Level 1: Prices quoted (un-adjusted) on active markets of similar assets and liabilities. |
| · | Level 2: Data other than quoted prices included in level 1, which may be directly or indirectly observed. |
| · | Level 3: Data not based on observable market information (valuation techniques not involving use of observable market data). Such techniques include using recent arm’s length market transactions; reference to the current market value of another instrument that is substantially the same; a discounted cash flow analysis or other valuation models. |
Changes in the underlying valuation assumptions could result in significant changes in the values of our assets and liabilities and our results of operations.
Treasury Shares
Our shares held by us and/or by our subsidiaries are recognized at cost and deducted from equity. Any gain or loss arising from a purchase, sale, issue or cancellation of treasury shares is recognized directly in equity.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenues in accordance with International Accounting Standard No. 18, or IAS 18. Under IAS 18 we generate income from licensing agreements with pharmaceutical companies. These agreements usually comprise license fees, annual license fees, milestone payments and potential royalty payments.
Revenues are recognized in profit or loss when the revenues can be measured reliably, it is probable that the economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the Company and the costs incurred or to be incurred in respect of the transaction can be reliably measured.
Arrangements with multiple elements:
Revenues from sale agreements that do not contain a general right of return and that are composed of multiple elements such as licenses and services are allocated to the various accounting units and recognized for each accounting unit separately. An element constitutes a separate accounting unit if and only if it has a separate value to the customer. Revenue from the various accounting units is recognized when the criteria for revenue recognition regarding the elements of that accounting unit have been met according to their type and only to the extent of the consideration that is not contingent upon completion or performance of the remaining elements in the contract.
| 79 |
Revenues from license fees:
As for revenues from preliminary license fees and annual license fees, we examine whether the license can be separated from our other performance obligations.
Revenues from milestone payments:
Revenues which are contingent on compliance with and attainment of milestones are recognized in profit or loss at the achievement of a milestone, provided that certain criteria have been met.
Revenues from royalties:
Revenues from royalties are recognized as they accrue in accordance with the terms of the relevant agreement.
Share-based Compensation
We account for share-based compensation arrangements in accordance with the provisions of IFRS 2. IFRS 2 requires companies to recognize share-based compensation expense for awards of equity instruments based on the grant-date fair value of those awards. The cost is recognized as compensation expense over the vesting period, based upon the grant-date fair value of the equity or liability instruments issued. We selected the binomial option pricing model as the most appropriate method for determining the estimated fair value of our share-based awards without market conditions. The determination of the grant date fair value of options using an option pricing model is affected by estimates and assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include the expected volatility of our share price over the expected term of the options, share option exercise and forfeiture rate, risk-free interest rates, expected dividends and the price of our ordinary shares on the TASE. As our ordinary shares are publicly traded on the TASE, we do not need to estimate the fair value of our ordinary shares. Rather, we use the actual closing market price of our ordinary shares on the date of grant, as reported by the TASE.
If any of the assumptions used in the binomial option pricing model change significantly, share-based compensation for future awards may differ materially compared with the awards previously granted.
The cost of equity-settled transactions is recognized in profit or loss, together with a corresponding increase in equity, during the period which the service are to be satisfied, ending on the date on which the relevant employees or other service providers become fully entitled to the award.
If the Company modifies the conditions on which equity-instruments are granted, an additional expense is recognized for any modification that increases the total fair value of the share-based payment arrangement or is otherwise beneficial to the employee or other service provider at the modification date.
Warrants
In connection with our Israeli public offering on November 16, 2011, we issued Series 6 and Series 7 Warrants, which are publicly traded on the TASE and exercisable into our publicly traded ordinary shares. In accordance with IFRS, we allocated a portion of the consideration received for such warrants based on their market value at that time. The consideration allocated to such warrants is generally reflected in non-current liabilities due to the fact that the exercise price of the warrants is linked to the Israeli consumer price index. In the public offering, we issued 4,953,750 Series 6 Warrants exercisable for 198,150 of our ordinary shares. The Series 6 Warrants have an exercise price of 0.63 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index). Although the Series 6 Warrants were originally set to expire on May 16, 2012, on August 18, 2013, the Company filed an urgent application to the Petah-Tikva District Court to approve the convening of a general meeting of the Company's shareholders and a general meeting of the holders of Series 6 Warrants to extend the exercise period of the Series 6 Warrants until September 1, 2014. On August 26, 2013, the District Court in Petah-Tikva, Israel approved the extension of the exercise period until October 30, 2013. In the same offering, we issued 9,907,500 Series 7 Warrants exercisable for 396,300 of our ordinary shares. The Series 7 Warrants have an exercise price of 0.80 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index) and are scheduled to expire on November 16, 2013.
| 80 |
In connection with our Israeli public offering on May 1, 2012, we issued Series 8 and Series 9 Warrants, which are publicly traded on the TASE and exercisable into our publicly traded ordinary shares. In accordance with IFRS, we allocated a portion of the consideration received for such warrants based on their market value at the time. The consideration allocated to warrants is generally reflected in non-current liabilities due to the fact that the exercise price of such warrants is linked to the Israeli consumer price index. We issued 8,112,000 Series 8 Warrants exercisable for 324,480 of our ordinary shares in the offering. Although the Series 8 Warrants had an exercise price of 0.55 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index) and were set to expire on June 30, 2013, on June 11, 2013, the shareholders assembly and the Series 8 Warrants holders assembly approved a settlement according to which the exercise price was changed to 0.75 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index) and the exercise period was extended until December 31, 2013 (the "Settlement"). On June 24, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel approved the Settlement. We also issued 12,168,000 Series 9 Warrants exercisable for 486,720 of our ordinary shares in this offering. In accordance with IFRS, we allocated a portion of the consideration received from the Series 9 Warrants based on their market value at the time. The consideration allocated to the Series 9 Warrants is generally reflected in shareholders’ equity due to the fact that the exercise price of such warrants is fixed. The Series 9 Warrants have a fixed exercise price of 0.85 NIS per ordinary share and are set to expire on May 1, 2015.
In connection with our Israeli public offering on February 5, 2013, we issued Series 10 and Series 11 Warrants, which are publicly traded on the TASE and exercisable into our publicly traded ordinary shares. In accordance with IFRS, we allocated a portion of the consideration received for such warrants based on their market value at the time. The consideration allocated to warrants is generally reflected in non-current liabilities due to the fact that the exercise price of such warrants is linked to the Israeli consumer price index. We issued 39,067,000 Series 10 Warrants exercisable for 1,562,680 of our ordinary shares in the offering. The Series 10 Warrants have an exercise price of 0.394 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index) and are set to expire on October 31, 2015. We also issued 37,385,000 Series 11 Warrants exercisable for 1,495,400 of our ordinary shares in this offering. In accordance with IFRS, we allocated a portion of the consideration received from the Series 11 Warrants based on their market value at the time. The consideration allocated to the Series 11 Warrants is generally reflected in shareholders’ equity due to the fact that the exercise price of such warrants is fixed. The Series 11 Warrants have a fixed exercise price of 0.392 NIS per ordinary share and are set to expire on April 30, 2016. Our Board of Directors has decided that the exercise price of the Series 10 and Series 11 Warrants will no longer be linked to the Israeli consumer price index. On August 1, 2013 and August 4, 2013, the shareholders assembly and the holders of the Series 10 and Series 11 Warrants, respectively, approved a settlement according to which the exercise price of Series 10 and 11 Warrants will no longer be linked to the Israeli consumer price index. On August 20, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel, approved such settlement.
As of August 26, 2013, other than 6,000 Series 8 Warrants exercised on June 23, 2013 to purchase 240 ordinary shares for an aggregate exercise price of NIS 3,358, none of the foregoing warrants have been exercised.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
IAS 19 (Revised) - Employee Benefits
The IASB made several changes to IAS 19, the principal of which are as follows:
| · | The remeasurement of the net defined benefit liability (formerly - actuarial gains and losses) are recognized in other comprehensive income and not in profit or loss. |
| · | The “corridor” approach which allowed the deferral of actuarial gains or losses has been eliminated. |
| · | Income from the plan assets is recognized in profit or loss based on the discount rate used to measure the employee benefit liabilities. The return on plan assets excluding the aforementioned income recognized in profit or loss is included in the remeasurement of the net defined benefit liability. |
| · | The distinction between short-term employee benefits and long-term employee benefits is based on the expected settlement date and not on the date on which the employee first becomes entitled to the benefits. |
| · | Past service cost arising from changes in the plan is recognized immediately. |
| · | The standard is to be applied retrospectively in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013, or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted. |
| · | We estimate that the standard is not expected to have a material impact on our financial statements. |
| 81 |
IAS 32 - Financial Instruments: Presentation and IFRS 7 - Financial Instruments: Disclosure
The IASB issued certain amendments to IAS 32 (“the amendments to IAS 32”) regarding the offsetting of financial assets and liabilities. The amendments to IAS 32 clarify, among others, the meaning of "currently has a legally enforceable right of set-off" (“the right of set-off”).
The IASB also issued amendments to IFRS 7 (“the amendments to IFRS 7”) regarding the offsetting of financial assets and liabilities.
The amendments to IAS 32 are to be applied retrospectively commencing from the financial statements for periods beginning on January 1, 2014, or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted, but disclosure of early adoption is required as well as the disclosures required by the amendments to IFRS 7 as described above. The amendments to IFRS 7 are to be applied retrospectively commencing from the financial statements for periods beginning on January 1, 2013, or thereafter.
We estimate that the amendments to IAS 32 are not expected to have a material impact on our financial statements. The required disclosures pursuant to the amendments to IFRS 7 will be included in the Company's financial statements.
IFRS 9—Financial Instruments
In November 2009, the IASB issued the first part of Phase I of IFRS 9, “Financial Instruments”, as part of a project to replace IAS 39, “Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement”. IFRS 9 focuses mainly on the classification and measurement of financial assets and it applies to all financial assets within the scope of IAS 39. According to IFRS 9, upon initial recognition, all the financial instruments will be measured at fair value. In subsequent periods, all debt instruments and financial assets will be at fair value, except for debt instruments, which can be measured at amortized cost in certain conditions. Financial assets that are equity instruments will be measured in subsequent periods at fair value and the changes will be recognized in profit or loss or in other comprehensive income (loss), in accordance with the election of the accounting policy on an instrument-by-instrument basis. When a liability is measured at fair value, the amount of the fair value adjustment attributed to changes in credit risk will be carried to other comprehensive income. All other fair value adjustments will be carried to the statement of income. Liabilities in respect of certain unquoted equity instrument derivatives can no longer be measured at cost, but rather only at fair value. IFRS 9 will be effective starting January 1, 2015. Earlier adoption is permitted. We estimate that this standard is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
IFRS 10—Consolidated Financial Statements
IFRS 10 supersedes IAS 27 regarding the accounting treatment of consolidated financial statements and includes the accounting treatment for the consolidation of structured entities previously accounted for under SIC 12, “Consolidation—Special Purpose Entities”. IFRS 10 does not prescribe changes to the consolidation procedures but rather modifies the definition of control for the purpose of consolidation and introduces a single consolidation model. According to IFRS 10, in order for an investor to control an investee, the investor must have power over the investee and exposure, or rights, to variable returns from the investee. Power is defined as the ability to influence and direct the investee’s activities that significantly affect the investor’s return. IFRS 10 is to be applied retrospectively in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013, or thereafter. We estimate that this standard is not expected to have a material impact on our financial statements.
IFRS 12—Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities
IFRS 12 prescribes disclosure requirements for our investees, including subsidiaries, joint arrangements, associates and structured entities. IFRS 12 expands the disclosure requirements to include the judgments and assumptions used by management in determining the existence of control, joint control or significant influence over investees, and in determining the type of joint arrangement. IFRS 12 also provides disclosure requirements for material investees. The required disclosures will be included in our financial statements upon initial adoption of IFRS 12.
| 82 |
IFRS 13—Fair Value Measurement
IFRS 13 establishes guidance for the measurement of fair value, to the extent that such measurement is required according to IFRS. IFRS 13 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. IFRS 13 also specifies the characteristics of market participants and determines that fair value is based on the assumptions that would have been used by market participants. According to IFRS 13, fair value measurement is based on the assumption that the transaction will take place in the asset’s or the liability’s principal market, or in the absence of a principal market, in the most advantageous market. IFRS 13 requires an entity to maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. IFRS 13 also includes a fair value hierarchy based on the inputs used to determine fair value. IFRS 13 also prescribes certain specific disclosure requirements. The new disclosures, and the measurement of assets and liabilities pursuant to IFRS 13, are to be applied prospectively for periods commencing after the Standard’s effective date, in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013 or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted. The new disclosures will not be required for comparative data.
Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012
We are an emerging growth company within the meaning of the rules under the Securities Act, and we will utilize certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to public companies that are not emerging growth companies. The JOBS Act permits us, as an “emerging growth company,” to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with certain new or revised accounting standards if such standards apply to companies that are not issuers. We are choosing to “opt out” of this provision and, as a result, we will comply with new or revised accounting standards when they are required to be adopted by issuers. This decision to opt out of the extended transition period under the JOBS Act is irrevocable.
A. Results of Operations
Revenues
We have set forth below a summary of our revenues generated by region for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2011 and 2012.
Year ended December 31, (in thousands NIS) | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Japan | 1,894 | 1,785 | - | |||||||||
| Korea | 750 | - | - | |||||||||
| Total | 2,644 | 1,785 | - | |||||||||
For additional information with respect to our revenues, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements” and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Revenues.”
Cost of revenues
Cost of revenues consists of royalty payments due to the licensors under our in-licensing agreements with the NIH and Leiden University. We did not record any cost of revenues during the year ended December 31, 2012.
Comparison of the Year Ended December 31, 2012 to Year Ended December 31, 2011
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses for the year ended December 31, 2012 were NIS 13.16 million, an increase of NIS 0.19 million, or 1.5%, compared to NIS 12.97 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. The Company believes that the increase in research and development expenses is not material.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses were NIS 9.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 and NIS 7.1 million for year ended December 31, 2011. The increase in 2012 as compared to 2011 was primarily from the activities of OphthaliX. This increase was mainly from professional services (consisting of an increase of NIS 1.2 million), directors’ fees (consisting of NIS 0.8 million in stock-based compensation awarded to an OphthaliX director) and insurance (consisting of the purchase of a directors’ and officers’ insurance policy in 2012 for NIS 0.2 million). We expect that we will continue to experience increases in expenses through 2013 and beyond.
| 83 |
Financial income, net
We recognized net financial income of NIS 0.51 million for year ended December 31, 2012, a decrease of NIS 0.93 million, or 65%, compared to net financial income of NIS 1.44 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. The decrease in net financial income resulted primarily from the net change in fair value of financial liabilities. In both 2012 and 2011 we had a decrease in the market value of the various series of our traded warrants which was recorded as financial income. The decrease in 2011 was greater than it was in 2012 (i.e., NIS 1.5 million in 2011 compared to NIS 0.4 million in 2012) and therefore the net financial income in that year was also greater.
Comparison of the Year Ended December 31, 2011 to the Year Ended December 31, 2010
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses for the year ended December 31, 2011 were NIS 12.97 million, an increase of NIS 2.97 million, or 30%, compared to NIS 10 million for the year ended December 31, 2010. The increase was due to the completion of Phase II/III psoriasis clinical trials and the preparation for a Phase III DES clinical trial.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses were NIS 7.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2011, an increase of NIS 1.1 million, or 18%, compared to NIS 6.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2010. The increase in general and administrative expenses resulted from the growth in professional services (consisting of an increase of NIS 0.6 million in 2012, from NIS 1.5 million to NIS 2.1 million), payroll updates (consisting of an increase of NIS 0.6 million in 2012, from NIS 1.2 million to NIS 1.8 million) and travel.
Merging expenses
We recognized merging expenses of NIS 11.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2011, an increase of NIS 11.5 million, compared to NIS 0.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2010. The merging expenses resulted from the transaction in which OphthaliX become a subsidiary of the Company and Eye-Fite became a wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX. See “Item 10. Additional Information—Material Contracts—OphthaliX Agreements”.
Financial income, net
We recognized net financial income of NIS 1.44 million for the year ended December 31, 2011, an increase of NIS 0.9 million, or 165%, compared to net financial income of NIS 0.54 million for the year ended December 31, 2010. The increase in net financial income resulted primarily from the decrease in the market value of various series of our traded warrants and from changes in exchange rates. In both 2011 and 2010 we had a decrease in the market value of the various series of our traded warrants which was recorded as financial income. The decrease in 2011 was greater than it was in 2010 (i.e., NIS 1.5 million in 2011 compared to NIS 0.7 million in 2010) and therefore the net financial income in that year was also greater. In addition, in 2010, due to a change in the applicable exchange rate, we recorded a NIS 0.2 million decrease in the market value of the various series of our traded warrants as compared to approximately a zero decrease in 2011, which also resulted in an increase in our net financial income in 2011.
B. Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since inception, we have funded our operations primarily through public (in Israel) and private offerings of our equity securities and payments received under our strategic licensing arrangements. On February 5, 2013, we completed a public offering in which we issued ordinary shares, Series 10 and Series 11 Warrants and raised an aggregate of NIS 26,498,488. Since inception, we have raised approximately NIS 240 million in net proceeds from sales of our equity securities, including NIS 41.8 million, after deduction of offering expenses, from our initial public offering, or IPO, of our ordinary shares and warrants on the TASE in September 29, 2005, after deduction of offering expenses. In total, we have raised approximately NIS 92 million, after deduction of offering expenses, as a private company until the consummation of the IPO and approximately NIS 148 million, after deduction of offering expenses, as a public company since the completion of the IPO. At December 31, 2012, we held approximately NIS 4,278,000 in cash and cash equivalents, and have invested substantially all of our available cash funds in short-term bank deposits. We may be able to use U.S. taxes withheld as credits against Israeli corporate income tax when we have income, if at all, but there can be no assurance that we will be able to realize the credits. In addition, we believe that we may be entitled to a refund of such withholding tax from the U.S. government but there can be no assurance that we will be entitled to such a refund. For information regarding the revenues and expenses associated with our licensing agreements, see “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements”, “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—In-Licensing Agreements” and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Revenues.”
| 84 |
Net cash used in operating activities was NIS 16.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared with net cash used in operating activities of NIS 20.9 million and NIS 12.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively. The NIS 4.7 million decrease in the net cash used in operating activities during 2012, compared to 2011, was primarily the result of a decrease in accounts receivable, which had increased the year before. The NIS 8.0 million increase in net cash used in operating activities during 2011, compared to 2010, was primarily the result of an increase in accounts receivable and a decrease in the fair value of options exercisable into ordinary shares.
Net cash provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2012 was NIS 0.07 million, compared to net cash provided by investing activities of NIS 0.08 million for the year ended December 31, 2011 and net cash provided by investing activities of NIS 0.1 for the year ended December 31, 2010. The changes in cash flows from investing activities relate to sales of fixed assets.
Net cash provided by financing activities was NIS 5.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to net cash provided by financing activities of NIS 17.67 million for the year ended December 31, 2011 and net cash provided by financing activities of NIS 12 million for the year ended December 31, 2010. The changes in cash flows from financing activities relate to the capital raised by OphthaliX of NIS 11.5 million during 2011.
Developing drugs, conducting clinical trials and commercializing products is expensive and we will need to raise substantial additional funds to achieve our strategic objectives. Although we believe our existing cash resources will be sufficient to fund our projected cash requirements through December 31, 2013, we will require significant additional financing after 2013 to fund our operations. Additional financing may not be available on acceptable terms, if at all. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| · | the progress and costs of our preclinical studies, clinical trials and other research and development activities; |
| · | the scope, prioritization and number of our clinical trials and other research and development programs; |
| · | the amount of revenues we receive under our licensing arrangements; |
| · | the costs of the development and expansion of our operational infrastructure; |
| · | the costs and timing of obtaining regulatory approval of our platform and products; |
| · | the ability of us or our collaborators to achieve development milestones, marketing approval and other events or developments under our licensing agreements; |
| · | the costs of filing, prosecuting, enforcing and defending patent claims and other intellectual property rights; |
| · | the costs and timing of securing manufacturing arrangements for clinical or commercial production; |
| · | the costs of contracting with third parties to provide sales and marketing capabilities for us; |
| · | the costs of acquiring or undertaking development and commercialization efforts for any future products or platforms; |
| · | the magnitude of our general and administrative expenses; |
| · | any cost that we may incur under current and future licensing arrangements relating to our platform and products; and |
| · | payments to the OCS. |
| 85 |
Until we can generate significant continuing revenues, we expect to satisfy our future cash needs through payments received under our license agreements, debt or equity financings, or by out-licensing other product candidates. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If funds are not available, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of, or eliminate one or more of our research or development programs or our commercialization efforts.
C. Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, Etc.
For information concerning our research and development policies and a description of the amount spent during each of the last three fiscal years on company-sponsored research and development activities, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Operating Results.”
D. Trend Information.
We are a development stage company and it is not possible for us to predict with any degree of accuracy the outcome of our research, development or commercialization efforts. As such, it is not possible for us to predict with any degree of accuracy any significant trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events that are reasonably likely to have a material effect on our net sales or revenues, income from continuing operations, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or that would cause financial information to not necessarily be indicative of future operating results or financial condition. However, to the extent possible, certain trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments and events are identified in the preceding subsections of this Item 5.
E. Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements.
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements that have had or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources that are material to investors.
F. Contractual Obligations.
The following table summarizes our significant contractual obligations in NIS at December 31, 2012:
| Total | Less than 1 year | 1 – 3 years | More than 3 years | |||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | ||||||||||||||||
| NIH milestones(1) | 1,586,525 | 559,950 | 1,026,575 | - | ||||||||||||
| Leiden University milestones(2) | 393,649 | 49,207 | 344,442 | - | ||||||||||||
| Car lease obligations | 224,355 | 131,191 | 93,164 | - | ||||||||||||
| Severance pay | 68,000 | - | - | 68,000 | ||||||||||||
| Total | 2,272,529 | 740,348 | 1,464,181 | 68,000 | ||||||||||||
__________________________
(1)Includes a $50,000 annual royalty and $375,000 in milestone payments, assuming the initiation of new clinical trials. Does not include a potential milestone payment of $500,000 upon approval by the FDA or any regulatory authority as the NIH Agreement will terminate in 2015 upon the expiration of the last patent licensed thereunder, which will be prior to achieving such milestone.
(2) Includes a €10,000 annual royalty and €50,000 upon the initiation of a Phase I study. The Company will update its milestone payment obligations upon releasing the Phase I data from such study. As such, the obligations above do not include a potential milestone payment of €100,000 upon the initiation of a Phase II study, €200,000 upon the initiation of a Phase III study or €500,000 upon marketing approval by any regulatory authority.
ITEM 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees
A. Directors and Senior Management.
The following table sets forth the members of our senior management and Board of Directors (1):
| Member | Position | Age | ||
| Ilan Cohn, Ph.D. | Chairman of the Board | 58 | ||
| Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. | Chief Executive Officer, Director | 64 | ||
| Motti Farbstein | Chief Operating and Financial Officer | 49 | ||
| Barak Singer | Vice President, Business Development | 41 | ||
| Guy Regev | Director | 44 | ||
| Liora Lev | Director, Audit Committee and Compensation Committee member | 59 | ||
| Avraham Sartani, M.D. | Director | 66 | ||
| Yechezkel Barenholz, Ph.D. | Director, Audit Committee and Compensation Committee member | 71 | ||
| Gil Oren | Director, Audit Committee and Compensation Committee member | 60 |
_______________
(1) Avigdor Kaplan, our former Chairman of the Board, was not re-elected to the Board of Directors at the annual shareholders meeting held on May 2, 2013. On May 30, 2013, Ilan Cohn was appointed as the new Chairman of the Board.
| 86 |
Ilan Cohn, Ph.D. Ilan Cohn, Ph.D. is a patent attorney and senior partner at the patent attorney firm Reinhold Cohn and Partners, where he has been an attorney since 1986. Dr. Cohn co-founded Can-Fite, served as its Chief Executive Officer until September 2004 and is currently the Chairman of the Can-Fite Board of Directors. Dr. Cohn has also been a director of OphthaliX since November 21, 2011. Dr. Cohn holds a Ph.D. in biology and is a patent attorney with many years of experience in the biopharmaceutical field. He has served on the board of directors of a number of life science companies, including Ansan Pharmaceuticals, a U.S. public company. Dr. Cohn has also been involved in the past in management of venture capital funds focused on investments in the life sciences industry. Dr. Cohn served a number of years as a co-chairman of the Biotech Committee of the US-Israeli Science and Technology Commission. Dr. Cohen is also currently a member of the board of directors of I.C.R.C Management Ltd, Famillion BVI Ltd. and Famillion Ltd. (a subsidiary of Famillion BVI Ltd.).
Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. co-founded Can-Fite, has served as Chief Executive Officer of Can-Fite since September 2005 and is a Can-Fite board member. She has also served as the Chief Executive Officer of OphthaliX from November 21, 2011 through December 31, 2012. Dr. Fishman is the scientific founder of Can-Fite and was previously a professor of Life Sciences and headed the Laboratory of Clinical and Tumor Immunology at the Felsenstein Medical Research Institute, Rabin Medical Center, Israel. Dr. Fishman has authored or co-authored over 150 publications and presented the findings of her research at many major scientific meetings. Her past managerial experience included seven years as Chief Executive Officer of Mor Research Application, the technology transfer arm of Clalit Health Services, the largest healthcare provider in Israel. Mor Research Application was also the first clinical research organization in Israel. Dr. Fishman currently also serves as a member of the board of directors of F.D Consulting Ltd., Ultratrend Ltd., EyeFite Ltd. and OphthaliX Inc.
Motti Farbstein. Motti Farbstein has been with Can-Fite since 2003 and currently serves as Chief Operating and Financial Officer. Mr. Farbstein’s past managerial experience includes seven years as Vice President of Mor Research Application, a company that managed the commercialization of the intellectual property of all hospitals and research centers affiliated with Clalit Health Services, which is the largest healthcare provider in Israel and was Israel’s first clinical CRO. Mr. Farbstein also has extensive experience in the data management of clinical trials.
Barak Singer. Barak Singer has more than ten years of experience in investment banking, venture capital and business development. Mr. Singer has been Vice President of Business Development at Can-Fite since 2011. Prior to joining Can-Fite, Mr. Singer was Vice President of Business Development at Xenia Venture Capital, or Xenia. Before joining Xenia and from 2001 to 2009, Mr. Singer was Managing Director and Co-Head of Investment Banking at Tamir Fishman & Co, the Israeli strategic affiliate of RBC Capital Markets. Mr. Singer focused on capital raising and mergers and acquisitions, and led Tamir Fishman investment banking activities in the life science field. Before joining Tamir Fishman, Mr. Singer was a paralegal at S. Horowitz & Co, a leading Israeli commercial law firm. Since February 28, 2013, Mr. Singer has also served as the Chief Executive Officer of OphthaliX.
| 87 |
Guy Regev. Guy Regev is currently the Chief Executive Officer of Shaked Global Group, a privately-held equity investment firm that provides value added capital to environmental-related companies and technologies, or Shaked. Mr. Regev joined Shaked at the beginning of 2008. Shaked is a major shareholder in Can-Fite and Mr. Regev is a director of Can-Fite. Mr. Regev has also been a director of OphthaliX since November 21, 2011. Prior to joining Shaked, from 2001 to 2008, Mr. Regev was Vice President of Commercial Business at Housing & Construction Holding, or HCH, Israel’s largest infrastructure company. His duties included being responsible for the consolidation and financial recovery of various business units within HCH. Prior to that, Mr. Regev carried several roles within the group including as a Chief Financial Officer and later the Chief Executive Officer of Blue-Green Ltd., the environmental services subsidiary of HCH. Between 1999 and 2001, Mr. Regev was a manager at Deloitte & Touche, Israel. Mr. Regev holds an LLB degree in Law (Israel) and is a licensed lawyer and has been a licensed CPA since 1999. Mr. Regev has over 12 years of experience in accounting, financial management and control and general management of commercial enterprises. Mr. Regev is also a director of Knollan Ltd, The Green Way Ltd, Shtang Construction and Engineering Ltd, TGW Holdings Ltd, Aeronautics Ltd, Blue I Water Technologies Ltd. and R.I.B.E. Consulting & Investment Ltd., Can-Fite, Shaked and Aqua Investments Ltd.
Liora Lev. Liora Lev is a co-founder and general partner of Ascend Technology Ventures, or Ascend, an investor in Can-Fite. She is an accomplished certified public accountant with over 20 years of experience in business management, information systems management and finance of public and private companies. From 2006 to 2009 she served as the Chief Executive Officer and as a board member at Advanced Technology Acquisition Corp. (AMEX: ATAC). Prior to founding Ascend, and from 1994 to 2000, Mrs. Lev served as the Commissioner at the Israeli Securities Authority. From 1992 to 1998, she worked at Ashtrom, a leading Israeli holding group, in several executive positions, including as Chief Financial Officer beginning in 1995. Mrs. Lev currently serves on the board of directors of IntellinX Ltd and several private companies.
Avraham Sartani, M.D. Avraham Sartani has over 30 years of experience in the pharmaceuticals industry. Dr. Sartani is a member of a number of scientific and management societies and the author or co-author of numerous publications and patents in the urology, pain treatment and hypertension fields. Dr. Sartani also currently serves on the board of directors of Akkadeas Pharma Srl. From 1985 until 2008, Dr. Sartani was the Vice-President of Pharmaceutical Research and Development, Licensing Division, of Recordati, a European specialty pharmaceutical company. Prior to joining Recordati, from 1980 until 1985, Dr. Sartani was employed at Farmitalia-Carlo Erba, serving in a number of capacities, including as the Medical Director for Europe.
Yechezkel (Chezi) Barenholz, Ph.D. Since 1978, Professor Emeritus Barenholz, the Daniel G. Miller Professor in Cancer Research, has been the head of the Liposome and Membrane Research Lab on the faculty of Hebrew University in Jerusalem, Israel, where has also been a professor since 1981. From 1973 to 2005, Professor Barenholz was a visiting professor in the Department of Biochemistry at the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville, Virginia. Professor Barenholz was also a visiting professor at the following universities: the University of Utrecht in the Netherlands (1992); the University of Kyoto in Japan (1998); La Sapeinza University in Rome, Italy (2006); Jaiotung University in Shanghai, China (2006); Kings College, University of London in the UK (2006); and the Danish Technical University in Copenhagen, Denmark (2010). His current research focuses on the development of drugs based on drug delivery systems. In particular, Professor Barenholz assisted in the development of DOXILTM, the first FDA approved and globally-used anticancer nano-drug and liposomal. Professor Barenholz is also an author of more than 360 scientific publications, with an aggregate of more than 10,000 citations, and is a co-inventor of more than 30 approved patent families. He was an executive editor of Progress in Lipid Research, an editor of four special issues of the same publication and is on the editorial board of six other scientific journals. Professor Barenholz is a co-founder of NasVax LTD, Mobeius Medical LTD and Lipocure LTD, all of which are in the advanced stages of clinical development of liposomal drugs based on his inventions and knowhow. Professor Barenholz was awarded: the Donder’s Chair and the Kaye award (both in 1995 and 1997); the Alec D. Bangham award (1998); the Teva Founders Prize (2001); an honorary doctorate degree from the Technical University of Denmark (2012); and the international Controlled Release Society’s Founders Award (2012). In 2003, Professor Barenholz founded the Barenholz Prize to encourage excellence and innovation among Ph.D. students in Israel in the field of applied sciences. Professor Barenholz currently serves on the board of directors of Lipocure LTD and Moebius Medical LTD.
| 88 |
Gil Oren. Gil Oren is the founder of a private consulting firm he started in 2008. Mr. Oren has over 25 years of experience in top managerial positions in various public companies in Israel and the United States and currently serves on the board of directors of Pointer Telocation Ltd. From 1976 to 1992, Mr. Oren served in various positions within the Tadiran Group, including serving for five years as the Chief Financial Officer of Tadiran Electronic’s U.S. subsidiary. After serving in such capacity, Mr. Oren returned to Israel and joined Cargal, first as Vice President of Finance and then as Chief Executive Officer and General Manager. From 2002 to 2007, Mr. Oren joined SFK, a leading Israeli investment group, and served in various capacities in its portfolio companies, including as the deputy chief executive office of Urdan Industries, the chief executive officer of Itong Industries and the chairman of the board of directors of Orlite Industries. Mr. Oren has also served, on behalf of SFK, on the board of directors of various other public and private companies, including Nirlat, Aloni and Scope. Mr. Oren currently serves as a member of the board of directors of Pointer Telocation Ltd.
B. Compensation.
The following table sets forth the annual compensation (excluding option grants) of members of our senior management and Board of Directors for the year ended December 31, 2012.
| Annual Compensation (excluding option grants) | ||||||
| Name | Salary and related benefits | Bonus | ||||
| NIS | ||||||
| Ilan Cohn | - | - | ||||
| Pnina Fishman | 1,050,000 as management fees and 62,000 as reimbursement of expenses | - | ||||
| Motti Farbstein | 714,000 as salary | - | ||||
| Barak Singer | 506,000 as salary | - | ||||
| Avigdor Kaplan (1) | 180,000 as director fees (which includes consulting fees) | - | ||||
| Yechezkel Barenholz | 73,000 as director fees | - | ||||
| Gil Oren | 90,000 as director fees | - | ||||
| Liora Lev | - | - | ||||
| Guy Regev | - | - | ||||
| Avraham Sartani | 43,000 as director fees (which includes consulting fees and reimbursement of travel expenses) | - | ||||
_______________
(1) Avigdor Kaplan, our former Chairman of the Board, was not re-elected to the Board of Directors at the annual shareholders meeting held on May 2, 2013. On May 30, 2013, Ilan Cohn was appointed as the new Chairman of the Board.
The following table sets forth information with respect to the options granted to the members of our senior management and Board of Directors for the year ended December 31, 2012.
| Name | Date
of Grant | Purchase
Price | Number of Options | Vesting
Period | Expiration Date | Total
Benefit (in NIS) | Benefit
recognized in 2012 (in NIS) | |||||||||||||||
| Motti Farbstein | 5/3/2012 | 0.385 | 100,000 | (1) | 1/16 per quarter | 5/2/2022 | 21,500 | 4,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Barak Singer | 5/3/2012 | 0.385 | 100,000 | (1) | 1/16 per quarter | 5/2/2022 | 21,500 | 11,000 | (2) | |||||||||||||
(1) Exercisable for 4,000 of our ordinary shares
(2) Includes NIS 7,000 of benefit recognized in 2012 from the vesting of options granted in 2011.
We set aside or accrued approximately NIS 69,000, in the aggregate, for pension or other retirement benefits for the named executive officers in 2012.
| 89 |
Employment and Consulting Agreements
We have or have had written employment and non-competition agreements with each of Barak Singer, our Vice President of Business Development, Motti Farbstein, our Chief Operating and Financial Officer, Sari Furman, our Director of Clinical Operations and written consulting agreements with each of Reinhold Cohn and Partners, an Israeli partnership, through which Ilan Cohn, Ph.D., our Chairman of the Board of Directors, is a partner, Avraham Sartani, one of our directors, Avigdor Kaplan, our former Chairman of the Board of Directors, and BioStrategies Consulting Ltd., a U.S. company, or BioStrategies, through its President Michael Silverman, our Medical Director. We have also entered into a service management agreement with F.D. Consulting International and Marketing Ltd., an Israeli limited company, or F.D. Consulting, which is partially owned by Pnina Fishman, Ph.D., our Chief Executive Officer and director, and master services agreement with Accellient Partners LLC, a Massachusetts limited liability company, or Accellient Partners, through its Chief Executive Officer William Kerns, our Vice President of Drug Development. As of August 26, 2013, the foregoing agreements were still in full force and effect, with the exception of the consulting agreement with Reinhold Cohn and Partners, which expired by its terms in September 2011 and was not subsequently extended, the consulting agreement with Avraham Sartani, which we terminated in July 2011, and the consulting agreement with Avigdor Kaplan, which was terminated in May 2013.
All of these agreements contain customary provisions regarding noncompetition, confidentiality of information and assignment of proprietary information and inventions. However, the enforceability of the noncompetition provisions may be limited under applicable law. The compensation payable under the foregoing agreements consists of share-based awards and/or an hourly rate for services rendered, reimbursement of certain expenses, and in the case of the employment and non-competition agreements, contributions to study funds.
The following are summary descriptions of each of the foregoing agreements to which we are a party. The descriptions provided below do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the complete agreements, which are attached as exhibits to this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
Employment and Non-Competition Agreement with Motti Farbstein: Motti Farbstein began serving as our Director of Clinical Operations and Administrative Affairs on September 1, 2003 and is currently serving as our Chief Operating and Financial Officer. Mr. Farbstein’s current gross monthly salary is NIS 43,000. In accordance with his employment and non-competition agreement, Mr. Farbstein is entitled to an allocation to a manager’s insurance policy equivalent to an amount up to 13-1/3% of his gross monthly salary, up to 2-1/2% of his gross monthly salary for disability insurance and 7-1/2% of his gross monthly salary for a study fund. The foregoing amounts are paid by the Company. Five percent of his gross monthly salary is deducted for the manager’s insurance policy and 2-1/2% is deducted for the study fund. Mr. Farbstein is also entitled to reimbursement for reasonable out-of-pocket expenses, including travel expenses, and use of a company automobile and mobile phone.
In addition, pursuant to his employment and non-competition agreement, and in accordance with our 2003 Share Option Plan, Mr. Farbstein is also entitled to receive options exercisable into our ordinary shares from time to time. As of August 26, 2013, we have granted him options to purchase 44,196 ordinary shares.
The term of Mr. Farbstein’s employment and non-competition agreement is indefinite, unless earlier terminated (i) for just cause by either party, (ii) upon the death, disability or retirement age (as such term is defined in the Israeli Equal Retirement Age for the Employee Act – 1987, as amended from time to time), or (iii) without cause by either party, subject to 60 days’ advanced notice.
Employment and Non-Competition Agreement with Barak Singer: Barak Singer began serving as our Vice President of Business Development on March 20, 2011. Mr. Singer’s current gross monthly salary is NIS 45,000 (50% of this amount is consideration for services provided to the Company and 50% is for services provided to OphthaliX). In accordance with his employment and non-competition agreement, Mr. Singer is entitled to an allocation to a manager’s insurance policy equivalent to an amount up to 13-1/3% of his gross monthly salary, up to 2-1/2% of his gross monthly salary for disability insurance and 7-1/2% of his gross monthly salary for a study fund. The foregoing amounts are paid by the Company. Five percent of his gross monthly salary is deducted for the manager’s insurance policy and 2-1/2% is deducted for the study fund. Mr. Singer is also entitled to reimbursement for reasonable out-of-pocket expenses and use of a company automobile and mobile phone.
In addition, pursuant to his employment and non-competition agreement, and in accordance with our 2003 Share Option Plan, Mr. Singer is also entitled to receive options exercisable into our ordinary shares from time to time. As of August 26, 2013, we have granted him options to purchase 17,200 ordinary shares.
| 90 |
The term of Mr. Singer’s employment and non-competition agreement is indefinite, unless earlier terminated (i) for just cause by either party, (ii) upon the death, disability or retirement age, or (iii) without cause by either party, subject to 60 days’ advanced notice.
Consulting Agreement with BioStrategies: Michael Silverman began serving as our Medical Director on September 27, 2005 pursuant to a consulting agreement with BioStrategies, a company for which Mr. Silverman serves as President. Dr. Silverman has extensive experience in clinical development acquired through his involvement in clinical development in large pharmaceutical and small biopharmaceutical companies. He was involved in international clinical research, market-oriented strategic planning, and the challenges of managing research and development portfolios in various capacities at Sterling Winthrop Research Institute and subsequently at Sandoz Research Institute.
BioStrategies’ current fee is $325 per hour with a maximum daily fee of $2,600. In addition, BioStrategies is entitled to reimbursement for reasonable pre-approved expenses. The term of the consulting agreement is currently on a year-to-year basis, unless earlier terminated: (i) by either party upon 30 days’ prior written notice or (ii) immediately by either party if such termination is for cause.
Service Management Agreement with F.D. Consulting: Pnina Fishman began serving as our Chief Scientific Officer on June 27, 2002 pursuant to a service management agreement with F.D. Consulting, a company wholly-owned by Dr. Fishman. Ms. Fishman is currently our Chief Executive Officer and is a member of our Board of Directors and continues to be employed through this service management agreement. F.D. Consulting’s current gross monthly salary is NIS 75,000, which is linked to the Israeli CPI and fluctuates accordingly. Dr. Fishman, through F.D. Consulting, is also entitled to reimbursement for reasonable out-of-pocket expenses and use of a company automobile and mobile phone.
In addition, pursuant to the service management agreement, and in accordance with our 2003 Share Option Plan, Dr. Fishman is also entitled to receive options exercisable into our ordinary shares from time to time. As of August 26, 2013, we have granted her options to purchase 302,830 ordinary shares.
The term of F.D. Consulting’s service management agreement is indefinite, unless earlier terminated (i) for cause by the Company or (ii) without cause by either party, subject to three months’ advanced notice.
Master Services Agreement with Accellient Partners: Accellient Partners became the Company’s consultant on May 10, 2010. William Kerns, our current Vice President of Drug Development, serves as the current Chief Executive Officer of Accellient Partners. Dr. Kerns has over 20 years of experience in Pharmaceutical Research and Development at SmithKline Beecham and Eisai Pharmaceuticals. As a Senior Executive he has participated in the development of drugs for over 100 Phase I studies and 13 NDAs and/or Marketing Authorization Applications. Dr. Kerns has chaired a FDA committee on biomarkers and he is an expert in preclinical development and regulatory strategy.
According to the master services agreement, consulting services are provided by Accellient Partners’ personnel in accordance with individual work orders that are executed from time to time. Each individual work order defines the scope of work to be provided and sets forth the fees to be paid to Accellient Partners.
As of May 10, 2012, the term of the master services agreement is on a month-to-month basis, unless terminated: (i) by the Company upon 30 days’ prior written notice; (ii) by the Company at any time if Accellient Partners commit a breach and fails to cure; or (iii) by Accellient Partners upon 30 days’ prior written notice if the Company commits a breach and fails to cure.
| 91 |
C. Board Practices
General
According to the Israeli Companies Law, the management of our business is vested in our Board of Directors. Our Board of Directors may exercise all powers and may take all actions that are not specifically granted to our shareholders. Our executive officers are responsible for our day-to-day management and have individual responsibilities established by our Board of Directors. Executive officers are appointed by and serve at the discretion of our Board of Directors, subject to any applicable employment agreements we have entered into with the executive officers. See “Item 6—Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Compensation—Employment and Consulting Agreements.”
Election of Directors and Terms of Office
Our Board of Directors currently consists of seven members. Other than our two external directors, our directors are elected by an ordinary resolution at the annual general meeting of our shareholders. The nomination of our directors is proposed by the Board of Directors. Our board has the authority to add additional directors up to the maximum number of 12 directors allowed under our Articles. Such directors appointed by the board serve until the next annual general meeting of the shareholders. Unless they resign before the end of their term or are removed in accordance with our Articles of Association, all of our directors, other than our external directors, will serve as directors until our next annual general meeting of shareholders. On May 2, 2013, at an annual general meeting of our shareholders, Pnina Fishman, Ilan Cohn, Liora Lev, Avi Sartani and Guy Regev were re-elected to serve as directors of our company. Yechezkel Barenholtz was re-elected to serve as an external director of our Company at the December 19, 2011 extraordinary general meeting. Gil Oren was re-elected to serve as an external director of our company at the July 3, 2011 extraordinary general meeting. Yechezkel Barenholtz and Gil Oren are serving as external directors pursuant to the provisions of the Israeli Companies Law, for a three-year term ending in December 25, 2014 and July 9, 2014, respectively. After these dates, Gil Oren’s term as external director may be renewed for one additional three-year term. Yechezkel Barenholtz may not be re-elected to serve as an external director as he was elected for three terms, the maximum term according to the provisions of the Israeli Companies Law. On May 30, 2013, Ilan Cohn was appointed as Chairman of the Board.
None of our directors or officers has any family relationship with any other director or officer. None of our directors have service contracts that provide for benefits upon termination of his or her directorship with the Company, other than the payment of salary due, accrued and unpaid as of and through the date of termination. See “Item 6—Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Compensation—Employment and Consulting Agreements.”
Chairman of the Board. Under the Israeli Companies Law, without shareholder approval, a person cannot hold the role of both chairman of the board of directors and chief executive officer of a company. Furthermore, a person who is directly or indirectly subordinate to a chief executive officer of a company may not serve as the chairman of the board of directors of that company and the chairman of the board of directors may not otherwise serve in any other capacity in a company or in a subsidiary of that company other than as the chairman of the board of directors of such a subsidiary.
The Israeli Companies Law provides that an Israeli company may, under certain circumstances, exculpate an office holder from liability with respect to a breach of his duty of care toward the company if appropriate provisions allowing such exculpation are included in its articles of association. Our Articles of Association permit us to maintain directors’ and officers’ liability insurance and to indemnify our directors and officers for actions performed on behalf of us, subject to specified limitations. We maintain a directors and officers insurance policy which covers the liability of our directors and officers as allowed under the Israeli Companies Law.
The term office holder is defined in the Israeli Companies Law as a director, general manager, chief business manager, deputy general manager, vice general manager, executive vice president, vice president, any other manager directly subordinate to the general manager or any other person assuming the responsibilities of any of the foregoing positions, without regard to such person’s title. Each person listed above in “Item 6—Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Directors and Senior Management” is an office holder, as defined in the Israeli Companies Law.
| 92 |
External and Independent Directors
Under the Israeli Companies Law, the boards of directors of companies whose shares are publicly traded, either within or outside of Israel, are required to include at least two members who qualify as external directors.
External directors must be elected by a majority vote of the shares present and voting at a shareholders meeting, provided that either:
| · | the majority of the shares that are voted at the meeting, including at least a majority of the shares held by non-controlling shareholders who do not have a personal interest in the election of the external director (other than a personal interest not deriving from a relationship with a controlling shareholder) who voted at the meeting, excluding abstentions, vote in favor of the election of the external director; or |
| · | the total number of shares held by non-controlling, disinterested shareholders (as described in the preceding bullet point) that are voted against the election of the external director does not exceed 2% of the aggregate voting rights in the company. |
A person may not serve as an external director of a company if (i) such person is a relative of a controlling shareholder of a company or (ii) at the date of such person’s appointment or within the prior two years, such person, such person’s relative, partner, employer or any entity under such person’s control or anyone to whom such person is subordinate, whether directly or indirectly, has or had any affiliation with (a) the company, (b) the company’s controlling shareholder at the time of such person’s appointment or (c) any entity that is either controlled by the company or under common control with the company at the time of such appointment or during the prior two years. If a company does not have a controlling shareholder or a shareholder who holds company shares entitling him to vote at least 25% of the votes in a shareholders meeting, then a person may not serve as an external director if, such person or such person’s relative, partner, employer or any entity under such person’s control, has or had, on or within the two years preceding the date of the person’s appointment to serve as an external director, any affiliation with the chairman of the company’s board of directors, chief executive officer, a substantial shareholder who holds at least 5% of the issued and outstanding shares of the company or voting rights which entitle him to vote at least 5% of the votes in a shareholders meeting, or the chief financial officer of the company.
The term affiliation includes:
| · | an employment relationship; |
| · | a business or professional relationship even if not maintained on a regular basis (excluding insignificant relationships); |
| · | control; and |
| · | service as an office holder, excluding service as a director in a private company prior to the first offering of its shares to the public if such director was appointed as a director of the private company in order to serve as an external director following the public offering. |
The term relative is defined as a spouse, sibling, parent, grandparent or descendant; a spouse’s sibling, parent or descendant; and the spouse of each of the foregoing persons.
| 93 |
In addition, no person may serve as an external director if that person’s professional activities create, or may create, a conflict of interest with that person’s responsibilities as a director or otherwise interfere with that person’s ability to serve as an external director or if the person is an employee of the ISA or of an Israeli stock exchange. Furthermore, a person may not continue to serve as an external director if he or she received direct or indirect compensation from the company for his or her role as a director. This prohibition does not apply to compensation paid or given in accordance with regulations promulgated under the Israeli Companies Law or amounts paid pursuant to indemnification and/or exculpation contracts or commitments and insurance coverage. If, at the time an external director is appointed, all current members of the board of directors not otherwise affiliated with the company are of the same gender, then that external director must be of the other gender. In addition, a director of a company may not be elected as an external director of another company if, at that time, a director of the other company is acting as an external director of the first company.
Following the termination of an external director’s service on a board of directors, such former external director and his or her spouse and children may not be provided with a direct or indirect benefit by the company, its controlling shareholder or any entity under its controlling shareholder’s control. This includes engagement to serve as an executive officer or director of the company or a company controlled by its controlling shareholder, or employment by, or providing services to, any such company for consideration, either directly or indirectly, including through a corporation controlled by the former external director, for a period of two years (and for a period of one year with respect to relatives of the former external director).
The Israeli Companies Law provides that an external director must meet certain professional qualifications or have financial and accounting expertise and that at least one external director must have financial and accounting expertise. However, if at least one of our other directors (i) meets the independence requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, (ii) meets the standards of the NYSE MKT rules for membership on the audit committee and (iii) has financial and accounting expertise as defined in the Israeli Companies Law and applicable regulations, then neither of our external directors is required to possess financial and accounting expertise as long as both possess other requisite professional qualifications. Our Board of Directors is required to determine whether a director possesses financial and accounting expertise by examining whether, due to the director’s education, experience and qualifications, the director is highly proficient and knowledgeable with regard to business-accounting issues and financial statements, to the extent that the director is able to engage in a discussion concerning the presentation of financial information in the company’s financial statements, among others. The regulations define a director with the requisite professional qualifications as a director who satisfies one of the following requirements: (i) the director holds an academic degree in either economics, business administration, accounting, law or public administration; (ii) the director either holds an academic degree in any other field or has completed another form of higher education in the company’s primary field of business or in an area which is relevant to the office of an external director; or (iii) the director has at least five years of experience serving in any one of the following, or at least five years of cumulative experience serving in two or more of the following capacities: (a) a senior business management position in a corporation with a substantial scope of business; (b) a senior position in the company’s primary field of business; or (c) a senior position in public administration.
The Israeli Companies Law defines an independent director as a director who complies with the following and was appointed as such in accordance with Chapter 1 of Part 56 of the Israeli Companies Law: (1) the director complies with the qualification to serve as an external director as set out in Sections 240 (b)-(f) of the Israeli Companies Law and the Audit Committee has approved such compliance; and (2) the director has not served as a director of the company for more than nine consecutive years (which, for such purpose, does not include breaks in such service for periods of less than two year).
Yechezkel Barenholtz and Gil Oren serve as external directors on our Board of Directors pursuant to the provisions of the Israeli Companies Law. They both serve on our Audit Committee and our Compensation Committee. Our Board of Directors has determined that Gil Oren possesses accounting and financial expertise, and that both of our external directors possess the requisite professional qualifications.
Audit Committee
The Israeli Companies Law requires public companies to appoint an audit committee. The responsibilities of the audit committee include identifying irregularities in the management of the company’s business and approving related party transactions as required by law. An audit committee must consist of at least three directors, including all of its external directors and a majority of independent directors. The chairman of the board of directors, any director employed by or otherwise providing services to the company, and a controlling shareholder or any relative of a controlling shareholder, may not be a member of the audit committee. An audit committee may not approve an action or a transaction with a controlling shareholder, or with an office holder, unless at the time of approval two external directors are serving as members of the audit committee and at least one of the external directors was present at the meeting in which an approval was granted.
| 94 |
Our Audit Committee is currently comprised of three independent non-executive directors. The audit committee is chaired by Gil Oren, who serves as the audit committee financial expert, with Yechezkel Barenholtz and Liora Lev as members. Our Audit Committee meets at least four times a year and monitors the adequacy of our internal controls, accounting policies and financial reporting. It regularly reviews the results of the ongoing risk self-assessment process, which we undertake, and our interim and annual reports prior to their submission for approval by the full Board of Directors. The Audit Committee oversees the activities of the internal auditor, sets its annual tasks and goals and reviews its reports. The Audit Committee reviews the objectivity and independence of the external auditors and also considers the scope of their work and fees.
We have adopted a written charter for our Audit Committee, setting forth its responsibilities as outlined by the regulations of the SEC. In addition, our Audit Committee has adopted procedures for the receipt, retention and treatment of complaints we may receive regarding accounting, internal accounting controls or auditing matters and the submission by our employees of concerns regarding questionable accounting or auditing matters. In addition, SEC rules mandate that the audit committee of a listed issuer consist of at least three members, all of whom must be independent, as such term is defined by rules and regulations promulgated by the SEC. We are in compliance with the independence requirements of the SEC rules.
The Israeli Companies Law regulations require each public company to appoint a committee that examines the financial statements, which shall consist of at least three members, of which the majority among them shall be independent directors and such committee’s chairman shall be an external director. The committee’s duties are, among others, to examine the company’s financial statements and to recommend and report to the board of directors of the company regarding any problem or defect found in such financial statements.
Any person who is not eligible to serve on the audit committee is further restricted from participating in its meetings and votes, unless the chairman of the audit committee determines that such person’s presence is necessary in order to present a certain matter; provided, however, that company employees who are not controlling shareholders or relatives of such shareholders may be present in the meetings, but not for actual voting, and likewise, company counsel and secretary who are not controlling shareholders or relatives of such shareholders may be present in the meetings and for actual voting if such presence is requested by the audit committee.
In addition to the above, all such committee’s members must apply with the following requirements:
| · | All members shall be members of the board of directors of the company. |
| · | At least one of the committee’s members shall have financial and accounting expertise and the rest of the committee’s members must have the ability to read and understand financial statements. |
The Company, through our Audit Committee, is in full compliance with the above requirements.
Financial Statement Examination Committee
Under the Israeli Companies Law, the board of directors of a public company must appoint a financial statement examination committee, which consists of members with accounting and financial expertise or the ability to read and understand financial statements. According to a resolution of our Board of Directors, the Audit Committee has been assigned the responsibilities and duties of a financial statements examination committee, as permitted under relevant regulations promulgated under the Israeli Companies Law. From time to time as necessary and required to approve our financial statements, the Audit Committee holds separate meetings, prior to the scheduled meetings of the entire Board of Directors regarding financial statement approval. The function of a financial statements examination committee is to discuss and provide recommendations to its board of directors (including the report of any deficiency found) with respect to the following issues: (i) estimations and assessments made in connection with the preparation of financial statements; (ii) internal controls related to the financial statements; (iii) completeness and propriety of the disclosure in the financial statements; (iv) the accounting policies adopted and the accounting treatments implemented in material matters of the company; (v) value evaluations, including the assumptions and assessments on which evaluations are based and the supporting data in the financial statements. Our independent auditors and our internal auditors are invited to attend all meetings of Audit Committee when it is acting in the role of the financial statements examination committee.
| 95 |
Compensation Committee
Amendment no. 20 to the Companies Law was published on November 12, 2012 and became effective on December 12, 2012 ("Amendment no. 20"). In general, Amendment no. 20 requires public companies to appoint a compensation committee and to adopt a compensation policy with respect to its officers (the "Compensation Policy"). In addition, Amendment no. 20 addresses the corporate approval process required for a public company's engagement with its officers (with specific reference to a director, a non-director officer, a chief executive officer and controlling shareholders and their relatives who are employed by the company).
The compensation committee shall be nominated by the board of directors and be comprised of its members. The compensation committee must consist of at least three members. All of the external directors must serve on the compensation committee and constitute a majority of its members. The remaining members of the compensation committee must be directors who qualify to serve as members of the audit committee (including the fact that they are independent) and their compensation should be identical to the compensation paid to the external directors of the company.
Amendment no. 20 does not set a date for the appointment of the compensation committee. However, the Compensation Policy should be approved by the general meeting of shareholders (after discussions and recommendation of the compensation committee and approval by the board of directors) by September 11, 2013. Moreover, the approval of the compensation committee is required in order to approve terms of office and/or employment of office holders.
Similar to the rules that apply to the audit committee, the compensation committee may not include the chairman of the board, or any director employed by the company, by a controlling shareholder or by any entity controlled by a controlling shareholder, or any director providing services to the company, to a controlling shareholder or to any entity controlled by a controlling shareholder on a regular basis, or any director whose primary income is dependent on a controlling shareholder, and may not include a controlling shareholder or any of its relatives. Individuals who are not permitted to be compensation committee members may not participate in the committee’s meetings other than to present a particular issue; provided, however, that an employee that is not a controlling shareholder or relative may participate in the committee’s discussions, but not in any vote, and the company’s legal counsel and corporate secretary may participate in the committee’s discussions and votes if requested by the committee.
The roles of the compensation committee are, among others, to: (i) recommend to the board of directors the Compensation Policy for office holders and recommend to the board once every three years the extension of a Compensation Policy that had been approved for a period of more than three years; (ii) recommend to the directors any update of the Compensation Policy, from time to time, and examine its implementation; (iii) decide whether to approve the terms of office and of employment of office holders that require approval of the compensation committee; and (iv) decide, in certain circumstances, whether to exempt the approval of terms of office of a chief executive officer from the requirement of shareholder approval.
The compensation policy requires the approval of the general meeting of shareholders with a “Special Majority”, which requires a majority of the shareholders of the company who are not either a controlling shareholder or an "interested party" in the proposed resolution, or that shareholders holding less than 2% of the voting power in the company voted against the proposed resolution at such meeting. However, under special circumstances, the board of directors may approve the compensation policy without shareholder approval, if the compensation committee and thereafter the board of directors decided, based on substantiated reasons after they have reviewed the compensation policy again, that the compensation policy is in the best interest of the company.
Amendment no. 20 details the considerations that should be taken into account in determining the Compensation Policy and certain issues which the Compensation Policy should include.
Mr. Gil Oren is the chairman of our compensation committee. Mr. Chezy Barenholz and Mrs. Liora Lev serve as the other members of our compensation committee.
| 96 |
Approval of Related Party Transactions under the Israeli Companies Law
Fiduciary duties of the office holders
The Israeli Companies Law imposes a duty of care and a duty of loyalty on all office holders of a company. The duty of care of an office holder is based on the duty of care set forth in connection with the tort of negligence under the Israeli Torts Ordinance (New Version) 5728-1968. This duty of care requires an office holder to act with the degree of proficiency with which a reasonable office holder in the same position would have acted under the same circumstances. The duty of care includes a duty to use reasonable means, in light of the circumstances, to obtain:
| · | information on the advisability of a given action brought for his or her approval or performed by virtue of his or her position; and |
| · | All other important information pertaining to these actions. |
The duty of loyalty requires an office holder to act in good faith and for the benefit of the company, and includes the duty to:
| · | refrain from any act involving a conflict of interest between the performance of his or her duties in the company and his or her other duties or personal affairs; |
| · | refrain from any activity that is competitive with the business of the company; |
| · | refrain from exploiting any business opportunity of the company for the purpose of gaining a personal advantage for himself or herself or others; and |
| · | disclose to the company any information or documents relating to the company’s affairs which the office holder received as a result of his or her position as an office holder. |
We may approve an act performed in breach of the duty of loyalty of an office holder provided that the office holder acted in good faith, the act or its approval does not harm the company, and the office holder discloses his or her personal interest, as described below.
Disclosure of personal interests of an office holder and approval of acts and transactions
The Israeli Companies Law requires that an office holder promptly disclose to the company any personal interest that he or she may have and all related material information or documents relating to any existing or proposed transaction by the company. An interested office holder’s disclosure must be made promptly and in any event no later than the first meeting of the board of directors at which the transaction is considered. An office holder is not obligated to disclose such information if the personal interest of the office holder derives solely from the personal interest of his or her relative in a transaction that is not considered as an extraordinary transaction.
The term personal interest is defined under the Israeli Companies Law to include the personal interest of a person in an action or in the business of a company, including the personal interest of such person’s relative or the interest of any corporation in which the person is an interested party, but excluding a personal interest stemming solely from the fact of holding shares in the company. A personal interest furthermore includes the personal interest of a person for whom the office holder holds a voting proxy or the interest of the office holder with respect to his or her vote on behalf of the shareholder for whom he or she holds a proxy even if such shareholder itself has no personal interest in the approval of the matter. An office holder is not, however, obliged to disclose a personal interest if it derives solely from the personal interest of his or her relative in a transaction that is not considered an extraordinary transaction.
| 97 |
Under the Israeli Companies Law, an extraordinary transaction which requires approval is defined as any of the following:
| · | a transaction other than in the ordinary course of business; |
| · | a transaction that is not on market terms; or |
| · | a transaction that may have a material impact on the company’s profitability, assets or liabilities. |
Under the Israeli Companies Law, once an office holder has complied with the disclosure requirement described above, a company may approve a transaction between the company and the office holder or a third party in which the office holder has a personal interest, or approve an action by the office holder that would otherwise be deemed a breach of duty of loyalty. However, a company may not approve a transaction or action that is adverse to the company’s interest or that is not performed by the office holder in good faith.
Under the Companies Law, unless the articles of association of a company provide otherwise, a transaction with an office holder, a transaction with a third party in which the office holder has a personal interest, and an action of an office holder that would otherwise be deemed a breach of duty of loyalty requires approval by the board of directors. Our Articles of Association do not provide otherwise. If the transaction or action considered is (i) an extraordinary transaction, (ii) an action of an office holder that would otherwise be deemed a breach of duty of loyalty and may have a material impact on a company’s profitability, assets or liabilities, (iii) an undertaking to indemnify or insure an office holder who is not a director, or (iv) for matters considered an undertaking concerning the terms of compensation of an office holder who is not a director, including, an undertaking to indemnify or insure such office holder, then approval by the audit committee is required prior to approval by the board of directors. Arrangements regarding the compensation, indemnification or insurance of a director require the approval of the audit committee, board of directors and shareholders, in that order.
A director who has a personal interest in a matter that is considered at a meeting of the board of directors or the audit committee may generally not be present at the meeting or vote on the matter, unless a majority of the directors or members of the audit committee have a personal interest in the matter or the chairman of the audit committee or board of directors, as applicable, determines that he or she should be present to present the transaction that is subject to approval. If a majority of the directors have a personal interest in the matter, such matter would also require approval of the shareholders of the company.
Disclosure of personal interests of a controlling shareholder and approval of transactions
Under the Israeli Companies Law and a recent amendment thereto, the disclosure requirements that apply to an office holder also apply to a controlling shareholder of a public company. See “— Audit Committee” for a definition of controlling shareholder. Extraordinary transactions with a controlling shareholder or in which a controlling shareholder has a personal interest, including a private placement in which a controlling shareholder has a personal interest, as well as transactions for the provision of services whether directly or indirectly by a controlling shareholder or his or her relative, or a company such controlling shareholder controls, and transactions concerning the terms of engagement of a controlling shareholder or a controlling shareholder’s relative, whether as an office holder or an employee, require the approval of the audit committee, the board of directors and a majority of the shares voted by the shareholders of the company participating and voting on the matter in a shareholders’ meeting. In addition, such shareholder approval must fulfill one of the following requirements:
| · | at least a majority of the shares held by shareholders who have no personal interest in the transaction and are voting at the meeting must be voted in favor of approving the transaction, excluding abstentions; or |
| · | the shares voted by shareholders who have no personal interest in the transaction who vote against the transaction represent no more than 2% of the voting rights in the company. |
| 98 |
To the extent that any such transaction with a controlling shareholder is for a period extending beyond three years, approval is required once every three years, unless the audit committee determines that the duration of the transaction is reasonable given the circumstances related thereto.
Duties of shareholders
Under the Israeli Companies Law, a shareholder has a duty to refrain from abusing its power in the company and to act in good faith and in an acceptable manner in exercising its rights and performing its obligations to the company and other shareholders, including, among other things, voting at general meetings of shareholders on the following matters:
| · | an amendment to the articles of association; |
| · | an increase in the company’s authorized share capital; |
| · | a merger; |
| · | an increase in the company’s authorized share capital; and |
| · | the approval of related party transactions and acts of office holders that require shareholder approval. |
A shareholder also has a general duty to refrain from discriminating against other shareholders.
The remedies generally available upon a breach of contract will also apply to a breach of the above mentioned duties, and in the event of discrimination against other shareholders, additional remedies are available to the injured shareholder.
In addition, any controlling shareholder, any shareholder that knows that its vote can determine the outcome of a shareholder vote and any shareholder that, under a company’s articles of association, has the power to appoint or prevent the appointment of an office holder, or has another power with respect to a company, is under a duty to act with fairness towards the company. The Israeli Companies Law does not describe the substance of this duty except to state that the remedies generally available upon a breach of contract will also apply in the event of a breach of the duty to act with fairness, taking the shareholder’s position in the company into account.
Approval of Compensation to Our Officers
The Israeli Companies Law prescribes that compensation to officers must be approved by a company’s Board of Directors.
As detailed above, our compensation committee consists of three independent directors: Yechezkel Barenholtz, Gil Oren and Liora Lev. The responsibilities of the compensation committee are to set our overall policy on executive remuneration and to decide the specific remuneration, benefits and terms of employment for directors, officers and the Chief Executive Officer.
The objectives of the compensation committee’s policies are that such individuals should receive compensation which is appropriate given their performance, level of responsibility and experience. Compensation packages should also allow us to attract and retain executives of the necessary caliber while, at the same time, motivating them to achieve the highest level of corporate performance in line with the best interests of shareholders. In order to determine the elements and level of remuneration appropriate to each executive director, the compensation committee reviews surveys on executive pay, obtains external professional advice and considers individual performance.
| 99 |
Internal Auditor
Under the Israeli Companies Law, the board of directors must appoint an internal auditor, nominated by the audit committee. The role of the internal auditor is to examine, among other matters, whether the company’s actions comply with the law and orderly business procedure. Under the Israeli Companies Law, an internal auditor may not be:
| · | a person (or a relative of a person) who holds more than 5% of the company’s shares; |
| · | a person (or a relative of a person) who has the power to appoint a director or the general manager of the company; |
| · | an executive officer or director of the company; or |
| · | a member of the company’s independent accounting firm. |
We comply with the requirement of the Israeli Companies Law relating to internal auditors. Our internal auditors examine whether our various activities comply with the law and orderly business procedure.
D. Employees.
As of December 31, 2011, we had 11 employees, three of whom were employed in management and administration and eight of whom were employed in research and development. All of these employees were located in Israel.
As of December 31, 2012, we had eight employees, three of whom were employed in management and administration, three of whom were employed in research and development and two of whom were employed in management, research and development. All of these employees were located in Israel. The decrease in the number of employees from 2011 to 2012 was the result of a change in our activity from pre-clinical to clinical studies, which require less employees in research and development.
While none of our employees are party to any collective bargaining agreements, certain provisions of the collective bargaining agreements between the Histadrut (General Federation of Labor in Israel) and the Coordination Bureau of Economic Organizations (including the Industrialists’ Associations) are applicable to our employees by order of the Israel Ministry of Labor. These provisions primarily concern the length of the workday, minimum daily wages for professional workers, pension fund benefits for all employees, insurance for work-related accidents, procedures for dismissing employees, determination of severance pay and other conditions of employment. We generally provide our employees with benefits and working conditions beyond the required minimums. We have never experienced any employment-related work stoppages and believe our relationship with our employees is good.
E. Share Ownership.
The following table sets forth information regarding the beneficial ownership of our outstanding ordinary shares as of August 26, 2013 by the members of our senior management and Board of Directors, individually and as a group.
| Name of Beneficial Owner | Number of Ordinary Shares | Percentage of Class* | ||||||
| Ilan
Cohn, PhD. Chairman of the Board | 202,532 | (1) | 1.02 | |||||
| Pnina Fishman, PhD. Chief Executive Officer and Director | 572,263 | (2) | 2.87 | |||||
| Motti Farbstein Chief Operating Officer | 38,196 | (3) | 0.19 | |||||
| Guy Regev Director | 52,265 | (4) | 0.26 | |||||
| Liora Lev Director | 44,590 | (5) | 0.22 | |||||
| Avraham Sartani,
Ph.D. Director | 11,095 | (6) | 0.06 | |||||
Gil
Oren | - | - | ||||||
Yechezkel
Barenholz | - | - | ||||||
| Barak Singer VP for Business Development | 8,575 | (7) | 0.04 | |||||
| Directors and Executive Officers as a group (9 persons) | 929,516 | 4.65 | ||||||
—————————
| * | Percentages and number of ordinary shares calculated in accordance with SEC rules and based upon 14,273,074 ordinary shares, 4,463,730 registered warrants, or warrants that are publicly traded on the TASE (which include our Series 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11 Warrants), and 1,208,539 unregistered options, or options that are not publicly traded, outstanding as of August 26, 2013. The exercise prices and expiration dates of the series included in this table are as follows: (i) Series 8 - NIS 0.75 per warrant, which expire on December 31, 2013; (ii) Series 9 - NIS 0.85 per warrant, which expire on May 1, 2015; (iii) Series 10 - NIS 0.394 per warrant, which expire on October 31, 2015; and (iv) Series 11 - NIS 0.392 per warrant, which expire on April 30, 2016. |
| (1) | Includes 118,447 ordinary shares, 28,000 registered warrants (Series 8) to purchase 1,120 ordinary shares, 42,000 registered warrants (Series 9) to purchase 1,680 ordinary shares and 2,032,136 unregistered options with an exercise price of NIS 1.247 per option to purchase 81,285 ordinary shares. All such options are vested and expire on March 20, 2017. |
| (2) | Includes 263,433 ordinary shares, 60,000 registered warrants (Series 8) to purchase 2,400 ordinary shares, 90,000 registered warrants (Series 9) to purchase 3,600 ordinary shares and 7,570,761 unregistered options to purchase 302,830 ordinary shares, of which 195,630 options have an exercise price of NIS 0.50 per option and expire on August 23, 2016 and 107,200 options have an exercise price of NIS 0.644 per option and expire on January 13, 2021. All such options are vested. |
| (3) | Includes 954,903 unregistered options to purchase 38,196 ordinary shares, of which 28,341 have an exercise price of NIS 0.01 per option to purchase 1,134 ordinary shares and expire on August 3, 2013, 322,175 have an exercise price of NIS 0.45 per option to purchase 12,887 ordinary shares and expire on November 29, 2015, 554,387 have an exercise price of NIS 0.307 per option to purchase 22,175 ordinary shares and expire on November 26, 2018, 37,500 have an exercise price of NIS 0.385 per option to purchase 1,500 ordinary shares and expire on May 2, 2022 and 12,500 have an exercise price of NIS 0.326 per option to purchase 500 ordinary shares and expire on March 20, 2023. All such options are vested or will vest within 60 days. |
| (4) | Includes 24,240 ordinary shares, 24,000 registered warrants (Series 8) to purchase 960 ordinary shares and 36,000 registered warrants (Series 9) to purchase 1,440 ordinary shares, 250,000 registered warrants (Series 10) to purchase 10,000 ordinary shares and 250,000 registered warrants (Series 11) to purchase 10,000 ordinary shares and 140,625 have an exercise price of NIS 0.60 per option to purchase 5,625 ordinary shares and expire on May 2, 2023. |
| (5) | Includes 34,965 ordinary shares and 240,625 unregistered options with an exercise price of NIS 0.60 per option to purchase 9,625 ordinary shares. All such options are vested and expire on August 14, 2022. |
| (6) | Includes 613 ordinary shares and 262,055 unregistered options to purchase 10,482 ordinary shares, of which 193,305 have an exercise price of NIS 0.45 per option to purchase 7,732 ordinary shares and expire on August 23, 2016 and 68,750 have an exercise price of NIS 0.60 per option to purchase 2,750 ordinary shares and expire on August 14, 2022. All such options are vested. |
| (7) | Includes 214,375 unregistered options to purchase 8,575 ordinary shares, of which 158,125 have an exercise price of NIS 0.754 per option to purchase 6,325 ordinary shares and expire on February 21, 2021 and 37,500 have an exercise price of NIS 0.385 per option to purchase 1,500 ordinary shares and expire on May 2, 2022 and 18,750 have an exercise price of NIS 0.326 per option to purchase 500 ordinary shares and expire on March 20, 2023. All such options are vested or will vest within 60 days. |
| 100 |
Share Option Plans
We maintain the following share option plans for our and our subsidiary’s employees, directors and consultants. In addition to the discussion below, see Note 16b of our consolidated financial statements, included in “Item 18. Financial Statements.”
Our Board of Directors administers our share option plans and has the authority to designate all terms of the options granted under our plans including the grantees, exercise prices, grant dates, vesting schedules and expiration dates, which may be no more than ten years after the grant date. Options may not be granted with an exercise price of less than the fair market value of our ordinary shares on the date of grant, unless otherwise determined by our Board of Directors.
| 101 |
As of December 31, 2012, we have granted to employees, directors and consultants options that are outstanding to purchase up to 1,009,280 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25, pursuant to the 2003 share option plan, or the 2003 Plan, and pursuant to certain grants apart from these plans also discussed below under Non-Plan Share Options.
2003 Share Option Plan
Under the 2003 Plan we granted options during the period between 2003 and 2012, at exercise prices between NIS 0.01 and NIS 1.247 per ordinary share, par value NIS 0.25. Options to purchase up to 1,099,366 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25, were available to be granted under the 2003 Plan. As of December 31, 2012, 25,377,488 options to purchase 1,015,099 ordinary shares were outstanding. Options granted to Israeli employees were in accordance with section 102 of the Income Tax Ordinance, 1961, or the Tax Ordinance, under the capital gains option set forth in section 102(b)(2) of the Tax Ordinance. The options are non-transferable.
The option term is for a period of ten years from the grant date. The options were granted for no consideration. The options vest over a four or two year period. As of December 31, 2012, options to purchase 984,549 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25, were fully vested.
Non-Plan Share Options
In addition to the options granted under our share option plans, at December 31, 2012, there were outstanding and exercisable options to purchase 503,878 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25, which had been granted to consultants and members of our Scientific Advisory Board, not under the 2003 Plan. The options were granted at exercise prices of NIS 0.01 and NIS 0.6. As of December 31, 2012, options to purchase 503,878 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25, were fully vested.
ITEM 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions
A. Major Shareholders.
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the beneficial ownership of our outstanding ordinary shares as of August 26, 2013, by each person who we know beneficially owns 5.0% or more of the outstanding ordinary shares. Each of our shareholders has identical voting rights with respect to its shares. All of the information with respect to beneficial ownership of the ordinary shares is given to the best of our knowledge.
| Name of Beneficial Owner | Number of Ordinary Shares | Percentage of Class* | ||||||
| Shaked Group (Tal Shaked & Haya Shaked) | 1,223,796 | (1) | 8.57 | |||||
| IBI Investment House Ltd. | 792,951 | 5.56 | ||||||
| * | Percent of outstanding ordinary shares. |
| (1) | Includes 372,622 ordinary shares held by Mrs. Haya Shaked and 851,174 ordinary shares held by her daughter, Mrs. Tal Shaked. |
On June 17, 2013, OphthaliX sold 268,095 ordinary shares on the TASE, for aggregate consideration of US$ 510,714. After such sale, OphthaliX owns 446,827 post-reverse split ordinary shares of the Company.
To the best of our knowledge, there is currently one registered U.S. holder of our ADSs. This registered U.S. holder holds 47,182 ADSs, representing approximately 0.66% of our issued and outstanding ordinary shares.
| 102 |
B. Related Party Transactions.
The following is a description of some of the transactions with related parties to which we, or our subsidiaries, are party, and which were in effect within the past three fiscal years. The descriptions provided below are summaries of the terms of such agreements, do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the complete agreements.
We believe that we have executed all of our transactions with related parties on terms no less favorable to us than those we could have obtained from unaffiliated third parties. We are required by Israeli law to ensure that all future transactions between us and our officers, directors and principal shareholders and their affiliates are approved by a majority of our Board of Directors, including a majority of the independent and disinterested members of our Board of Directors, and that they are on terms no less favorable to us than those that we could obtain from unaffiliated third parties.
Employment and Consulting Agreements
We have or have had employment, consulting or related agreements with each member of our senior management. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Compensation—Employment and Consulting Agreements”.
Indemnification Agreements
Our Articles of Association permit us to exculpate, indemnify and insure our directors and officeholders to the fullest extent permitted by the Israeli Companies Law. We have obtained directors’ and officers’ insurance for each of our officers and directors and have entered into indemnification agreements with all of our current officers and directors.
Agreements with Subsidiaries
See “Item 10. Additional Information—Material Contracts—OphthaliX Agreements” for a description of agreements with OphthaliX and Eye-Fite.
C. Interests of Experts and Counsel.
Not applicable.
ITEM 8. Financial Information
A. Consolidated Financial Statements and Other Financial Information
See “Item 18. Financial Statements” for a list of all financial statements filed as part of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
Legal Matters
We are not involved in any legal or arbitration proceedings that may have or have had in the recent past, significant effects on our financial position or profitability.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid cash dividends to our shareholders. Currently we do not intend to pay cash dividends. We intend to reinvest any earnings in developing and expanding our business. Any future determination relating to our dividend policy will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on a number of factors, including future earnings, our financial condition, operating results, contractual restrictions, capital requirements, business prospects, applicable Israeli law and other factors our Board of Directors may deem relevant.
| 103 |
B. Significant Changes
On February 5, 2013, we completed a public offering in which we issued ordinary shares, Series 10 Warrants and Series 11 Warrants for aggregate proceeds of NIS 26,498,488. On May 12, 2013, we effected a reverse share split of our ordinary shares, options and warrants at a ratio of 1-for-25. The impact of such reverse share split on the Company, its shareholders and the information contained in this Registration Statement is reflected herein. Other than such offering and reverse share split, no significant changes with respect to our consolidated financial statements have occurred since December 31, 2012. For other important events that have occurred since December 31, 2012, see “Item 3. Key Information” and “Item 4. Information on the Company”.
ITEM 9. The Offer and Listing
A. Offer and Listing Details.
Our ordinary shares have been trading on the TASE under the symbol “CFBI” since October 2005 and our ADSs currently trade on the OTC in the United States under the symbol “CANFY” since October 2012. We intend to apply to have our ADSs, each of which will represent 50 of our ordinary shares, to be listed on the NYSE MKT under the symbol “CANFY”. We make no representation that such application will be approved or that our ADSs will trade on such market either now or at any time in the future. The shares will be registered and the ADSs may be in certificated or uncertificated form, as more fully described in “Item 12—Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities—American Depositary Shares.” No new shares will be issued in connection with this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. As of August 26, 2013 the Company had 14,273,074 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. The shares have a NIS 0.25 par value. See “Item 10—Additional Information—Memorandum and Articles of Association” for a detailed description of the rights attaching to the shares. Also see “Item 12—Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities—American Depositary Shares” for a description of the rights attaching to the ADSs.
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the reported high and low closing sale prices of our ordinary shares on the TASE in NIS and U.S. dollars. U.S. dollar per ordinary share amounts are calculated using the U.S. dollar representative rate of exchange on the date to which the high or low market price is applicable, as reported by the Bank of Israel.
| NIS Price Per Ordinary Share | U.S.$ Price Per Ordinary Share | |||||||||||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||||||
| Annual: | ||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 0.496 | 0.293 | 0.129 | 0.072 | ||||||||||||
| 2011 | 0.920 | 0.365 | 0.254 | 0.098 | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 0.760 | 0.472 | 0.209 | 0.124 | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 1.610 | 0.264 | 0.385 | 0.069 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 0.813 | 0.225 | 0.236 | 0.059 | ||||||||||||
| Quarterly: | ||||||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter 2012 | 0.439 | 0.310 | 0.116 | 0.083 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter 2012 | 0.399 | 0.293 | 0.099 | 0.072 | ||||||||||||
| Second Quarter 2012 | 0.476 | 0.304 | 0.127 | 0.077 | ||||||||||||
| First Quarter 2012 | 0.496 | 0.378 | 0.129 | 0.102 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter 2011 | 0.598 | 0.396 | 0.164 | 0.105 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter 2011 | 0.708 | 0.365 | 0.208 | 0.098 | ||||||||||||
| Second Quarter 2011 | 0.848 | 0.644 | 0.245 | 0.187 | ||||||||||||
| First Quarter 2011 | 0.920 | 0.705 | 0.254 | 0.198 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter 2010 | 0.760 | 0.573 | 0.209 | 0.157 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter 2010 | 0.596 | 0.472 | 0.161 | 0.124 | ||||||||||||
| Second Quarter 2010 | 0.721 | 0.495 | 0.195 | 0.128 | ||||||||||||
| First Quarter 2010 | 0.736 | 0.608 | 0.198 | 0.165 | ||||||||||||
| Most Recent Six Months: | ||||||||||||||||
| August 2013 (through August 26)(1) | 7.793 | 7.037 | 2.094 | 1.970 | ||||||||||||
| July 2013(1) | 7.800 | 7.284 | 2.149 | 2.025 | ||||||||||||
| June 2013(1) | 7.148 | 6.752 | 1.963 | 1.854 | ||||||||||||
| May 2013(1) | 7.875 | 7.058 | 2.139 | 1.917 | ||||||||||||
| April 2013 | 0.338 | 0.297 | 0.094 | 0.083 | ||||||||||||
| March 2013 | 0.338 | 0.325 | 0.092 | 0.088 | ||||||||||||
| February 2013 | 0.425 | 0.320 | 0.115 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| January 2013 | 0.433 | 0.329 | 0.116 | 0.087 | ||||||||||||
| December 2012 | 0.376 | 0.310 | 0.099 | 0.083 | ||||||||||||
___________________
(1) Reflects the impact of the reverse stock split effected on May 12, 2013.
| 104 |
On August 26, 2013, the last reported sales price of our ordinary shares on the TASE was NIS 6.979 per share, or $1.937 per share. On August 26, 2013, the exchange rate of the NIS to the dollar was $1.00 = NIS 3.603 as reported by the Bank of Israel. As an Israeli public company the information regarding the number of shareholders of record of our ordinary shares, warrants or options is not available.
For information with respect to our warrants, see “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects—Warrants”.
B. Plan of Distribution.
Not applicable.
C. Markets.
Our ordinary shares have been trading on the TASE and our ADSs currently trade on the OTC. We intend to apply to have our ADSs listed on the NYSE MKT under the symbol “CANFY.” We make no representation that such application will be approved or that our ADSs will trade on such market either now or at any time in the future.
D. Selling Shareholders.
Not applicable.
E. Dilution.
Not applicable.
F. Expenses of the Issue.
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. Additional Information
A. Share Capital.
On May 12 2013, the Company effected a reverse share split at a ratio of 1-for-25. All ordinary shares, warrants, options and per share amounts presented below have been adjusted accordingly to give retroactive effect to the reverse share split.
At December 31, 2012, our authorized share capital was NIS 5,000,000 consisting of 20,000,000 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share. Of such shares, the Company had issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2012, 10,935,196 ordinary shares (of which 714,922 are held by OphthaliX and are therefore without any voting rights); 4,953,750 Series 6 warrants that are exercisable into 198,150 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 9,907,500 Series 7 warrants that are exercisable into 396,300 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 8,112,000 Series 8 warrants that are exercisable into 324,480 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 12,168,000 Series 9 warrants that are exercisable into 486,720 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share and 38,055,439 unregistered options and warrants that are exercisable into 1,522,217 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share.
At December 31, 2012, our authorized share capital consisted of 20,000,000 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share, of which 10,935,196 shares were issued and outstanding as of the date of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. All of our outstanding ordinary shares have been validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable. Our ordinary shares are not redeemable and are not subject to any preemptive right.
At December 31, 2012, an additional 1,522,217 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options to purchase our ordinary shares. The exercise price of the options and warrants outstanding is between NIS 0.01 and NIS 1.247 per option or warrant. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees - Share Ownership - Share Option Plans” for a more detailed discussion on our outstanding options.
At December 31, 2012, an additional 198,150 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 6 Warrants. The Series 6 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.63 per warrant. The Series 6 Warrants were originally scheduled to expire on May 16, 2013. However, on August 26, 2013, the District Court in Petah-Tikva, Israel approved the extension of such exercise period until October 30, 2013 .
| 105 |
At December 31, 2012, an additional 396,300 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 7 Warrants. The Series 7 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.80 per warrant. The Series 7 Warrants are scheduled to expire on November 16, 2013.
At December 31, 2012, an additional 324,480 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 8 Warrants. The Series 8 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.55 per warrant. The Series 8 Warrants were originally scheduled to expire on May 1, 2013. However, our Board of Directors has decided to extend the exercise period of the Series 8 Warrants until December 31, 2013 and increase the exercise price to NIS 0.75 per warrant, subject to court and other approvals.
At December 31, 2012, an additional 486,720 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 9 Warrants. The Series 9 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.85 per warrant. The Series 9 Warrants are scheduled to expire on May 1, 2015.
As of January 1, 2010, we had 8,530,412 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. During 2010, we issued an aggregate of 35,672 ordinary shares in connection with the exercise of warrants and share options. Total aggregate consideration received in consideration for these issuances was approximately NIS 1,075,500.
On October 28, 2010, we issued 720,000 shares in a shelf public offering to our shareholders by means of a shelf offering report published on October 28, 2010, under the shelf prospectus of May 27, 2010. The per share price at the issuance was NIS 0.60 per share.
As of January 1, 2011, we had 9,286,085 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. During 2011, we issued an aggregate of 653,000 ordinary shares in connection with the exercise of warrants and share options. Total aggregate consideration received in consideration for these issuances was approximately NIS 294,500.
On November 16, 2011, we issued 396,300 shares, Series 6 Warrants exercisable for 198,150 of our ordinary shares and Series 7 Warrants exercisable for 396,300 of our ordinary shares, in a public offering in Israel on the TASE. The per share offering price at the issuance was NIS 12.50 per share, and the ordinary shares were offered in units consisting of 100 ordinary shares with 1,250 Series 6 (exercisable for 50 of our ordinary shares) Warrants and 2,500 Series 7 Warrants (exercisable for 100 of our ordinary shares), which were offered for no further consideration. The ordinary shares and the Series 6 and 7 Warrants are all listed for trading on the TASE and the Series 6 and Series 7 Warrants trade separately from the ordinary shares. The exercise price of the Series 6 Warrants is NIS 0.63 per warrant and the exercise price of the Series 7 Warrants is NIS 0.80 per warrant.
On November 20, 2011, we issued 714,922 shares in a private placement in accordance with report published on November 21, 2011. The per share price at the issuance was NIS 12.525 per share.
As of January 1, 2012, we had 486,720 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. During 2012, we issued an aggregate of 25,049 ordinary shares in connection with the exercise of warrants and share options. Total aggregate consideration received in consideration for these issuances was approximately NIS 251,000.
On May 1, 2012, we issued 486,720 shares, Series 8 Warrants exercisable into 324,480 of our ordinary shares and Series 9 Warrants exercisable into 486,720 of our ordinary shares, in a public offering in Israel on the TASE. The per share offering price at the issuance was NIS 11.925 per share, and the ordinary shares were offered in units consisting of 120 ordinary shares with 2,000 Series 8 Warrants (exercisable for 80 of our ordinary shares) and 3,000 Series 9 Warrants (exercisable for 120 of our ordinary shares), which were offered for no further consideration. The ordinary shares and the Series 8 and 9 Warrants are all listed for trading on the TASE and the Series 8 and Series 9 Warrants trade separately from the ordinary shares. The exercise price of the Series 8 Warrants is NIS 0.55 per warrant and the exercise price of the Series 9 Warrants is NIS 0.85 per warrant. However, our Board of Directors has decided to extend the exercise period of the Series 8 Warrants until December 31, 2013 and increase the exercise price to NIS 0.75 per warrant, which on June 24, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel approved the extension of such exercise period to December 31, 2013 and the increase of the exercise price to NIS 0.75 per warrant.
As of January 1, 2013, we had 10,935,196 ordinary shares issued and outstanding. During 2013, we issued an aggregate of 346,225 ordinary shares in connection with the exercise of warrants and share options. Total aggregate consideration received in consideration for these issuances was approximately NIS 86,500.
On February 5, 2013, we issued 2,990,800 shares, Series 10 Warrants exercisable into 1,495,400 of our ordinary shares and Series 11 Warrants exercisable into 1,495,400 of our ordinary shares, in a public offering in Israel on TASE. The per share offering price at the issuance was NIS 7.86 per share, and the ordinary shares were offered in units consisting of 400 ordinary shares with 5,000 Series 10 Warrants and 5,000 Series 11 Warrants, which were offered for no further consideration. The ordinary shares and the Series 10 and 11 Warrants are all listed for trading on the TASE and the Series 10 and Series 11 Warrants trade separately from the ordinary shares. The exercise price of the Series 10 Warrants is NIS 0.394 per warrant and the exercise price of the Series 11 Warrants is NIS 0.392 per warrant.
| 106 |
On March 17, 2013, we issued Series 10 Warrants exercisable into 67,280 ordinary shares in a private placement in accordance with report published on February 21, 2013. The price per share at the issuance was NIS 9.85.
On April 2, 2013, 3,239 exercisable options were cancelled from the outstanding option pool of the Company.
At August 26, 2013, our authorized share capital was NIS 10,000,000 consisting of 40,000,000 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share. Of such shares, the Company has issued and outstanding as of August 26, 2013, 14,273,074 ordinary shares (of which 446,827 are held by OphthaliX and are therefore without any voting rights); 4,953,750 Series 6 warrants that are exercisable into 198,150 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 9,907,500 Series 7 warrants that are exercisable into 396,300 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 8,106,000 Series 8 warrants that are exercisable into 324,240 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 12,168,000 Series 9 warrants that are exercisable into 486,720 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share; 39,067,000 Series 10 warrants that are exercisable into 1,562,680 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.394; 37,385,000 Series 11 warrants that are exercisable into 1,495,400 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.392 per share and 28,213,486 unregistered options and warrants that are exercisable into 1,128,539 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share.
At August 26, 2013, our authorized share capital consisted of 40,000,000 ordinary shares, par value NIS 0.25 per share, of which 14,273,486 shares were issued and outstanding as of the date of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. All of our outstanding ordinary shares have been validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable. Our ordinary shares are not redeemable and are not subject to any preemptive right.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 1,208,539 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options to purchase our ordinary shares. The exercise price of the options and warrants outstanding is between NIS 0.01 and NIS 1.247 per option or warrant. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees - Share Ownership - Share Option Plans” for a more detailed discussion on our outstanding options.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 198,150 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 6 Warrants. The Series 6 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.63 per warrant. The Series 6 Warrants were originally scheduled to expire on May 16, 2013. However, on August 26, 2013, the District Court in Petah-Tikva, Israel approved the extension of such exercise period until October 30, 2013.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 396,300 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 7 Warrants. The Series 7 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.80 per warrant. The Series 7 Warrants are scheduled to expire on November 16, 2013.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 324,240 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 8 Warrants. The Series 8 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.55 per warrant. The Series 8 Warrants were originally scheduled to expire on June 30, 2013. However, our Board of Directors has decided to extend the exercise period of the Series 8 Warrants until December 31, 2013 and increase the exercise price to NIS 0.75 per warrant, which on June 24, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel approved the extension of such exercise period to December 31, 2013 and the increase of the exercise price to NIS 0.75 per warrant.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 486,720 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 9 Warrants. The Series 9 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.85 per warrant. The Series 9 Warrants are scheduled to expire on May 1, 2015.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 1,562,680 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 10 Warrants. The Series 10 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.394 per warrant. The Series 10 Warrants are scheduled to expire on October 31, 2015.
At August 26, 2013, an additional 1,495,400 ordinary shares are issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our ordinary shares. All of such warrants have been designated as our Series 11 Warrants. The Series 11 Warrants have an exercise price of NIS 0.392 per warrant. The Series 11 Warrants are scheduled to expire on April 30, 2016.
B. Memorandum and Articles of Association.
Our number with the Israeli Registrar of Companies is 512022153. Our purpose is set forth in Section 3 of our Articles of Association and includes every lawful purpose.
| 107 |
Our ordinary shares that are fully paid for are issued in registered form and may be freely transferred under our Articles of Association, unless the transfer is restricted or prohibited by applicable law or the rules of a stock exchange on which the shares are traded. The ownership or voting of our ordinary shares by non-residents of Israel is not restricted in any way by our Articles of Association or the laws of the State of Israel, except for ownership by nationals of some countries that are, or have been, in a state of war with Israel.
Pursuant to the Israeli Companies Law and our Articles of Association, our Board of Directors may exercise all powers and take all actions that are not required under law or under our Articles of Association to be exercised or taken by our shareholders, including the power to borrow money for company purposes.
Our Articles of Association enable us to increase or reduce our share capital. Any such changes are subject to the provisions of the Israeli Companies Law and must be approved by a resolution duly passed by our shareholders at a general or special meeting by voting on such change in the capital. In addition, transactions that have the effect of reducing capital, such as the declaration and payment of dividends in the absence of sufficient retained earnings and profits and an issuance of shares for less than their nominal value, require a resolution of our Board of Directors and court approval.
Dividends
We may declare a dividend to be paid to the holders of our ordinary shares in proportion to their respective shareholdings. Under the Israeli Companies Law, dividend distributions are determined by the board of directors and do not require the approval of the shareholders of a company unless such company’s articles of association provide otherwise. Our Articles of Association do not require shareholder approval of a dividend distribution and provide that dividend distributions may be determined by our Board of Directors.
Pursuant to the Israeli Companies Law, we may only distribute dividends from our profits accrued over the previous two years, as defined in the Israeli Companies Law, according to our then last reviewed or audited financial reports, or we may distribute dividends with court approval. In each case, we are only permitted to pay a dividend if there is no reasonable concern that payment of the dividend will prevent us from satisfying our existing and foreseeable obligations as they become due.
Election of Directors
Our ordinary shares do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. As a result, the holders of a majority of the voting power represented at a shareholders meeting have the power to elect all of our directors, subject to the special approval requirements for external directors described under “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees — Board Practices — External Directors.”
Pursuant to our Articles of Association, other than the external directors, for whom special election requirements apply under the Israeli Companies Law, our directors are elected at a general or special meeting of our shareholders and serve on the Board of Directors until the end of the next general meeting or they are removed by the majority of our shareholders at a general or special meeting of our shareholders or upon the occurrence of certain events, in accordance with the Israeli Companies Law and our Articles of Association. In addition, our Articles of Association allow our Board of Directors to appoint directors to fill vacancies on the Board of Directors to serve until the next general meeting or special meeting, or earlier if required by our Articles of Association or applicable law. We have held elections for each of our non-external directors at each annual meeting of our shareholders since our initial public offering in Israel. External directors are elected for an initial term of three years and may be removed from office pursuant to the terms of the Israeli Companies Law. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees — Board Practices — External Directors.”
Shareholder Meetings
Under Israeli law, we are required to hold an annual general meeting of our shareholders once every calendar year that must be no later than 15 months after the date of the previous annual general meeting. All meetings other than the annual general meeting of shareholders are referred to as special meetings. Our Board of Directors may call special meetings whenever it sees fit, at such time and place, within or outside of Israel, as it may determine. In addition, the Israeli Companies Law and our Articles of Association provide that our Board of Directors is required to convene a special meeting upon the written request of (i) any two of our directors or one quarter of our Board of Directors or (ii) one or more shareholders holding, in the aggregate, either (1) 5% of our outstanding shares and 1% of our outstanding voting power or (2) 5% of our outstanding voting power.
| 108 |
Subject to the provisions of the Israeli Companies Law and the regulations promulgated thereunder, shareholders entitled to participate and vote at general meetings are the shareholders of record on a date to be decided by the board of directors, which may be between four and 40 days prior to the date of the meeting. Furthermore, the Israeli Companies Law and our Articles of Association require that resolutions regarding the following matters must be passed at a general meeting of our shareholders:
| · | amendments to our Articles of Association; |
| · | appointment or termination of our auditors; |
| · | appointment of directors and appointment and dismissal of external directors; |
| · | approval of acts and transactions requiring general meeting approval pursuant to the Israeli Companies Law; |
| · | director compensation, indemnification and change of the principal executive officer; |
| · | increases or reductions of our authorized share capital; |
| · | a merger; and |
| · | the exercise of our Board of Director’s powers by a general meeting, if our Board of Directors is unable to exercise its powers and the exercise of any of its powers is required for our proper management. |
The Israeli Companies Law requires that a notice of any annual or special shareholders meeting be provided at least 21 days prior to the meeting and if the agenda of the meeting includes the appointment or removal of directors, the approval of transactions with office holders or interested or related parties, or an approval of a merger, notice must be provided at least 35 days prior to the meeting.
The Israeli Companies Law does not allow shareholders of publicly traded companies to approve corporate matters by written consent. Consequently, our Articles of Association does not allow shareholders to approve corporate matters by written consent.
Pursuant to our Articles of Association, holders of our ordinary shares have one vote for each ordinary share held on all matters submitted to a vote before the shareholders at a general meeting.
Quorum
The quorum required for our general meetings of shareholders consists of at least two shareholders present in person, by proxy or written ballot who hold or represent between them at least 25% of the total outstanding voting rights.
A meeting adjourned for lack of a quorum is adjourned to the same day in the following week at the same time and place or on a later date if so specified in the summons or notice of the meeting. At the reconvened meeting, any number of our shareholders present in person or by proxy shall constitute a lawful quorum.
Resolutions
Our Articles of Association provide that all resolutions of our shareholders require a simple majority vote, unless otherwise required by applicable law.
| 109 |
Israeli law provides that a shareholder of a public company may vote in a meeting and in a class meeting by means of a written ballot in which the shareholder indicates how he or she votes on resolutions relating to the following matters:
| · | an appointment or removal of directors; |
| · | an approval of transactions with office holders or interested or related parties; |
| · | an approval of a merger or any other matter in respect of which there is a provision in the articles of association providing that decisions of the general meeting may also be passed by written ballot; |
| · | authorizing the chairman of the board of directors or his relative to act as the company’s chief executive officer or act with such authority; or authorize the company’s chief executive officer or his relative to act as the chairman of the board of directors or act with such authority; and |
| · | other matters which may be prescribed by Israel’s Minister of Justice. |
The provision allowing the vote by written ballot does not apply where the voting power of the controlling shareholder is sufficient to determine the vote. Our Articles of Association provides that our Board of Directors may prevent voting by means of a written ballot and this determination is required to be stated in the notice convening the general meeting.
The Israeli Companies Law provides that a shareholder, in exercising his or her rights and performing his or her obligations toward the company and its other shareholders, must act in good faith and in a customary manner, and avoid abusing his or her power. This is required when voting at general meetings on matters such as changes to the articles of association, increasing the company’s registered capital, mergers and approval of related party transactions. A shareholder also has a general duty to refrain from depriving any other shareholder of its rights as a shareholder. In addition, any controlling shareholder, any shareholder who knows that its vote can determine the outcome of a shareholder vote and any shareholder who, under such company’s articles of association, can appoint or prevent the appointment of an office holder, is required to act with fairness towards the company. The Israeli Companies Law does not describe the substance of this duty except to state that the remedies generally available upon a breach of contract will also apply to a breach of the duty to act with fairness, and, to the best of our knowledge, there is no binding case law that addresses this subject directly.
Under the Israeli Companies Law, unless provided otherwise in a company’s articles of association, a resolution at a shareholders meeting requires approval by a simple majority of the voting rights represented at the meeting, in person, by proxy or written ballot, and voting on the resolution. A resolution for the voluntary winding up of the company requires the approval of holders of 75% of the voting rights represented at the meeting, in person, by proxy or by written ballot and voting on the resolution.
In the event of our liquidation, after satisfaction of liabilities to creditors, our assets will be distributed to the holders of our ordinary shares in proportion to their shareholdings. This right, as well as the right to receive dividends, may be affected by the grant of preferential dividend or distribution rights to the holders of a class of shares with preferential rights that may be authorized in the future.
Access to Corporate Records
Under the Israeli Companies Law, all shareholders of a company generally have the right to review minutes of the company’s general meetings, its shareholders register and principal shareholders register, articles of association, financial statements and any document it is required by law to file publicly with the Israeli Companies Registrar and the ISA. Any of our shareholders may request access to review any document in our possession that relates to any action or transaction with a related party, interested party or office holder that requires shareholder approval under the Israeli Companies Law. We may deny a request to review a document if we determine that the request was not made in good faith, that the document contains a commercial secret or a patent or that the document’s disclosure may otherwise prejudice our interests.
| 110 |
Acquisitions under Israeli Law
Full Tender Offer
A person wishing to acquire shares of a public Israeli company and who would as a result hold over 90% of the target company’s issued and outstanding share capital is required by the Israeli Companies Law to make a tender offer to all of the company’s shareholders for the purchase of all of the issued and outstanding shares of the company. A person wishing to acquire shares of a public Israeli company and who would as a result hold over 90% of the issued and outstanding share capital of a certain class of shares is required to make a tender offer to all of the shareholders who hold shares of the same class for the purchase of all of the issued and outstanding shares of the same class. If the shareholders who do not accept the offer hold less than 5% of the issued and outstanding share capital of the company or of the applicable class, all of the shares that the acquirer offered to purchase will be transferred to the acquirer by operation of law (provided that a majority of the offerees that do not have a personal interest in such tender offer shall have approved the tender offer except that if the total votes to reject the tender offer represent less than 2% of the company’s issued and outstanding share capital, in the aggregate, approval by a majority of the offerees that do not have a personal interest in such tender offer is not required to complete the tender offer). However, a shareholder that had its shares so transferred may petition the court within six months from the date of acceptance of the full tender offer, whether or not such shareholder agreed to the tender or not, to determine whether the tender offer was for less than fair value and whether the fair value should be paid as determined by the court unless the acquirer stipulated in the tender offer that a shareholder that accepts the offer may not seek appraisal rights. If the shareholders who did not accept the tender offer hold 5% or more of the issued and outstanding share capital of the company or of the applicable class, the acquirer may not acquire shares of the company that will increase its holdings to more than 90% of the company’s issued and outstanding share capital or of the applicable class from shareholders who accepted the tender offer.
Special Tender Offer
The Israeli Companies Law provides that an acquisition of shares of a public Israeli company must be made by means of a special tender offer if as a result of the acquisition the purchaser would become a holder of 25% or more of the voting rights in the company, unless one of the exemptions in the Israeli Companies Law is met. This rule does not apply if there is already another holder of at least 25% of the voting rights in the company. Similarly, the Israeli Companies Law provides that an acquisition of shares in a public company must be made by means of a tender offer if as a result of the acquisition the purchaser would become a holder of 45% or more of the voting rights in the company, if there is no other shareholder of the company who holds 45% or more of the voting rights in the company, unless one of the exemptions in the Israeli Companies Law is met.
A special tender offer must be extended to all shareholders of a company but the offeror is not required to purchase shares representing more than 5% of the voting power attached to the company’s outstanding shares, regardless of how many shares are tendered by shareholders. A special tender offer may be consummated only if (i) at least 5% of the voting power attached to the company’s outstanding shares will be acquired by the offeror and (ii) the number of shares tendered in the offer exceeds the number of shares whose holders objected to the offer.
If a special tender offer is accepted, then the purchaser or any person or entity controlling it or under common control with the purchaser or such controlling person or entity may not make a subsequent tender offer for the purchase of shares of the target company and may not enter into a merger with the target company for a period of one year from the date of the offer, unless the purchaser or such person or entity undertook to effect such an offer or merger in the initial special tender offer.
Merger
The Israeli Companies Law permits merger transactions if approved by each party’s board of directors and, unless certain requirements described under the Israeli Companies Law are met, a majority of each party’s shares voted on the proposed merger at a shareholders’ meeting called with at least 35 days’ prior notice.
| 111 |
For purposes of the shareholder vote, unless a court rules otherwise, the merger will not be deemed approved if a majority of the shares represented at the shareholders meeting that are held by parties other than the other party to the merger, or by any person who holds 25% or more of the outstanding shares or the right to appoint 25% or more of the directors of the other party, vote against the merger. If the transaction would have been approved but for the separate approval of each class or the exclusion of the votes of certain shareholders as provided above, a court may still approve the merger upon the request of holders of at least 25% of the voting rights of a company, if the court holds that the merger is fair and reasonable, taking into account the value of the parties to the merger and the consideration offered to the shareholders.
Upon the request of a creditor of either party to the proposed merger, the court may delay or prevent the merger if it concludes that there exists a reasonable concern that, as a result of the merger, the surviving company will be unable to satisfy the obligations of any of the parties to the merger, and may further give instructions to secure the rights of creditors.
In addition, a merger may not be completed unless at least 50 days have passed from the date that a proposal for approval of the merger was filed by each party with the Israeli Registrar of Companies and 30 days have passed from the date the merger was approved by the shareholders of each party.
Antitakeover Measures
The Israeli Companies Law allows us to create and issue shares having rights different from those attached to our ordinary shares, including shares providing certain preferred rights, distributions or other matters and shares having preemptive rights. As of the date of this annual report, we do not have any authorized or issued shares other than our ordinary shares. In the future, if we do create and issue a class of shares other than ordinary shares, such class of shares, depending on the specific rights that may be attached to them, may delay or prevent a takeover or otherwise prevent our shareholders from realizing a potential premium over the market value of their ordinary shares. The authorization of a new class of shares will require an amendment to our Articles of Association which requires the prior approval of the holders of a majority of our shares at a general meeting. In addition, the rules and regulations of the TASE also limit the terms permitted with respect to a new class of shares and prohibit any such new class of shares from having voting rights. Shareholders voting in such meeting will be subject to the restrictions provided in the Israeli Companies Law as described above.
C. Material Contracts.
The following are summary descriptions of certain material agreements to which we are a party. The descriptions provided below do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by the complete agreements, which are attached as exhibits to this Registration Statement on Form 20-F.
OphthaliX Agreements
On November 21, 2011, we consummated a series of transactions resulting in the acquisition of 82.3% of the issued and outstanding share capital of OphthaliX, Inc., a Delaware corporation (formerly, Denali Concrete Management Inc., a Nevada corporation), whose common shares are traded in the United States on the OTC under the symbol “OPLI”.
The transactions were consummated pursuant to a series of agreements that we executed on November 21, 2011 with OphthaliX to spin-off our activity in the ophthalmology field to OphthaliX, or the Spin-Off Agreements. Prior to entering into the Spin-Off Agreements, we obtained a pre-ruling from the Israeli Tax Authority which prohibits us from selling more than 10% of the OphthaliX common stock that we hold until at least November 21, 2013. If we sell any of such shares prior to such date, we will be subject to a significant tax by the Israeli Tax Authority.
Spin-Off Agreements
Pursuant to the Spin-Off Agreements, we formed Eye-Fite as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ours and transferred to all of the issued and outstanding share capital of Eye-Fite to OphthaliX, such that Eye-Fite became a wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX. In consideration for the transfer of Eye-Fite, OphthaliX issued us 36,000,000 shares of OphthaliX common stock, which represented 86.7% of the issued and outstanding share capital of OphthaliX. In addition to the 36,000,000 shares of OphthaliX common stock that were issued to us in consideration for the transfer of Eye-Fite, we also acquired (i) 2,097,626 shares of OphthaliX common stock that were issued to us in exchange for 17,873,054 (or 714,922 after the reverse stock split) of our ordinary shares, which reflected a price of $1.144 per share of OphthaliX common stock, and (ii) 437,005 shares of OphthaliX common stock that were issued to us as consideration for our investment of $500,000 in OphthaliX, also at a price of $1.144 per share of OphthaliX common stock. We were also granted 1,267,316 warrants exercisable for the equivalent number of shares of OphthaliX common stock. Such warrants have an exercise price of US$1.72 per share and expire on November 20, 2016. As of August 26, 2013, none of the warrants had been exercised.
| 112 |
As a result of the Spin-Off Agreements, we appointed all of the members of the OphthaliX board of directors. According to the terms of the Spin-Off Agreements, OphthaliX will continue the development processes, clinical trials and registration of the ophthalmic indications of CF101.
As part of the acquisition transactions, OphthaliX raised approximately $3.33 million from a group of investors in a private placement of 2,910,456 shares of OphthaliX common stock, which represented approximately 6.2% of the issued and outstanding share capital of OphthaliX. As part of the private placement, Pnina Fishman, our Chief Executive Officer, invested $50,000 in OphthaliX and Guy Regev purchased shares of OphthaliX common stock from former OphthaliX shareholders for $75,000, each after approval by our audit committee and Board of Directors.
The acquisition transactions valued OphthaliX at approximately $50 million.
In connection with the acquisition transactions, we agreed not to withdraw any money from Eye-Fite or OphthaliX, except for the payments under the Services Agreement pursuant to which we are reimbursed for our costs plus 15%. See “—OphthaliX Agreements—Service Agreement”.
For additional information with respect to the Spin-Off Agreements, see “—OphthaliX Agreements—Service Agreement” and “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements—Eye-Fite Agreement”.
Services Agreement
On November 21, 2011, we entered into a services agreement, or the Services Agreement, with OphthaliX and Eye-Fite, pursuant to which we provide management services to OphthaliX and Eye-Fite with respect to (i) all pre-clinical and clinical research studies of CF101 in the ophthalmic field, (ii) drug manufacturing and supply with respect to the compounds related to the Eye-Fite Agreement, (iii) QT studies in human beings, and (iv) payments to consultants that are listed in the Services Agreement for their involvement in the clinical trials and in all other activities necessary to launch CF101 for the treatment of ophthalmic diseases. As consideration for the foregoing services, we will be reimbursed by OphthaliX for our costs and expenses incurred in rendering such services plus 15% (not including VAT, if applicable) and in relation to expenses and costs of intellectual property maintenance, we will “pass through” any such payments and expenses made to third parties and will receive reimbursement for such costs and expenses from OphthaliX. In addition, OphthaliX must abide by all current ongoing clinical trial agreements that we are party to and OphthaliX must pay all payments under those agreements from November 21, 2011 onwards. Further, we are entitled to an additional payment of 2.5%, or the additional payment, of any revenues received by OphthaliX and Eye-Fite in connection with the use of CF101 in the ophthalmic field.
During the five-year period following the date of the execution of the Services Agreement, we are entitled to convert our right to the additional payment into 2,160,102 shares of OphthaliX common stock, representing approximately 5% of the shares of OphthaliX common stock on a fully diluted basis as of the date of closing of the Spin-Off Agreements and the Services Agreement. The Services Agreement is for an unlimited duration. However, following the first anniversary of the execution of the Services Agreement, each party is entitled to terminate the agreement if at least six months’ prior notice, or less with respect to termination for “cause”, as defined in the Services Agreement, is provided to the counterparty.
In February 2013, we sent a formal letter to OphthaliX agreeing to defer payments owed to us under the Services Agreement beginning on January 31, 2013 for the performance of the clinical trials of CF101 in ophthalmic indications until the completion of a fundraising by OphthaliX. Any such deferred payments will bear interest at a rate of 3% per annum from the due date of each invoice issued by us to OphthaliX until the time of payment by OphthaliX.
| 113 |
License Agreement
See “Item 4. Information on the Company—Business Overview—Out-Licensing Agreements—Eye-Fite Agreement”.
Employment and Consulting Agreements
See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees—Compensation—Employment and Consulting Agreements”.
Other Material Contracts
Morningside Memorandum of Understanding
On January 19, 2010, we executed a memorandum of understanding with Morningside Asia Venture (HK) Limited, a Hong Kong limited company, or Morningside.
According to the memorandum of understanding, the parties will establish a joint venture with the exclusive right to develop and commercialize CF102 in the People’s Republic of China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, or the territory. Morningside will provide the entire $7.5 million in financing necessary for the joint venture and the expertise and necessary intellectual resources and contacts needed to advance the development of CF102 towards conclusion of Phase II trials. We will provide all pertinent information in our possession that is relevant to CF102 in order to obtain regulatory permits for it in the territory.
Among other rights set forth in the memorandum of understanding, we will have access to all the clinical and pre-clinical results and data to be developed by the joint venture and will have the right to use all of such information for purposes outside the territory. On the other hand, Morningside will have a right of first offer with respect to the commercial rights, including an exclusive license, in the territory with respect to CF101. Also, prior to the successful commercialization of CF102 in the territory, Morningside will have a right of first refusal with respect to the transfer of any of our shares in the proposed joint venture to a third party.
The memorandum of understanding is subject to the execution and delivery of the appropriate definitive agreements, which are pending as of the date of this Registration Statement.
D. Exchange Controls
There are no Israeli government laws, decrees or regulations that restrict or that affect our export or import of capital or the remittance of dividends, interest or other payments to non-resident holders of our securities, including the availability of cash and cash equivalents for use by us and our wholly-owned subsidiaries, except or otherwise as set forth under “Item 10.E. Additional Information — Taxation.”
E. Taxation
Certain Israeli Tax Considerations
The following is a summary of the material Israeli tax laws applicable to us. This section also contains a discussion of material Israeli tax consequences concerning the ownership and disposition of our ordinary shares. This summary does not discuss all the aspects of Israeli tax law that may be relevant to a particular investor in light of his or her personal investment circumstances or to some types of investors subject to special treatment under Israeli law. Examples of this kind of investor include residents of Israel or traders in securities who are subject to special tax regimes not covered in this discussion. Because certain parts of this discussion are based on new tax legislation that has not yet been subject to judicial or administrative interpretation, we cannot assure you that the appropriate tax authorities or the courts will accept the views expressed in this discussion. The discussion does not cover all possible tax consequences.
| 114 |
You are urged to consult your own tax advisor as to the Israeli and other tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our ADSs, including, in particular, the effect of any non-Israeli, state or local taxes.
General Corporate Tax Structure in Israel
Israeli companies are generally subject to a corporate tax at the rate of 25% of their taxable income in 2012 and thereafter (24% in 2011 and 25% in 2010). Capital gains derived by an Israeli company are generally subject to tax at a rate of 25%, or at the prevailing corporate tax rate, whichever is lower.
In 2006, transfer pricing regulations came into force, following the introduction of Section 85A of the Israeli Tax Ordinance under Amendment 132. The transfer pricing rules require that cross-border transactions between related parties be carried out implementing an arms’ length principle and reported and taxed accordingly.
In 2008, the Knesset passed an amendment to the Income Tax (Inflationary Adjustments) Law, 1985, which limits the scope of the law starting in 2008 and thereafter. Starting in 2008, the revenues for tax purposes are measured in nominal values, excluding certain adjustments for changes in the consumer price index carried out in the period up to December 31, 2007. The amended law includes, among other provisions, the elimination of the inflationary additions and deductions and the additional deduction for depreciation for the period starting in 2008.
Pre-Ruling from the Israeli Income Tax Authorities
In connection with the Spin-Off, the Company received a pre-ruling decision from the Israeli Income Tax Authority which confirms: (i) that the grant of the license to Eye-Fite is not liable for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 104a to the Income Tax Ordinance (New Version), 1961 ("the Ordinance"); (ii) that OphthaliX is considered the receiving company pursuant to section 103c(7)(b) to the Ordinance; (iii) that the sale of Eye-Fite shares to OphthaliX as consideration for OphthaliX shares does not create liability for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 103t to the Ordinance ("change in structure"); and (iv) the date for the change in structure was determined. According to the tax pre-ruling, the date of change in structure shall also be the date of exchange of shares with respect to the spin-off and notification to the tax assessor. The Company and Eye-Fite presented to the tax assessor and the merger and spin-off department of the tax assessor the forms required by the Ordinance and the regulations thereunder. The tax pre-ruling further provides that the grant of a license to Eye-Fite as consideration for the issuance of Eye-Fite shares to the Company does not create liability for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 104a to the Ordinance.
According to the pre-ruling, the Company must not sell more than 10% of its common stock holdings in OphthaliX issued in connection with the change in structure for at least two years from the date of the change (i.e., November 21, 2011), OphthaliX must not sell more than 10% of its ordinary share holdings in Eye-Fite received in connection with the change in structure for at least two years from the date of the change and Eye-Fite must retain the assets received from the Company in connection with the change in structure for at least two years from the date of the change.
The shares of Eye-Fite which were transferred to OphthaliX in connection with the change in structure will be held in escrow. The sale of these shares will be deemed as a sale by an Israeli company and will be taxed accordingly. The trustee will withhold tax at the source.
The shares of OphthaliX which were transferred to the Company in connection with the change in structure will be held in escrow. The sale of these shares will be deemed as a sale by an Israeli company and will be taxed accordingly. The trustee will withhold tax at the source.
Any dividend distributed by Eye-Fite to OphthaliX will be taxed in Israel in accordance with paragraph 125(b)5 of the Israeli Tax Ordinance.
A description of the terms of the pre-ruling is also included in the notes to the financial statements.
| 115 |
Tax Benefits and Grants for Research and Development
Israeli tax law allows, under certain conditions, a tax deduction for research and development expenditures, including capital expenditures, for the year in which they are incurred. These expenses must relate to scientific research and development projects and must be approved by the Office of the Chief Scientist, or the OCS, of the relevant Israeli government ministry, determined by the field of research. Furthermore, the research and development must be for the promotion of the company and carried out by or on behalf of the company seeking such tax deduction. The amount of such deductible expenses is reduced by the sum of any funds received through government grants for the funding of the scientific research and development projects. No deduction under these research and development deduction rules is allowed if such deduction is related to an expense invested in an asset depreciable under the general depreciation rules of the Tax Ordinance. Expenditures not so approved are deductible in equal amounts over three years.
On a yearly basis, we evaluate the applicability of the above tax deduction for research and development expenditures and, based on our evaluation, determine whether to apply to the OCS for approval of a tax deduction. There can be no assurance that any application for a tax deduction will be accepted.
Taxation of our Shareholders
Capital Gains Taxes Applicable to Non-Israeli Resident Shareholders. Shareholders that are not Israeli residents are generally exempt from Israeli capital gains tax on any gains derived from the sale, exchange or disposition of our shares, provided that such shareholders did not acquire their shares prior to our initial public offering on the TASE and such gains were not derived from a permanent establishment or business activity of such shareholders in Israel. However, non-Israeli corporations will not be entitled to the foregoing exemptions if an Israeli resident (i) has a controlling interest of 25% or more in such non-Israeli corporation or (ii) is the beneficiary of or is entitled to 25% or more of the revenues or profits of such non-Israeli corporation, whether directly or indirectly.
In addition, under the U.S.-Israel Income Tax Treaty, 1995, or the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty, the sale, exchange or disposition of our shares by a shareholder who is a U.S. resident (for purposes of the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty) holding the shares as a capital asset is exempt from Israeli capital gains tax unless either (i) the shareholder holds, directly or indirectly, shares representing 10% or more of our voting capital during any part of the 12-month period preceding such sale, exchange or disposition or (ii) the capital gains arising from such sale are attributable to a permanent establishment of the shareholder located in Israel. In either case, the sale, exchange or disposition of the shares would be subject to Israeli tax, to the extent applicable; however, under the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty, the U.S. resident would be permitted to claim a credit for the tax against the U.S. federal income tax imposed with respect to the sale, exchange or disposition, subject to the limitations in U.S. laws applicable to foreign tax credits. The U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty does not relate to U.S. state or local taxes.
Shareholders may be required to demonstrate that they are exempt from tax on their capital gains in order to avoid withholding at source at the time of sale.
Taxation of Non-Israeli Shareholders on Receipt of Dividends. Non-residents of Israel are generally subject to Israeli income tax on the receipt of dividends paid on our shares at the rate of 20%, which tax will be withheld at the source, unless a different rate is provided in a tax treaty between Israel and the shareholder’s country of residence. With respect to a person who is a “substantial shareholder” at the time receiving the dividend or on any date in the 12 months preceding such date, the applicable tax rate is 25%. A “substantial shareholder” is generally a person who alone, or together with his relative or another person who collaborates with him on a permanent basis, holds, directly or indirectly, at least 10% of any of the “means of control” of the corporation. “Means of control” generally include the right to vote, receive profits, nominate a director or an officer, receive assets upon liquidation, or order someone who holds any of the aforesaid rights how to act, and all regardless of the source of such right. Under the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty, the maximum rate of tax withheld in Israel on dividends paid to a holder of our ordinary shares who is a U.S. resident (for purposes of the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty) is 25%. However, generally, the maximum rate of withholding tax on dividends that are paid to a U.S. corporation holding 10% or more of our outstanding voting capital throughout the tax year in which the dividend is distributed as well as the previous tax year is 12.5%.
| 116 |
A non-resident of Israel who receives dividends from which tax was withheld is generally exempt from the duty to file returns in Israel in respect of such income, provided such income was not derived from a business conducted in Israel by the taxpayer, and the taxpayer has no other taxable sources of income in Israel.
Taxation of Israeli Shareholders on Receipt of Dividends
Residents of Israel are generally subject to Israeli income tax on the receipt of dividends paid on our shares at the rate of 25%, which tax will be withheld at the source. With respect to a person who is a “substantial shareholder” at the time of receiving the dividend or on any date within the 12 months preceding such date, the applicable tax rate is 30%.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences
The following is a general summary of what we believe to be material U.S. federal income tax consequences relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our ordinary shares and ADSs by U.S. Investors (as defined below) that hold such shares or ADSs as capital assets. This summary is based on the Internal Revenue Code, or the Code, the regulations of the U.S. Department of the Treasury issued pursuant to the Code, or the Treasury Regulations, and administrative and judicial interpretations thereof, all as in effect on the date hereof and all of which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect, or to different interpretation. No ruling has been sought from the IRS with respect to any United States federal income tax consequences described below, and there can be no assurance that the IRS or a court will not take a contrary position. This summary does not address all of the tax considerations that may be relevant to specific U.S. Investors in light of their particular circumstances or to U.S. Investors subject to special treatment under U.S. federal income tax law (such as banks, insurance companies, tax-exempt entities, retirement plans, regulated investment companies, partnerships, dealers in securities, brokers, real estate investment trusts, certain former citizens or residents of the United States, persons who acquire our shares or ADSs as part of a straddle, hedge, conversion transaction or other integrated investment, persons that have a “functional currency” other than the U.S. dollar, persons that own (or are deemed to own, indirectly or by attribution) 10% or more of our shares or ADSs or persons that generally mark their securities to market for U.S. federal income tax purposes). This summary does not address any U.S. state or local or non-U.S. tax considerations or any U.S. federal estate, gift or alternative minimum tax considerations or any U.S. federal tax consequences other than U.S. federal income tax consequences.
As used in this summary, the term “U.S. Investor” means a beneficial owner of our shares or ADSs that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (i) an individual citizen or resident of the United States, (ii) a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized in or under the laws of the United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia, (iii) an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source or (iv) a trust with respect to which a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over its administration and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all of its substantial decisions, or that has a valid election in effect under applicable Treasury Regulations to be treated as a “United States person.”
If an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds our shares or ADSs, the tax treatment of such partnership and each partner thereof will generally depend upon the status and activities of the partnership and such partner. A holder that is treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to it and its partners of the purchase, ownership and disposition of its shares or ADSs.
Prospective investors should be aware that this summary does not address the tax consequences to investors who are not U.S. Investors. Prospective investors should consult their own tax advisors as to the particular tax considerations applicable to them relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of their shares or ADSs, including the applicability of U.S. federal, state and local tax laws and non-U.S. tax laws.
Taxation of U.S. Investors
The discussions under “— Distributions” and under “— Sale, Exchange or Other Disposition of Ordinary Shares and ADSs” below assumes that we will not be treated as a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes. However, we have not determined whether we will be a PFIC in 2013, and it is possible that we will be a PFIC in 2013 or in any subsequent year. For a discussion of the rules that would apply if we are treated as a PFIC, see the discussion under “— Passive Foreign Investment Company.”
| 117 |
Distributions. We have no current plans to pay dividends. To the extent we pay any dividends, a U.S. Investor will be required to include in gross income as a taxable dividend the amount of any distributions made on the shares or ADSs, including the amount of any Israeli taxes withheld, to the extent that those distributions are paid out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Any distributions in excess of our earnings and profits will be applied against and will reduce the U.S. Investor’s tax basis in its shares or ADSs and to the extent they exceed that tax basis, will be treated as gain from the sale or exchange of those shares or ADSs. If we were to pay dividends, we expect to pay such dividends in NIS with respect to the shares and in U.S. dollars with respect to ADSs . A dividend paid in NIS, including the amount of any Israeli taxes withheld, will be includible in a U.S. Investor’s income as a U.S. dollar amount calculated by reference to the exchange rate in effect on the date such dividend is received, regardless of whether the payment is in fact converted into U.S. dollars. If the dividend is converted to U.S. dollars on the date of receipt, a U.S. Investor generally will not recognize a foreign currency gain or loss. However, if the U.S. Investor converts the NIS into U.S. dollars on a later date, the U.S. Investor must include, in computing its income, any gain or loss resulting from any exchange rate fluctuations. The gain or loss will be equal to the difference between (i) the U.S. dollar value of the amount included in income when the dividend was received and (ii) the amount received on the conversion of the NIS into U.S. dollars. Such gain or loss will generally be ordinary income or loss and United States source for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes. U.S. Investors should consult their own tax advisors regarding the tax consequences to them if we pay dividends in NIS or any other non-U.S. currency.
Subject to certain significant conditions and limitations, including potential limitations under the U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty, any Israeli taxes paid on or withheld from distributions from us and not refundable to a U.S. Investor may be credited against the investor’s U.S. federal income tax liability or, alternatively, may be deducted from the investor’s taxable income. This election is made on a year-by-year basis and applies to all foreign taxes paid by a U.S. Investor or withheld from a U.S. Investor that year. Dividends paid on the shares generally will constitute income from sources outside the United States and be categorized as “passive category income” or, in the case of some U.S. Investors, as “general category income” for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes.
Because the rules governing foreign tax credits are complex, U.S. Investors should consult their own tax advisor regarding the availability of foreign tax credits in their particular circumstances. In addition, the U.S. Treasury Department has expressed concerns that parties to whom ADSs are pre-released may be taking actions that are inconsistent with the claiming of foreign tax credits by U.S. holders of ADSs. Accordingly, the creditability of Israeli taxes could be affected by future actions that may be taken by the U.S. Treasury Department or parties to whom ADSs are pre-released.
Dividends paid on the shares and ADSs will not be eligible for the “dividends-received” deduction generally allowed to corporate U.S. Investors with respect to dividends received from U.S. corporations.
For taxable years beginning after December 31, 2012, certain distributions treated as dividends that are received by an individual U.S. Investor from “qualified foreign corporations” generally qualify for a 20% reduced maximum tax rate so long as certain holding period and other requirements are met. A non-US. corporation (other than a corporation that is treated as a PFIC for the taxable year in which the dividend is paid or the preceding taxable year) generally will be considered to be a qualified foreign corporation (i) if it is eligible for the benefits of a comprehensive tax treaty with the United States which the Secretary of Treasury of the United States determines is satisfactory for purposes of this provision and which includes an exchange of information program, or (ii) with respect to any dividend it pays on stock (or ADSs in respect of such stock) which is readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. Dividends paid by us in a taxable year in which we are not a PFIC and with respect to which we were not a PFIC in the preceding taxable year are expected to be eligible for the 20% reduced maximum tax rate, although we can offer no assurances in this regard. However, any dividend paid by us in a taxable year in which we are a PFIC or were a PFIC in the preceding taxable year will be subject to tax at regular ordinary income rates. As mentioned above, we have not determined whether we are currently a PFIC or not.
| 118 |
Sale, Exchange or Other Disposition of Ordinary Shares and ADSs. Subject to the discussion under “— Passive Foreign Investment Company” below, a U.S. Investor generally will recognize capital gain or loss upon the sale, exchange or other disposition of our shares or ADSs in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the sale, exchange or other disposition and the U.S. Investor’s adjusted tax basis in such shares. This capital gain or loss will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Investor’s holding period in our shares exceeds one year. Preferential tax rates for long-term capital gain (currently, with a maximum rate of 20% for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2012) will apply to individual U.S. Investors. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. The gain or loss will generally be income or loss from sources within the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes, subject to certain exceptions in U.S.-Israel Tax Treaty.
U.S. Investors should consult their own tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of receiving currency other than U.S. dollars upon the disposition of their shares or ADSs.
Passive Foreign Investment Company
In general, a corporation organized outside the United States will be treated as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes in any taxable year in which either (i) at least 75% of its gross income is “passive income” or (ii) on average at least 50% of its assets by value produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, certain dividends, interest, royalties, rents and gains from commodities and securities transactions and from the sale or exchange of property that gives rise to passive income. Passive income also includes amounts derived by reason of the temporary investment of funds, including those raised in the public offering. In determining whether a non-U.S. corporation is a PFIC, a proportionate share of the income and assets of each corporation in which it owns, directly or indirectly, at least a 25% interest (by value) is taken into account.
Under the tests described above, whether or not we are a PFIC will be determined annually based upon the composition of our income and the composition and valuation of our assets, all of which are subject to change.
We have not determined whether we were a PFIC in 2012 or will be in 2013. Because the PFIC determination is highly fact intensive, there can be no assurance that we were not a PFIC in 2012 or will be in any subsequent year.
U.S. Investors should be aware of certain tax consequences of investing directly or indirectly in us if we are a PFIC. A U.S. Investor is subject to different rules depending on whether the U.S. Investor makes an election to treat us as a “qualified electing fund,” known as a QEF election, for the first taxable year that the U.S. Investor holds shares or ADSs, which is referred to in this disclosure as a “timely QEF election,” makes a “mark-to-market” election with respect to the shares or ADSs (if such election is available), or makes neither election.
QEF Election. A U.S. Investor who makes a timely QEF election, referred to in this disclosure as an “Electing U.S. Investor,” with respect to us must report for U.S. federal income tax purposes his pro rata share of our ordinary earnings and net capital gain, if any, for our taxable year that ends with or within the taxable year of the Electing U.S. Investor. The “net capital gain” of a PFIC is the excess, if any, of the PFIC’s net long-term capital gains over its net short-term capital losses. The amount so included in income generally will be treated as ordinary income to the extent of such Electing U.S. Investor’s allocable share of the PFIC’s ordinary earnings and as long-term capital gain to the extent of such Electing U.S. Investor’s allocable share of the PFIC’s net capital gains. Such Electing U.S. Investor generally will be required to translate such income into U.S. dollars based on the average exchange rate for the PFIC’s taxable year with respect to the PFIC’s functional currency. Such income generally will be treated as income from sources outside the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes. Amounts previously included in income by such Electing U.S. Investor under the QEF rules generally will not be subject to tax when they are distributed to such Electing U.S. Investor. The Electing U.S. Investor’s tax basis in our shares or ADSs generally will increase by any amounts so included under the QEF rules and decrease by any amounts not included in income when distributed.
An Electing U.S. Investor will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on such amounts for each taxable year in which we are a PFIC, regardless of whether such amounts are actually distributed to such Electing U.S. Investor. However, an Electing U.S. Investor may, subject to certain limitations, elect to defer payment of current U.S. federal income tax on such amounts, subject to an interest charge. If an Electing U.S. Investor is an individual, any such interest will be treated as non-deductible “personal interest.”
| 119 |
Any net operating losses or net capital losses of a PFIC will not pass through to the Electing U.S. Investor and will not offset any ordinary earnings or net capital gain of a PFIC recognized by Electing U.S. Investors in subsequent years.
So long as an Electing U.S. Investor’s QEF election with respect to us is in effect with respect to the entire holding period for our shares or ADSs, any gain or loss recognized by such Electing U.S. Investor on the sale, exchange or other disposition of such shares or ADSs generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if such Electing U.S. Investor has held such shares or ADSs for more than one year at the time of such sale, exchange or other disposition. Preferential tax rates for long-term capital gain (currently, a maximum rate of 20% for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2012) will apply to individual U.S. Investors. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
In general, a U.S. Investor must make a QEF election on or before the due date for filing its income tax return for the first year to which the QEF election is to apply. A U.S. Investor makes a QEF election by completing the relevant portions of and filing IRS Form 8621 in accordance with the instructions thereto. Upon request, we will annually furnish U.S. Investors with information needed in order to complete IRS Form 8621 (which form would be required to be filed with the IRS on an annual basis by the U.S. Investor) and to make and maintain a valid QEF election for any year in which we or any of our subsidiaries that we control is a PFIC. There is no assurance, however, that we will have timely knowledge of our status as a PFIC, or that the information that we provide will be adequate to allow U.S. Investors to make a QEF election. A QEF election will not apply to any taxable year during which we are not a PFIC, but will remain in effect with respect to any subsequent taxable year in which we become a PFIC. Each U.S. Investor should consult its own tax advisor with respect to the advisability of, the tax consequences of, and the procedures for making a QEF election with respect to us.
Mark-to-Market Election. Alternatively, if our shares or ADSs are treated as “marketable stock,” a U.S. Investor would be allowed to make a “mark-to-market” election with respect to our shares or ADSs, provided the U.S. Investor completes and files IRS Form 8621 in accordance with the relevant instructions and related Treasury Regulations. If that election is made, the U.S. Investor generally would include as ordinary income in each taxable year the excess, if any, of the fair market value of our shares or ADSs at the end of the taxable year over such holder’s adjusted tax basis in such shares or ADSs. The U.S. Investor would also be permitted an ordinary loss in respect of the excess, if any, of the U.S. Investor’s adjusted tax basis in our shares or ADSs over their fair market value at the end of the taxable year, but only to the extent of the net amount previously included in income as a result of the mark-to-market election. A U.S. Investor’s tax basis in our shares or ADSs would be adjusted to reflect any such income or loss amount. Gain realized on the sale, exchange or other disposition of our shares or ADSs would be treated as ordinary income, and any loss realized on the sale, exchange or other disposition of our shares or ADSs would be treated as ordinary loss to the extent that such loss does not exceed the net mark-to-market gains previously included in income by the U.S. Investor, and any loss in excess of such amount will be treated as capital loss. Amounts treated as ordinary income will not be eligible for the favorable tax rates applicable to qualified dividend income or long-term capital gains.
Generally, stock will be considered marketable stock if it is “regularly traded” on a “qualified exchange” within the meaning of applicable Treasury Regulations. A class of stock is regularly traded on an exchange during any calendar year during which such class of stock is traded, other than in de minimis quantities, on at least 15 days during each calendar quarter. To be marketable stock, our shares and ADSs must be regularly traded on a qualifying exchange (i) in the United States that is registered with the SEC or a national market system established pursuant to the Exchange Act. or (ii) outside the United States that is properly regulated and meets certain trading, listing, financial disclosure and other requirements. Our shares should constitute “marketable stock” as long as they remain listed on the OTC and/or the NYSE MKT and are regularly traded. Our ADSs will be listed on the OTC and/or the NYSE MKT. While we believe that our ADSs may be treated as marketable stock for purposes of the PFIC rules so long as they are listed on the OTC and/or the NYSE MKT and are regularly traded, the IRS has not provided a list of the exchanges that meet the foregoing requirements and thus no assurance can be provided that our ADSs will be (or will remain) treated as marketable stock for purposes of the PFIC rules.
A mark-to-market election will not apply to our shares or ADSs held by a U.S. Investor for any taxable year during which we are not a PFIC, but will remain in effect with respect to any subsequent taxable year in which we become a PFIC. Such election will not apply to any PFIC subsidiary that we own. Each U.S. Investor is encouraged to consult its own tax advisor with respect to the availability and tax consequences of a mark-to-market election with respect to our shares and ADSs.
| 120 |
Default PFIC Rules. A U.S. Investor who does not make a timely QEF election or a mark-to-market election, referred to in this disclosure as a “Non-Electing U.S. Investor,” will be subject to special rules with respect to (i) any “excess distribution” (generally, the portion of any distributions received by the Non-Electing U.S. Investor on the shares or ADSs in a taxable year in excess of 125% of the average annual distributions received by the Non-Electing U.S. Investor in the three preceding taxable years, or, if shorter, the Non-Electing U.S. Investor’s holding period for the shares or ADSs), and (ii) any gain realized on the sale or other disposition of such shares or ADSs. Under these rules:
| · | the excess distribution or gain would be allocated ratably over the Non-Electing U.S. Investor’s holding period for such shares or ADSs; |
| · | the amount allocated to the current taxable year and any year prior to us becoming a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income; and |
| · | the amount allocated to each of the other taxable years would be subject to tax at the highest rate of tax in effect for the applicable class of taxpayer for that year, and an interest charge for the deemed deferral benefit would be imposed with respect to the resulting tax attributable to each such other taxable year. |
If a Non-Electing U.S. Investor who is an individual dies while owning our shares or ADSs, the Non-Electing U.S. Investor’s successor would be ineligible to receive a step-up in tax basis of such shares or ADSs. Non-Electing U.S. Investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the PFIC rules to their specific situation.
A Non-Electing U.S. Investor who wishes to make a QEF election for a subsequent year may be able to make a special “purging election” pursuant to Section 1291(d) of the Code. Pursuant to this election, a Non-Electing U.S. Investor would be treated as selling his or her shares or ADSs for fair market value on the first day of the taxable year for which the QEF election is made. Any gain on such deemed sale would be subject to tax under the rules for Non-Electing U.S. Investors as discussed above. Non-Electing U.S. Investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the availability of a “purging election” as well as other available elections.
To the extent a distribution on our shares or ADSs does not constitute an excess distribution to a Non-Electing U.S. Investor, such Non-Electing U.S. Investor generally will be required to include the amount of such distribution in gross income as a dividend to the extent of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes) that are not allocated to excess distributions. The tax consequences of such distributions are discussed above under “— Taxation of U.S. Investors — Distributions.” Each U.S. Holder is encouraged to consult its own tax advisor with respect to the appropriate U.S. federal income tax treatment of any distribution on our shares.
If we are treated as a PFIC for any taxable year during the holding period of a Non-Electing U.S. Investor, we will continue to be treated as a PFIC for all succeeding years during which the Non-Electing U.S. Investor is treated as a direct or indirect Non-Electing U.S. Investor even if we are not a PFIC for such years. A U.S. Investor is encouraged to consult its tax advisor with respect to any available elections that may be applicable in such a situation, including the “deemed sale” election of Code Section 1298(b)(1) (which will be taxed under the adverse tax rules described above). In addition, U.S. Investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the IRS information reporting and filing obligations that may arise as a result of the ownership of shares in a PFIC.
We may invest in the equity of foreign corporations that are PFICs or may own subsidiaries that own PFICs. If we are classified as a PFIC, under attribution rules U.S. Investors will be subject to the PFIC rules with respect to their indirect ownership interests in such PFICs, such that a disposition of the shares of the PFIC or receipt by us of a distribution from the PFIC generally will be treated as a deemed disposition of such shares or the deemed receipt of such distribution by the U.S. Investor, subject to taxation under the PFIC rules. There can be no assurance that a U.S. Investor will be able to make a QEF election or a mark-to-market election with respect to PFICs in which we invest. Each U.S. Investor is encouraged to consult its own tax advisor with respect to tax consequences of an investment by us in a corporation that is a PFIC.
| 121 |
The U.S. federal income tax rules relating to PFICs, QEF elections, and mark-to market elections are complex. U.S. Investors are urged to consult their own tax advisors with respect to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our shares or ADSs, any elections available with respect to such shares or ADSs and the IRS information reporting obligations with respect to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our shares or ADSs.
Certain Reporting Requirements
Certain U.S. Investors are required to file IRS Form 926, Return by U.S. Transferor of Property to a Foreign Corporation, and certain U.S. Investors may be required to file IRS Form 5471, Information Return of U.S. Persons With Respect to Certain Foreign Corporations, reporting transfers of cash or other property to us and information relating to the U.S. Investor and us. Substantial penalties may be imposed upon a U.S. Investor that fails to comply.
In addition, recently enacted legislation requires certain U.S. Investors to report information on IRS Form 8938 with respect to their investments in certain “foreign financial assets,” which under certain circumstances would include an investment in our shares and ADSs, to the IRS.
Investors who fail to report required information could become subject to substantial penalties. U.S. Investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the possible implications of these reporting requirements on their investment in our shares and ADSs.
Backup Withholding Tax and Information Reporting Requirements
Generally, information reporting requirements will apply to distributions on our shares or ADSs or proceeds on the disposition of our shares or ADSs paid within the United States (and, in certain cases, outside the United States) to U.S. Investors other than certain exempt recipients, such as corporations. Furthermore, backup withholding (currently at 28%) may apply to such amounts if the U.S. Investor fails to (i) provide a correct taxpayer identification number, (ii) report interest and dividends required to be shown on its U.S. federal income tax return, or (iii) make other appropriate certifications in the required manner. U.S. Investors who are required to establish their exempt status generally must provide such certification on IRS Form W-9.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Amounts withheld as backup withholding from a payment may be credited against a U.S. Investor’s U.S. federal income tax liability and such U.S. Investor may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by filing the appropriate claim for refund with the IRS and furnishing any required information in a timely manner.
New Legislative Developments
With respect to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2012, certain U.S. persons, including individuals, estates and trusts, will be subject to an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on unearned income. For individuals, the additional Medicare tax applies to the lesser of (i) “net investment income” or (ii) the excess of “modified adjusted gross income” over $200,000 ($250,000 if married and filing jointly or $125,000 if married and filing separately). “Net investment income” generally equals the taxpayer’s gross investment income reduced by the deductions that are allocable to such income. Investment income generally includes passive income such as interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, rents, and capital gains. U.S. Investors are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the implications of the additional Medicare tax resulting from their ownership and disposition of our shares or ADSs.
U.S. Investors should consult their own tax advisors concerning the tax consequences relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our shares or ADSs.
| 122 |
F. Dividends and Paying Agents.
We have never declared or paid cash dividends to our shareholders. Currently we do not intend to pay cash dividends. We intend to reinvest any earnings in developing and expanding our business. Any future determination relating to our dividend policy will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on a number of factors, including future earnings, our financial condition, operating results, contractual restrictions, capital requirements, business prospects, applicable Israeli law and other factors our Board of Directors may deem relevant. Accordingly, we have not appointed any paying agent.
G. Statements by Experts.
The consolidated financial statements of Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2012 and 2011 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2012 appearing in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F have been audited by Kost, Forer, Gabbay & Kasserier, a member of Ernst &Young Global, an independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
H. Documents on Display.
When this Registration Statement on Form 20-F becomes effective, we will be subject to the information reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, applicable to foreign private issuers and under those requirements will file reports with the SEC. Those other reports or other information and this Registration Statement may be inspected without charge at 10 Bareket Street, Kiryat Matalon, Petah-Tikva 4951778, Israel, and inspected and copied at the public reference facilities of the SEC located at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may also obtain copies of the documents at prescribed rates by writing to the Public Reference Section of the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the public reference room. The SEC also maintains a website at http://www.sec.gov from which certain filings may be accessed.
As a foreign private issuer, we will be exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act related to the furnishing and content of proxy statements, and our officers, directors and principal shareholders will be exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. In addition, we will not be required under the Exchange Act to file annual, quarterly and current reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as United States companies whose securities are registered under the Exchange Act. However, we will file with the SEC, within 120 days after the end of each fiscal year, or such applicable time as required by the SEC, an annual report on Form 20-F containing financial statements audited by an independent registered public accounting firm, and will submit to the SEC, on a Form 6-K, unaudited quarterly financial information.
In addition, because our ordinary shares are traded on the TASE, we have filed Hebrew language periodic and immediate reports with, and furnish information to, the TASE and the ISA, as required under Chapter Six of the Israel Securities Law, 1968. Copies of our filings with the ISA can be retrieved electronically through the MAGNA distribution site of the ISA (www.magna.isa.gov.il) and the TASE website (www.maya.tase.co.il).
We maintain a corporate website at www.canfite.com. Information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website does not constitute a part of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F. We have included our website address in this Registration Statement on Form 20-F solely as an inactive textual reference.
I. Subsidiary Information.
Not applicable.
| 123 |
ITEM 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Market risk is the risk of loss related to changes in market prices, including interest rates and foreign exchange rates, of financial instruments that may adversely impact our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Interest Rate Risk
Following the filing of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F, we do not anticipate undertaking any significant long-term borrowings. At present, our investments consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents. Following this filing, we may invest in investment-grade marketable securities with maturities of up to three years, including commercial paper, money market funds, and government/non-government debt securities. The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while maximizing the income that we receive from our investments without significantly increasing risk and loss. Our investments are exposed to market risk due to fluctuation in interest rates, which may affect our interest income and the fair market value of our investments, if any. We manage this exposure by performing ongoing evaluations of our investments. Due to the short-term maturities, if any, of our investments to date, their carrying value has always approximated their fair value. If we decide to invest in investments other than cash and cash equivalents, it will be our policy to hold such investments to maturity in order to limit our exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
Our foreign currency exposures give rise to market risk associated with exchange rate movements of the NIS, our functional and reporting currency, mainly against the dollar and the euro. Although the NIS is our functional currency, a significant portion of our expenses are denominated in both dollars and Euros and currently all of our revenues are denominated in dollars. Our U.S. dollar and euro expenses consist principally of payments made to sub-contractors and consultants for preclinical studies, clinical trials and other research and development activities. We anticipate that a sizable portion of our expenses will continue to be denominated in currencies other than the NIS. If the NIS fluctuates significantly against either the U.S. dollar or the euro, it may have a negative impact on our results of operations. To date, fluctuations in the exchange rates have not materially affected our results of operations or financial condition for the periods under review.
To date, we have not engaged in hedging transactions. In the future, we may enter into currency hedging transactions to decrease the risk of financial exposure from fluctuations in the exchange rates of our principal operating currencies. These measures, however, may not adequately protect us from the material adverse effects of such fluctuations.
ITEM 12. Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities
A. Debt Securities.
Not applicable.
B. Warrants and Rights.
Not applicable.
C. Other Securities.
Not applicable.
D. American Depositary Shares
The Bank of New York Mellon, as Depositary, will register and deliver American Depositary Shares, or ADSs. Each ADS will represent two (2) ordinary shares (or a right to receive two (2) ordinary shares) deposited with the principal Tel Aviv office of Bank Hapoalim, as custodian for the Depositary. Each ADS will also represent any other securities, cash or other property which may be held by the Depositary. The Depositary’s corporate trust office at which the ADSs will be administered is located at 101 Barclay Street, New York, New York 10286. The Bank of New York Mellon’s principal executive office is located at One Wall Street, New York, New York 10286.
| 124 |
You may hold ADSs either (i) directly (a) by having an American Depositary Receipt, or an ADR, which is a certificate evidencing a specific number of ADSs, registered in your name, or (b) by having ADSs registered in your name in the Direct Registration System, or DRS, or (ii) indirectly by holding a security entitlement in ADSs through your broker or other financial institution. If you hold ADSs directly, you are a registered ADS holder, or an ADS holder. The description in this section assumes you are an ADS holder. If you hold the ADSs indirectly, you must rely on the procedures of your broker or other financial institution to assert the rights of ADS holders described in this section. You should consult with your broker or financial institution to find out what those procedures are.
The DRS is a system administered by The Depository Trust Company, or DTC, pursuant to which the Depositary may register the ownership of uncertificated ADSs, which ownership is confirmed by periodic statements sent by the Depositary to the registered holders of uncertificated ADSs.
As an ADS holder, we will not treat you as one of our shareholders and you will not have shareholder rights. Israeli law governs shareholder rights. The Depositary will be the holder of the shares underlying your ADSs. As a registered holder of ADSs, you will have ADS holder rights. The Deposit Agreement, or the Deposit Agreement, among us, the Depositary and you, as an ADS holder, and all other persons indirectly holding ADSs sets out ADS holder rights as well as the rights and obligations of the Depositary. New York law governs the Deposit Agreement and the ADSs.
The following is a summary of the material provisions of the Deposit Agreement. For more complete information, you should read the entire Deposit Agreement and the form of ADS. Directions on how to obtain copies of those documents are provided under “Item 10.H. Documents on Display”.
Dividends and Other Distributions
How will you receive dividends and other distributions on the shares?
The Depositary has agreed to pay to ADS holders the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on shares or other deposited securities, after deducting its fees and expenses. You will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of ordinary shares your ADSs represent.
| · | Cash. The Depositary will convert any cash dividend or other cash distribution we pay on the shares into U.S. dollars, if it can do so on a reasonable basis and can transfer the U.S. dollars to the United States. If that is not possible or if any government approval is needed and cannot be obtained, the Deposit Agreement allows the Depositary to distribute the foreign currency only to those ADS holders to whom it is possible to do so. It will hold the foreign currency it cannot convert for the account of the ADS holders who have not been paid. It will not invest the foreign currency and it will not be liable for any interest. |
Before making a distribution, any withholding taxes, or other governmental charges that must be paid will be deducted. See “Item 10—Additional Information—Taxation—Certain Israeli Tax Considerations”. It will distribute only whole U.S. dollars and cents and will round fractional cents to the nearest whole cent. If the exchange rates fluctuate during a time when the Depositary cannot convert the foreign currency, you may lose some or all of the value of the distribution.
| · | Shares. The Depositary may distribute additional ADSs representing any shares we distribute as a dividend or free distribution. The Depositary will only distribute whole ADSs. It will sell shares which would require it to deliver a fractional ADS and distribute the net proceeds in the same way as it does with cash. If the Depositary does not distribute additional ADSs, the outstanding ADSs will also represent the new shares. The Depositary may sell a portion of the distributed shares sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution. |
| 125 |
| · | Rights to purchase additional shares. If we offer holders of our securities any rights to subscribe for additional shares or any other rights, the Depositary may make these rights available to ADS holders. If the Depositary decides it is not legal and practical to make the rights available but that it is practical to sell the rights, the Depositary will use reasonable efforts to sell the rights and distribute the proceeds in the same way as it does with cash. The Depositary will allow rights that are not distributed or sold to lapse. In that case, you will receive no value for them. |
If the Depositary makes rights available to ADS holders, it will exercise the rights and purchase the shares on your behalf. The Depositary will then deposit the shares and deliver ADSs to the persons entitled to them. It will only exercise rights if you pay it the exercise price and any other charges the rights require you to pay.
U.S. securities laws may restrict transfers and cancellation of the ADSs represented by shares purchased upon exercise of rights. For example, you may not be able to trade these ADSs freely in the United States. In this case, the Depositary may deliver restricted Depositary shares that have the same terms as the ADSs described in this section except for changes needed to put the necessary restrictions in place.
| · | Other Distributions. The Depositary will send to ADS holders anything else we distribute on deposited securities by any means it thinks is legal, fair and practicable. If it cannot make the distribution in that way, the Depositary has a choice. It may decide to sell what we distributed and distribute the net proceeds, in the same way as it does with cash. Or, it may decide to hold what we distributed, in which case ADSs will also represent the newly distributed property. However, the Depositary is not required to distribute any securities (other than ADSs) to ADS holders unless it receives satisfactory evidence from us that it is legal to make that distribution. The Depositary may sell a portion of the distributed securities or property sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution. |
The Depositary is not responsible if it decides that it is unlawful or impracticablele to make a distribution available to any ADS holders. We have no obligation to register ADSs, shares, rights or other securities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. We also have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of ADSs, shares, rights or anything else to ADS holders. This means that you may not receive the distributions we make on our shares or any value for them if it is illegal or impracticablele for us to make them available to you.
Deposit, Withdrawal and Cancellation
How are ADSs issued?
The Depositary will deliver ADSs if you or your broker deposit shares or evidence of rights to receive shares with the custodian. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or stock transfer taxes or fees, the Depositary will register the appropriate number of ADSs in the names you request and will deliver the ADSs to or upon the order of the person or persons that made the deposit.
How can ADS holders withdraw the deposited securities?
You may surrender your ADSs at the Depositary’s corporate trust office. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or stock transfer taxes or fees, the Depositary will deliver the shares and any other deposited securities underlying the ADSs to the ADS holder or a person the ADS holder designates at the office of the custodian. Or, at your request, risk and expense, the Depositary will deliver the deposited securities at its corporate trust office, if feasible.
How do ADS holders interchange between certificated ADSs and uncertificated ADSs?
You may surrender your ADR to the Depositary for the purpose of exchanging your ADR for uncertificated ADSs. The Depositary will cancel that ADR and will send to the ADS holder a statement confirming that the ADS holder is the registered holder of uncertificated ADSs. Alternatively, upon receipt by the Depositary of a proper instruction from a registered holder of uncertificated ADSs requesting the exchange of uncertificated ADSs for certificated ADSs, the Depositary will execute and deliver to the ADS holder an ADR evidencing those ADSs.
| 126 |
Voting Rights
How do you vote?
ADS holders may instruct the Depositary to vote the number of deposited shares their ADSs represent. The Depositary will notify ADS holders of shareholders’ meetings and arrange to deliver our voting materials to them if we ask it to. Those materials will describe the matters to be voted on and explain how ADS holders may instruct the Depositary how to vote. For instructions to be valid, they must reach the Depositary by a date set by the Depositary. Otherwise, you will not be able to exercise your right to vote unless you withdraw the shares. To do so, however, you would need to know about the meeting sufficiently in advance to withdraw the shares.
The Depositary will try, as far as practical, subject to the laws of Israel and of our Articles of Association or similar documents, to vote or to have its agents vote the shares or other deposited securities as instructed by ADS holders. The Depositary will only vote or attempt to vote as instructed.
We cannot assure you that you will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that you can instruct the Depositary to vote your shares. In addition, the Depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions or for the manner of carrying out voting instructions. This means that you may not be able to exercise your right to vote and there may be nothing you can do if your shares are not voted as you requested.
In order to give you a reasonable opportunity to instruct the Depositary as to the exercise of voting rights relating to deposited securities, if we request the Depositary to act, we agree to give the Depositary notice of any such meeting and details concerning the matters to be voted upon not less than 45 days in advance of the meeting date.
Fees and Expenses
| Persons depositing
or withdrawing shares or ADS holders must pay: |
For: | |
| $5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) | · Issuance of ADSs, including issuances resulting from a distribution of shares or rights or other property
· Cancellation of ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal, including if the Deposit Agreement terminates | |
| $.05 (or less) per ADS | · Any cash distribution to ADS holders | |
| A fee equivalent to the fee that would be payable if securities distributed to you had been shares and the shares had been deposited for issuance of ADSs | · Distribution of securities distributed to holders of deposited securities which are distributed by the Depositary to ADS holders | |
| $.05 (or less) per ADSs per calendar year | · Depositary services | |
| Registration or transfer fees | · Transfer and registration of shares on our share register to or from the name of the Depositary or its agent when you deposit or withdraw shares | |
| Expenses of the Depositary | · Cable, telex and facsimile transmissions (when expressly provided in the Deposit Agreement)
· Converting foreign currency to U.S. dollars | |
| Taxes and other governmental charges the Depositary or the custodian have to pay on any ADS or share underlying an ADS, for example, stock transfer taxes, stamp duty or withholding taxes | · As necessary
| |
| Any charges incurred by the Depositary or its agents for servicing the deposited securities | · As necessary |
| 127 |
The Depositary collects its fees for delivery and surrender of ADSs directly from investors depositing shares or surrendering ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal or from intermediaries acting for them. The Depositary collects fees for making distributions to investors by deducting those fees from the amounts distributed or by selling a portion of distributable property to pay the fees. The Depositary may collect its annual fee for depositary services by deduction from cash distributions, by directly billing investors or by charging the book-entry system accounts of participants acting for them. The Depositary may generally refuse to provide fee-attracting services until its fees for those services are paid.
From time to time, the Depositary may make payments to us to reimburse us for expenses and/or share revenue with us from the fees collected from ADS holders, or waive fees and expenses for services provided, generally relating to costs and expenses arising out of the establishment and maintenance of the ADS program. In performing its duties under the Deposit Agreement, the Depositary may use brokers, dealers or other service providers that are affiliates of the Depositary and that may earn or share fees or commissions.
Payment of Taxes
You will be responsible for any taxes or other governmental charges payable on your ADSs or on the deposited securities represented by any of your ADSs. The Depositary may refuse to register any transfer of your ADSs or allow you to withdraw the deposited securities represented by your ADSs until such taxes or other charges are paid. It may apply payments owed to you or sell deposited securities represented by your ADSs to pay any taxes owed and you will remain liable for any deficiency. If the Depositary sells deposited securities, it will, if appropriate, reduce the number of ADSs to reflect the sale and pay to ADS holders any proceeds, or send to ADS holders any property, remaining after it has paid the taxes.
| 128 |
Reclassifications, Recapitalizations and Mergers
| If we: | Then: | |
· Change the nominal or par value of our shares
· Reclassify, split up or consolidate any of the deposited securities
· Distribute securities on the shares that are not distributed to you
· Recapitalize, reorganize, merge, liquidate, sell all or substantially all of our assets, or take any similar action |
The cash, shares or other securities received by the Depositary will become deposited securities. Each ADS will automatically represent its equal share of the new deposited securities.
The Depositary may, and will if we ask it to, distribute some or all of the cash, shares or other securities it received. It may also deliver new ADRs or ask you to surrender your outstanding ADRs in exchange for new ADRs identifying the new deposited securities. |
Amendment and Termination
How may the Deposit Agreement be amended?
We may agree with the Depositary to amend the Deposit Agreement and the ADRs without your consent for any reason. If an amendment adds or increases fees or charges, except for taxes and other governmental charges or expenses of the Depositary for registration fees, facsimile costs, delivery charges or similar items, or prejudices a substantial right of ADS holders, it will not become effective for outstanding ADSs until 30 days after the Depositary notifies ADS holders of the amendment. At the time an amendment becomes effective, you are considered, by continuing to hold your ADSs, to agree to the amendment and to be bound by the ADRs and the Deposit Agreement, as amended.
How may the Deposit Agreement be terminated?
The Depositary will terminate the Deposit Agreement at our direction by mailing notice of termination to the ADS holders then outstanding at least 30 days prior to the date fixed in such notice for such termination. The Depositary may also terminate the Deposit Agreement by mailing notice of termination to us and the ADS holders if 60 days have passed since the Depositary told us it wants to resign but a successor depositary has not been appointed and accepted its appointment.
After termination, the Depositary and its agents will do the following under the Deposit Agreement, but nothing else: collect distributions on the deposited securities, sell rights and other property, and deliver shares and other deposited securities upon cancellation of ADSs. Four months after termination, the Depositary may sell any remaining deposited securities by public or private sale. After that, the Depositary will hold the money it received on the sale, as well as any other cash it is holding under the Deposit Agreement for the pro rata benefit of the ADS holders that have not surrendered their ADSs. It will not invest the money and has no liability for interest. The Depositary’s only obligations will be to account for the money and other cash. After termination, our only obligations will be to indemnify the Depositary and to pay fees and expenses of the Depositary that we agreed to pay.
| 129 |
Limitations on Obligations and Liability
Limits on our Obligations and the Obligations of the Depositary; Limits on Liability to ADS Holders
The Deposit Agreement expressly limits our obligations and the obligations of the Depositary. It also limits our liability and the liability of the Depositary. We and the Depositary:
| · | are only obligated to take the actions specifically set forth in the Deposit Agreement without negligence or bad faith; |
| · | are not liable if we are or it is prevented or delayed by law or circumstances beyond our control from performing our or its obligations under the Deposit Agreement; |
| · | are not liable if we or it exercises discretion permitted under the Deposit Agreement; |
| · | are not liable for the inability of any holder of ADSs to benefit from any distribution on deposited securities that is not made available to holders of ADSs under the terms of the Deposit Agreement, or for any special, consequential or punitive damages for any breach of the terms of the Deposit Agreement; |
| · | have no obligation to become involved in a lawsuit or other proceeding related to the ADSs or the Deposit Agreement on your behalf or on behalf of any other person; and |
| · | may rely upon any documents we believe or it believes in good faith to be genuine and to have been signed or presented by the proper person. |
In the Deposit Agreement, we and the Depositary agree to indemnify each other under certain circumstances.
Requirements for Depositary Actions
Before the Depositary will deliver or register a transfer of an ADS, make a distribution on an ADS, or permit withdrawal of shares, the Depositary may require:
| · | payment of stock transfer or other taxes or other governmental charges and transfer or registration fees charged by third parties for the transfer of any shares or other deposited securities; |
| · | satisfactory proof of the identity and genuineness of any signature or other information it deems necessary; and |
| · | compliance with regulations it may establish, from time to time, consistent with the Deposit Agreement, including presentation of transfer documents. |
The Depositary may refuse to deliver ADSs or register transfers of ADSs generally when the transfer books of the Depositary or our transfer books are closed or at any time if the Depositary or we think it advisable to do so.
Your Right to Receive the Shares Underlying your ADSs
ADS holders have the right to cancel their ADSs and withdraw the underlying shares at any time except:
| · | when temporary delays arise because: (i) the Depositary has closed its transfer books or we have closed our transfer books; (ii) the transfer of shares is blocked to permit voting at a shareholders’ meeting; or (iii) we are paying a dividend on our shares; |
| · | when you owe money to pay fees, taxes and similar charges; or |
| · | when it is necessary to prohibit withdrawals in order to comply with any laws or governmental regulations that apply to ADSs or to the withdrawal of shares or other deposited securities. |
This right of withdrawal may not be limited by any other provision of the Deposit Agreement.
| 130 |
Pre-release of ADSs
Subject to the provisions of the Deposit Agreement, the Depositary may issue ADSs before deposit of the underlying shares. This is called a pre-release of ADSs. The Depositary may also deliver shares prior to the receipt and cancellation of pre-released ADSs even if the ADSs are cancelled before the pre-release transaction has been closed out. A pre-release is closed out as soon as the underlying shares are delivered to the Depositary. The Depositary may receive ADSs instead of shares to close out a pre-release. The Depositary may pre-release ADSs only under the following conditions:
| · | before or at the time of the pre-release, the person to whom the pre-release is being made must represent to the Depositary in writing that it or its customer, as the case may be, |
| · | owns the shares or ADSs to be remitted; |
| · | will assign all beneficial rights, title and interest in the ADSs or shares to the Depositary and for the benefit of the ADS holders; and |
| · | will not take any action with respect to the ADSs or shares that is inconsistent with the assignment of beneficial ownership (including, without the consent of the Depositary, disposing of the ADSs or shares) other than in satisfaction of the pre-release; |
| · | the pre-release must be fully collateralized with cash or collateral that the Depositary considers appropriate; and |
| · | the Depositary must be able to close out the pre-release on not more than five business days’ notice. |
The pre-release will be subject to whatever indemnities and credit regulations that the Depositary considers appropriate. In addition, the Depositary will limit the number of ADSs that may be outstanding at any time as a result of pre-release, although the Depositary may disregard the limit from time to time, if it thinks it is appropriate to do so. At our instruction, a pre-release may be discontinued entirely.
Direct Registration System
In the Deposit Agreement, all parties to the Deposit Agreement acknowledge that the DRS and Profile Modification System, or Profile, will apply to uncertificated ADSs upon acceptance thereof to DRS by DTC. DRS is the system administered by DTC under which the Depositary may register the ownership of uncertificated ADSs, which ownership will be evidenced by periodic statements sent by the Depositary to the registered holders of uncertificated ADSs. Profile is a required feature of DRS that allows a DTC participant, claiming to act on behalf of a registered holder of ADSs, to direct the Depositary to register a transfer of those ADSs to DTC or its nominee and to deliver those ADSs to the DTC account of that DTC participant without receipt by the Depositary of prior authorization from the ADS holder to register that transfer.
In connection with and in accordance with the arrangements and procedures relating to DRS/Profile, the parties to the Deposit Agreement understand that the Depositary will not determine whether the DTC participant that is claiming to be acting on behalf of an ADS holder in requesting registration of transfer and delivery described in the paragraph above has the actual authority to act on behalf of the ADS holder (notwithstanding any requirements under the Uniform Commercial Code). In the Deposit Agreement, the parties agree that the Depositary’s reliance on and compliance with instructions received by the Depositary through the DRS/Profile and in accordance with the Deposit Agreement will not constitute negligence or bad faith on the part of the Depositary.
Shareholder Communications; Inspection of Register ADS Holders
The Depositary will make available for your inspection at its office all communications that it receives from us as a holder of deposited securities that we make generally available to holders of deposited securities. The Depositary will send you copies of those communications if we ask it to. You have a right to inspect the register of holders of ADSs, but not for the purpose of contacting those holders about a matter unrelated to our business or the ADSs.
| 131 |
Disclosure of Beneficial Ownership
The Company may from time to time request that ADS holders provide information as to the capacity in which they hold ADSs or a beneficial interest in such ADSs and regarding the identity of any other persons then or previously having a beneficial interest in ADSs, and the nature of such interest and various other matters. ADS holders agree to provide such information reasonably requested by the Company pursuant to the Deposit Agreement. The Depositary agrees to comply with reasonable written instructions received from time to time from the Company requesting that the Depositary forward any such written requests to the Owners and to forward to the Company any such responses to such requests received by the Depositary.
Each ADS holder agrees to comply with any applicable provision of Israeli law with regard to the notification to the Company of the holding or proposed holding of certain interests in the underlying ordinary shares and the obtaining of certain consents, to the same extent as if such ADS holder were a registered holder or beneficial owner of the underlying ordinary shares. The Depositary is not required to take any action with respect to such compliance on behalf of any ADS holder, including the provision of the notifications described below.
As of the date of the Deposit Agreement, under Israeli law, persons who hold a direct or indirect interest in 5% or more of the voting securities of the Company (including persons who hold such an interest through the holding of ADSs) are required to give written notice of their interest and any subsequent changes in their interest to the Company within the timeframes set forth in Israeli law. The foregoing is a summary of the relevant provision of Israeli law and does not purport to be a complete review of this or other provisions that may be applicable to ADS holders. The Company undertakes no obligation to update this summary in the future.
PART II
ITEM 13. Defaults, Dividend Arrearages and Delinquencies
Not applicable.
ITEM 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds
Not applicable.
ITEM 15. Controls and Procedures
Not applicable.
ITEM 16. [RESERVED]
ITEM 16A. Audit Committee Financial Expert
Not applicable.
ITEM 16B. Code of Ethics
Not applicable.
ITEM 16C. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
Not applicable.
| 132 |
ITEM 16D. Exemptions from the Listing Standards for Audit Committees
Not applicable.
ITEM 16E. Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
Not applicable.
ITEM 16F. Change in Registrant’s Certifying Accountant
Not applicable.
ITEM 16G. Corporate Governance
Not applicable.
ITEM 16H. Mine Safety Disclosure
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 17. Financial Statements
We have responded to Item 18 in lieu of responding to this item.
ITEM 18. Financial Statements
Please refer to the financial statements beginning on page F-1.
Page | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-1 |
| Audited Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2012 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Financial Position | F-2 |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss | F-4 |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity | F-5 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-9 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-11 |
The following financial statements and financial statement schedules are filed as part of this Registration Statement on Form 20-F, together with the report of the independent registered public accounting firm.
| 133 |
ITEM 19. Exhibits
Index to Exhibits
| Exhibit No. | Description | |
| 1.1 | Amended and Restated Articles of Association of Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. (2) | |
| 2.1 | Form of Amended and Restated Deposit Agreement, by and among Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., The Bank of New York Mellon and the Owners and Holders of American Depositary Shares, dated ____________ (incorporated herein by reference, filed as Exhibit 1 to the Registration Statement on Form F-6 filed with the SEC on August 21, 2013). | |
| 4.1 | Employment and Non-Competition Agreement with Barak Singer, dated February 22, 2011 (effective March 20, 2011). (1) | |
| 4.2 | Amendment to Employment and Non-Competition Agreement with Barak Singer, dated February 28, 2013. (1) | |
| 4.3 | Employment and Non-Competition Agreement with Motti Farbstein, dated June 10, 2003. (1) | |
| 4.4 | Consulting Agreement with BioStrategies Consulting, Ltd, dated September 27, 2005. (2) | |
| 4.5 | Service Management Agreement with F.D. Consulting International and Marketing Ltd., dated June 27, 2002. (2) | |
| 4.6 | Master Services Agreement with Accellient Partners, dated May 10, 2010. (2) | |
| 4.7 | Patent License Agreement—Exclusive, by and between the U.S. Public Health Service and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated January 29, 2003. (2) | |
| 4.8 | First Amendment to Exclusive Patent License Agreement L-249-2001/0, by and between the National Institutes of Health and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated August 15, 2005. (2) | |
| 4.9 | Second Amendment to L-249-2001/0, by and between the National Institutes of Health and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated February 4, 2013. (2) | |
| 4.10 | License Agreement, by and between the University of Leiden and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 2, 2009. (2) | |
| 4.11 | License Agreement, by and between Seikagaku Corporation and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated September 22, 2006. (2) | |
| 4.12 | Addendum to License Agreement, by and between Seikagaku Corporation and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated December 11, 2006. (2) | |
| 4.13 | Representative Agreement, by and between Fuji Techno Interface Ltd. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated September 22, 2006. (2) | |
| 4.14 | Letter Agreement, by and between Seikagaku Corporation and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated December 8, 2009. (2) | |
| 4.15 | License Agreement, by and between Kwang Dong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated December 14, 2008. (2) | |
| 4.16 | License Agreement, by and between Eye-Fite, Ltd. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) |
| 134 |
| Exhibit No. | Description | |
| 4.17 | Services Agreement, by and among Denali Concrete Management Inc., Eye-Fite Ltd. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.18 | Letter from Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. Regarding “Reimbursement for the Costs of the Clinical Trial”, dated February 24, 2013. (2) | |
| 4.19 | Agreement, by and between Denali Concrete Management Inc. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.20 | Stock Purchase Agreement, by and between Denali Concrete Management Inc. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.21 | Subscription Agreement, by and between Denali Concrete Management Inc. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.22 | Subscription Agreement, by and between Denali Concrete Management Inc. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.23 | Common Stock Purchase Warrant, by and between Denali Concrete Management Inc. and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated November 21, 2011. (2) | |
| 4.24 | Memorandum of Understanding, by and between Morningside Asia Venture (HK) Limited and Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd., dated January 19, 2010. (2) | |
| 4.25 | Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. 2003 Share Option Plan. (2) | |
| 8.1 | List of Subsidiaries of Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. | |
| 15.1 | Consent of Kost Forer Gabbay & Kasierer, an independent registered public accounting firm and member firm of Ernst & Young Global Limited. |
(1) Incorporated herein by reference to the Draft Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed with the SEC on April 15, 2013.
(2) Incorporated herein by reference to Amendment No. 1 to the Draft Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed with the SEC on May 10, 2013.
| 135 |
SIGNATURES
The Registrant hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this registration statement on its behalf.
| CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD. | ||
| By: | /s/ Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. | |
| Pnina Fishman, Ph.D. | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
Date: August 26, 2013
 |
Kost Forer Gabbay & Kasierer 3
Aminadav St.
Tel: 972 (3)6232525 Fax: 972 (3)5622555 www.ey.com |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Can-Fite BioPharma Ltd. ("the Company") and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive loss, changes in equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2012. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's board of directors and management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company's and its subsidiary internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's and its subsidiary internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, based on our audits, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of the Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2012, in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
| /s/ KOST FORER GABBAY & KASIERER | |
| Tel-Aviv, Israel | KOST FORER GABBAY & KASIERER |
| August 26, 2013 | A Member of Ernst & Young Global |
| F-1 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION |
| Convenience translation Into U.S. dollars. Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||||||||
| Note | in thousands | NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS: | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 5 | 1,146 | 4,278 | 14,622 | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 6 | 448 | 1,672 | 3,760 | ||||||||||||
| 1,594 | 5,950 | 18,382 | ||||||||||||||
| NON-CURRENT ASSETS: | ||||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 8 | 42 | 159 | 278 | ||||||||||||
| 1,636 | 6,109 | 18,660 | ||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-2 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION |
| Convenience translation Into U.S. dollars Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||||||||
| Note | in thousands | NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | ||||||||||||||||
| Trade payables | 9 | 756 | 2,821 | 1,930 | ||||||||||||
| Other accounts payable | 10 | 1,228 | 4,586 | 2,686 | ||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 5) | 15 | - | - | 138 | ||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 6) | 15 | 40 | 149 | 396 | ||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 7) | 15 | 207 | 773 | - | ||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 8) | 15 | 96 | 357 | - | ||||||||||||
| 2,327 | 8,686 | 5,150 | ||||||||||||||
| NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES: | ||||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 7) | 15 | - | - | 793 | ||||||||||||
| Employee benefit liabilities, net | 12 | 18 | 68 | 190 | ||||||||||||
| 18 | 68 | 983 | ||||||||||||||
| 2,345 | 8,754 | 6,133 | ||||||||||||||
| EQUITY ATTRIBUTABLE TO EQUITY HOLDERS OF THE COMPANY: | 15 | |||||||||||||||
| Share capital | 732 | 2,734 | 2,606 | |||||||||||||
| Share premium | 62,618 | 233,754 | 229,299 | |||||||||||||
| Capital reserve from share-based payment transactions | 4,093 | 15,279 | 14,670 | |||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 9) | 179 | 669 | - | |||||||||||||
| Treasury shares, at cost | (1,555 | ) | (5,805 | ) | (5,805 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 23 | 84 | 75 | |||||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (67,334 | ) | (251,359 | ) | (230,539 | ) | ||||||||||
| (1,244 | ) | (4,644 | ) | 10,306 | ||||||||||||
| Non-controlling interests | 535 | 1,999 | 2,221 | |||||||||||||
| Total deficit | (709 | ) | (2,645 | ) | 12,527 | |||||||||||
| 1,636 | 6,109 | 18,660 | ||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-3 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
| Convenience translation Into U.S. dollars Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, | Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||
| Note | in thousands | NIS
in thousands (except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues | - | - | 1,785 | 2,644 | ||||||||||||||||
| Research and development expenses | 17 | 3,525 | 13,160 | 12,969 | 9,993 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 18 | 2,484 | 9,272 | 7,081 | 6,005 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income | 19 | (11 | ) | (42 | ) | (88 | ) | - | ||||||||||||
| Operating loss | 5,998 | 22,390 | 18,177 | 13,354 | ||||||||||||||||
| Expenses relating to the merger transaction | - | - | 11,496 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Finance expenses | 20 | 7 | 27 | 232 | 356 | |||||||||||||||
| Finance income | 20 | (145 | ) | (541 | ) | (1,669 | ) | (897 | ) | |||||||||||
| Loss before taxes on income | 5,860 | 21,876 | 28,236 | 12,813 | ||||||||||||||||
| Taxes on income | 13 | 3 | 11 | 191 | 235 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss | 5,863 | 21,887 | 28,427 | 13,048 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss - Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | (2 | ) | (7 | ) | (92 | ) | - | |||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | 5,861 | 21,880 | 28,335 | 13,048 | ||||||||||||||||
| Loss Attributable to: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity holders of the Company | 5,577 | 20,820 | 25,499 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-controlling interests | 286 | 1,067 | 2,928 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| 5,863 | 21,887 | 28,427 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity holders of the Company | 5,574 | 20,811 | 25,424 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-controlling interests | 287 | 1,069 | 2,911 | - | ||||||||||||||||
| 5,861 | 21,880 | 28,335 | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Loss per share attributable to equity holders of the Company (in NIS): | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted loss per share | 0.55 | 2.07 | 2.73 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-4 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY |
| Attributable to equity holders of the Company | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share capital | Share premium | Capital reserve from share-based payment transactions | Warrants | Treasury shares | Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | Accumulated deficit | Total | Non- controlling interests | Total equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2012 | 2,606 | 229,299 | 14,670 | - | (5,805 | ) | 75 | (230,539 | ) | 10,306 | 2,221 | 12,527 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss | - | - | - | - | - | (20,820 | ) | (20,820 | ) | (1,067 | ) | (21,887 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | - | 9 | (2 | ) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | - | 9 | (20,820 | ) | (20,811 | ) | (1,069 | ) | (21,880 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of unlisted share options | 5 | 171 | - | - | - | - | - | 176 | - | 176 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants (series 5) | 1 | 75 | - | - | - | - | - | 76 | - | 76 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issue of share capital and warrants (series 9) -(net of issue expenses of NIS 491 thousand) | 122 | 4,209 | - | 669 | - | - | 5,000 | - | 5,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of share-based payment | - | - | 609 | - | - | - | - | 609 | 847 | 1,456 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | 2,734 | 233,754 | 15,279 | 669 | (5,805 | ) | 84 | (251,359 | ) | (4,644 | ) | 1,999 | (2,645 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-5 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY |
| Attributable to equity holders of the Company | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share capital | Share premium | Capital reserve from share-based payment transactions | Warrants | Treasury shares | Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | Accumulated deficit | Total | Non- controlling interests | Total equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2011 | 2,321 | 209,704 | 14,351 | - | - | - | (213,304 | ) | 13,072 | - | 13,072 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss | - | - | - | - | - | - | (25,499 | ) | (25,499 | ) | (2,928 | ) | (28,427 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | - | - | - | - | - | 75 | - | 75 | 17 | 92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | - | 75 | (25,499 | ) | (25,424 | ) | (2,911 | ) | (28,335 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allocation of share capital to subsidiary | 179 | 5,626 | - | - | (5,805 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of share-based payment | - | - | 319 | - | - | - | - | 319 | - | 319 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issue of share capital (net of issue expenses of NIS 406 thousand) | 99 | 4,611 | - | - | - | - | - | 4,710 | - | 4,710 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants | 7 | 289 | - | - | - | - | - | 296 | - | 296 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expenses relating to the merger transaction | - | 9,069 | - | - | - | - | - | 9,069 | 1,991 | 11,060 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Private placement in OphthaliX | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8,264 | 8,264 | 3,141 | 11,405 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | 2,606 | 229,299 | 14,670 | - | (5,805 | ) | 75 | (230,539 | ) | 10,306 | 2,221 | 12,527 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-6 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY |
| Attributable to equity holders of the Company | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share capital | Share premium | Capital reserve from share-based payment transactions | Warrants | Treasury shares | Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | Accumulated deficit | Total | Non- controlling interests | Total equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2010 | 2,132 | 194,925 | 13,723 | 2,962 | - | - | (200,256 | ) | 13,486 | - | 13,486 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | - | - | (13,048 | ) | (13,048 | ) | - | (13,048 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants (series 4) | 8 | 1,046 | - | - | - | - | - | 1,054 | - | 1,054 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expiration of warrants (series 3) | - | 2,962 | - | (2,962 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of share-based payment | - | - | 628 | - | - | - | 628 | - | 628 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issue of share capital (net of issue expenses of NIS 49 thousand) | 180 | 10,751 | - | - | - | - | - | 10,931 | - | 10,931 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants | 1 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 21 | - | 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2010 | 2,321 | 209,704 | 14,351 | - | - | - | (213,304 | ) | 13,072 | - | 13,072 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-7 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY |
| Attributable to equity holders of the Company - Convenience translation see Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share capital | Share Premium | Capital reserve from share-based payment transactions | Warrants | Treasury shares | Adjustments arising from translating financial statements of foreign operations | Accumulated deficit | Total | Non- controlling interests | Total equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convenience translation into USD in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2012 | 699 | 61,424 | 3,930 | - | (1,555 | ) | 20 | (61,757 | ) | 2,761 | 595 | 3,356 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss | - | - | - | - | - | - | (5,577 | ) | (5,577 | ) | (286 | ) | (5,863 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | - | 3 | (1 | ) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | (5,577 | ) | (5,574 | ) | (287 | ) | (5,861 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of unlisted share options | 1 | 46 | - | - | - | - | - | 47 | - | 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants (series 5) | *) - | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issue of warrants (series 9) –(net of issue expenses of USD 131 thousand) | 32 | 1,128 | - | 179 | - | - | - | 1,339 | - | 1,339 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of share-based payment | - | - | 163 | - | - | - | - | 163 | 227 | 390 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | 732 | 62,618 | 4,093 | 179 | (1,555 | ) | 23 | (67,334 | ) | (1,244 | ) | 535 | (709 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*) Less than 1 thousand
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-8 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS |
| Convenience translation Into U.S. dollars Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, | Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||
| in thousands | NIS in thousands | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Loss | (5,863 | ) | (21,887 | ) | (28,427 | ) | (13,048 | ) | ||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments to the profit or loss items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation of property, plant and equipment | 23 | 86 | 218 | 279 | ||||||||||||
| Cost of share-based payment | 390 | 1,456 | 319 | 628 | ||||||||||||
| Gain from sale of property, plant and equipment | (11 | ) | (42 | ) | (88 | ) | - | |||||||||
| Interest income on deposits | (13 | ) | (50 | ) | (89 | ) | (110 | ) | ||||||||
| Increase (Decrease) in employee benefit assets, net | (33 | ) | (122 | ) | 59 | 35 | ||||||||||
| Taxes on income | 3 | 11 | 191 | 224 | ||||||||||||
| Decrease in fair value of warrants exercisable into shares (series 4) | - | - | - | (387 | ) | |||||||||||
| Decrease in fair value of warrants exercisable into shares (series 5) | (37 | ) | (138 | ) | (1,262 | ) | (400 | ) | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in fair value of warrants exercisable into shares (series 6) | (66 | ) | (247 | ) | 94 | - | ||||||||||
| Decrease in fair value of warrants exercisable into shares (series 7) | (5 | ) | (20 | ) | (172 | ) | - | |||||||||
| Increase in fair value of warrants exercisable into shares (series 8) | 2 | 8 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on balances of cash and cash equivalents | (58 | ) | (217 | ) | (181 | ) | 417 | |||||||||
| Expenses relating to the merger transaction | - | - | 11,060 | - | ||||||||||||
| 195 | 725 | 10,149 | 686 | |||||||||||||
| Changes in asset and liability items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in accounts receivable | 559 | 2,088 | (3,390 | ) | (102 | ) | ||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in trade payable | 239 | 891 | 1,414 | (131 | ) | |||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in other accounts payable | 509 | 1,900 | (741 | ) | (258 | ) | ||||||||||
| 1,307 | 4,879 | (2,717 | ) | (491 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash paid and received during the year for: | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest received | 13 | 50 | 89 | 110 | ||||||||||||
| Taxes paid | (3 | ) | (11 | ) | (11 | ) | (224 | ) | ||||||||
| 10 | 39 | 78 | (114 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (4,351 | ) | (16,244 | ) | (20,917 | ) | (12,967 | ) | ||||||||
| F-9 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS |
| Convenience translation Into U.S. dollars Note 2.c.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, | Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | |||||||||||||
| in thousands | NIS in thousands | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (5 | ) | (17 | ) | (81 | ) | (107 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment | 25 | 92 | 163 | - | ||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 20 | 75 | 82 | (107 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Issue of share capital (net of issue expenses) | 1,160 | 4,331 | 4,710 | 10,931 | ||||||||||||
| Exercise of share warrants (series 4) | - | - | - | 1,054 | ||||||||||||
| Exercise of share warrants (series 5) | 20 | 76 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Issue of share warrants (net of issue expenses) | - | - | 1,266 | - | ||||||||||||
| Issue of share warrants (series 8 and 9) (net of issue expenses) | 273 | 1,018 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Exercise of warrants | 47 | 176 | 296 | 21 | ||||||||||||
| Sale of shares to non-controlling interest shareholders | - | - | 11,405 | - | ||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 1,500 | 5,601 | 17,677 | 12,006 | ||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on balances of cash and cash equivalents | 60 | 224 | 274 | (417 | ) | |||||||||||
| Decrease in cash and cash equivalents | (2,771 | ) | (10,344 | ) | (2,884 | ) | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 3,917 | 14,622 | 17,506 | 18,991 | ||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | 1,146 | 4,278 | 14,622 | 17,506 | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
| F-10 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
| NOTE 1:- | GENERAL |
| a. | Company description: |
Can-Fite Biopharma Ltd. was incorporated and started to operate in September 1994 as a private Israeli company. The Company is engaged in the development of drugs and medical diagnosis tools and is in the development stage of its products and has no sales yet (except exclusive license agreements, see Notes 14c(2) and 14c(3)). On October 6, 2005, the Company conducted an initial offering of securities to the public in Israel pursuant to a prospectus which it had published.
On October 4, 2012, the Company announced the beginning of Level 1 OTC trading of its American Depository Receipts ("ADRs") in the U.S. (CANFY: OTC US). The trading in ADRs will be done by licensed U.S. brokers.
| b. | During 2006, the Company founded a subsidiary in the UK under the name of Ultratrend Limited whose main purpose is to focus on coordinating the logistics for the multi-national PHASE IIb clinical studies. As of the reporting date, Ultratrend Limited has not commenced its operation. |
| c. | The Company has a subsidiary, OphthaliX Inc., owned 82% by the Company, which is developing the CF101 drug for treatment of ophthalmic indications. The license to develop this drug was transferred from the Company to OphthaliX Inc. in the context of the ophthalmic activity spinoff transaction, see Note 7 below. OphthaliX Inc. is traded over the counter (OTC) in the U.S. |
| d. | In the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company incurred losses of NIS 20,820 thousand and it has negative cash flows from operating activities in the amount of NIS 5,810 thousand as well as accumulated losses from previous years. In addition, based on the decision of the Board, the Company has undertaken to finance the subsidiary's clinical development, including management fees, until the latter manages to raise capital. The Company has not yet generated any material revenues from the sale of its own developed products and has financed its activities by raising capital and by collaborating with multinational companies in the industry. On February 5, 2013, the Company raised a gross total of NIS 26,498 thousand (approximately $ 7,098 thousand), see Note 23e). Furthermore, the Company is acting to continue to finance its operating activities by raising capital and collaborating with multinational companies in the industry. The Company has other alternative plans for financing its ongoing activities, such as adding to the Company's existing flexibility in the progress of carrying out clinical trials and obtaining the Chief Scientist's approval for participation in financing the Company's research activities in 2013 for a total of approximately NIS 1,700 thousand. The Company's management and board of directors are of the opinion that these financial resources will be used for operating activities at least until the end of 2014. |
| F-11 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
| NOTE 1:- | GENERAL (Cont.) |
| e. | Definitions: |
In these consolidated financial statements:
| The Company | - | Can-Fite Biopharma Ltd. |
| The Group | - | The Company and its subsidiaries (as defined below). |
| Subsidiaries | - | Companies that are controlled by the Company (as defined in IAS 27 (2008)) and whose accounts are consolidated with those of the Company. |
| The subsidiary | - | OphthaliX Inc. ("OphthaliX") (formerly: Denali Concrete Management, Inc.). |
| Related company | - | Eye-Fite Ltd. (OphthaliX Inc.’s wholly owned subsidiary). |
| Related parties | - | As defined in IAS 24. |
| Interested parties and controlling shareholder | - | As defined in the Israeli Securities Regulations (Annual Financial Statements), 2010. |
| Dollar | - | U.S. dollar. |
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
The following accounting policies have been applied consistently in the financial statements for all periods presented, unless otherwise stated.
| a. | Basis of presentation of the financial statements |
These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards ("IFRS") as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board. Furthermore, the financial statements have been prepared in conformity with the provisions of the Israeli Securities Regulations (Annual Financial Statements), 2010. The Company's financial statements have been prepared on a cost basis, except for financial assets and liabilities (including derivatives) which are presented at fair value through profit or loss. The Company has elected to present profit or loss items using the function of expense method.
The preparation of the financial statements requires management to make critical accounting estimates as well as exercise judgment in the process of adopting significant accounting policies. The matters which required the exercise of significant judgment and the use of estimates, which have a material effect on amounts recognized in the financial statements, are specified in Note 3 below.
| F-12 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| b. | Consolidated financial statements |
The consolidated financial statements comprise the financial statements of companies that are controlled by the Company (i.e., subsidiaries). Control exists when the Company has the power, directly or indirectly, to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity. The effect of potential voting rights that are exercisable at the end of the reporting period is considered when assessing whether an entity has control. The consolidation of the financial statements commences on the date on which control is obtained and ends when such control ceases.
The financial statements of the Company and of the subsidiaries are prepared as of the same dates and periods. The consolidated financial statements are prepared using uniform accounting policies by all companies in the Group. Significant intragroup balances and transactions and gains or losses resulting from intragroup transactions are eliminated in full in the consolidated financial statements.
Non-controlling interests of subsidiaries represent the non-controlling shareholders' share of the total comprehensive income of the subsidiaries and their share of the net assets. The non-controlling interests are presented in equity separately from the equity attributable to the equity holders of the Company. Losses are attributed to non-controlling interests even if they result in a negative balance of non-controlling interests in the consolidated statement of financial position.
| c. | Functional currency, presentation currency and foreign currency: |
| 1. | Functional currency and presentation currency: |
The functional currency of the Company and presentation currency of the financial statements is the NIS.
The Group determines the functional currency of the group subsidiaries and this currency is used to separately measure each Group entity's financial position and operating results.
When a subsidiary’s functional currency differs from the Company's functional currency, the subsidiary financial statements are translated into the Company's functional currency so that they can be included in the consolidated financial statements.
Assets and liabilities are translated at the closing rate at the end of each reporting period.
Profit or loss items are translated at average exchange rates for all the relevant periods. All resulting translation differences are recognized as a separate component of other comprehensive income (loss) in equity under "adjustments arising from translating financial statements".
| F-13 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
| NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| c. | Functional currency, presentation currency and foreign currency (Cont.) |
| 1. | Functional currency and presentation currency (Cont.) |
For the convenience of the reader, the reported NIS amounts as of December 31, 2012 have been translated into U.S. dollars, at the representative rate of exchange on December 31, 2012 (U.S. $ 1 = NIS 3.733). The U.S. dollar amounts presented in these financial statements should not be construed as representing amounts that are receivable or payable in dollars or convertible into U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated. The U.S. dollar amounts were rounded to whole numbers of convenience.
| 2. | Transactions, assets and liabilities in foreign currency: |
Transactions denominated in foreign currency are recorded upon initial recognition at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. After initial recognition, monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are translated at the end of each reporting period into the functional currency at the exchange rate at that date. Exchange rate differences are recognized in profit or loss. Non-monetary assets and liabilities measured at cost in foreign currency are translated at the exchange rate at the date of the transaction. Non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency and measured at fair value are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rate prevailing at the date when the fair value was determined.
| 3. | Index-linked monetary items: |
Monetary assets and liabilities linked to the changes in the Israeli Consumer Price Index ("Israeli CPI") are adjusted at the relevant index at the end of each reporting period according to the terms of the agreement. Linkage differences arising from the adjustment, as above, are recognized in profit or loss.
| d. | Cash equivalents |
Cash equivalents are considered as highly liquid investments, including unrestricted short-term bank deposits with an original maturity of three months or less from the investment date.
| F-14 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| e. | Revenue recognition |
The Company generates income from licensing agreements with pharmaceutical companies. These agreements usually comprise license fees, annual license fees, milestone payments and potential royalty payments.
Revenues are recognized in profit or loss when the revenues can be measured reliably, it is probable that the economic benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the Company and the costs incurred or to be incurred in respect of the transaction can be reliably measured.
Arrangements with multiple elements:
Revenues from sale agreements that do not contain a general right of return and that are composed of multiple elements such as licenses and services are allocated to the various accounting units and recognized for each accounting unit separately. An element constitutes a separate accounting unit if and only if it has a separate value to the customer. Revenue from the various accounting units is recognized when the criteria for revenue recognition regarding the elements of that accounting unit have been met according to their type and only to the extent of the consideration that is not contingent upon completion or performance of the remaining elements in the contract.
Revenues from license fees:
| As for revenues from preliminary license fees and annual license fees, the Company examines whether the license can be separated from the Company's other performance obligations, if at all: |
| a) | If the Company has material performance obligations, it determines that the revenues from preliminary license fees and annual license fees will not be immediately recognized as a sale. Therefore, revenues from the license and the related obligations must be recognized on a cumulative basis according to the nature of the agreement, for example, according to the development terms. |
| b) | When the Company has no material performance obligations, it determines that the revenues from license fees and annual license fees will be recognized in the period in which they are received. |
| F-15 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| e. | Revenue recognition (Cont.) |
Revenues from milestone payments:
| Revenues which are contingent on compliance with milestones are recognized in profit or loss at the achievement of milestones, provided that the following criteria have been met: |
| a) | The milestone payments are non-recoverable; |
| b) | The achievement of a certain milestone involves a level of risk that is not reasonably secured at the inception of the agreement; |
| c) | The achievement of the milestone involves exercising a real effort; |
| d) | The milestone payments are reasonable in proportion to the efforts exercised or in proportion to the risk involving the achievement of the milestone; |
| e) | The time that elapses between payments is equivalent to the effort required to achieve the milestone. |
Revenues from royalties:
| Revenues from royalties are recognized as they accrue in accordance with the terms of the relevant agreement. |
| f. | Taxes on income |
As it is not likely that taxable income will be generated in the foreseeable future, deferred tax assets due to accumulated losses is not recognized in the Group's financial statements (see also Note 13).
| g. | Property, plant and equipment |
Property, plant and equipment are measured at cost, including directly attributable costs, less accumulated depreciation, accumulated impairment losses and excluding day-to-day servicing expenses.
Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the useful life of the assets at annual rates as follows:
| % | Mainly % | |||||
| Laboratory equipment and Leasehold improvements | 10 | |||||
| Computers, office furniture and equipment | 6 - 33 | 33 | ||||
The useful life, depreciation method and residual value of an asset are reviewed at least each year-end and any changes are accounted for prospectively as a change in accounting estimates.
| F-16 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| g. | Property, plant and equipment (Cont.) |
Depreciation of an asset ceases at the earlier of the date that the asset is classified as held for sale and the date that the asset is derecognized. An asset is derecognized on disposal or when no further economic benefits are expected from its use. The gain or loss arising from the derecognition of the asset (determined as the difference between the net disposal proceeds and the carrying amount in the financial statements) is included in the statement of comprehensive income when the asset is derecognized.
| h. | Research and development expenditures |
Research expenditures are recognized in the statement of comprehensive income when incurred.
| i. | Impairment of non-financial assets |
The Group evaluates the need to record an impairment of the carrying amount of property, plant and equipment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount is not recoverable. If the carrying amount of property, plant and equipment exceeds their recoverable amount, the property, plant and equipment are reduced to their recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of fair value less costs of sale and value in use. In measuring value in use, the expected future cash flows are discounted using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects the risks specific to the asset.
| j. | Financial instruments |
| 1. | Financial liabilities |
Financial liabilities within the scope of IAS 39 are classified as either financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss.
The Group determines the classification of the liability on the date of initial recognition. All liabilities are initially recognized at fair value. After initial recognition, the accounting treatment of financial liabilities is based on their classification as follows:
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss include financial liabilities designated upon initial recognition as at fair value through profit or loss.
A liability may be designated upon initial recognition at fair value through profit or loss, subject to the provisions of IAS 39.
Financial liabilities at amortized cost:
After initial recognition, payables and other payables , are measured based on their terms at amortized cost less directly attributable transaction costs using the effective interest method. The amortization of the effective interest is recognized in profit or loss in the line item, "financing".
| F-17 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| 2. | Fair value |
The fair value of financial instruments that are traded in an active market is determined by reference to market prices at the end of the reporting period. For financial instruments where there is no active market, fair value is determined using valuation techniques. Such techniques include using recent arm's length market transactions, reference to the current market value of another instrument which is substantially the same, discounted cash flow and other valuation models. A detailed analysis of the fair value measurement of financial instruments is provided in Note 11 below.
| 3. | Issue of a unit of securities |
The issue of a unit of securities involves the allocation of the proceeds received (before issue expenses) to the components of the securities issued in the unit based on the following order: financial derivatives and other financial instruments measured at fair value in each period. Then fair value is determined for financial liabilities and compound instruments that are presented at amortized cost. The consideration allocated to the equity instruments is determined as the residual value. The issuance costs are allocated to each component based on the amounts allocated to each component in the unit.
| 4. | Derecognition of financial instruments |
Financial liabilities:
A financial liability is derecognized when it is extinguished, that is when the obligation is discharged, realized, cancelled or expires. A financial liability is extinguished when the debtor (i.e., the Group) discharges the liability by paying in cash, other financial assets, goods or services or shares, or is legally released from the liability.
When an existing financial liability is exchanged with another liability from the same lender on substantially different terms, or the terms of an existing liability are substantially modified, such an exchange or modification is accounted for as an extinguishment of the original liability and the recognition of a new liability. The difference between the carrying amount of the above liabilities is recognized in profit or loss. If the exchange or modification is not substantial, it is accounted for as a change in the terms of the original liability and no gain or loss is recognized on the exchange.
| k. | Treasury shares |
Company shares held by the subsidiary are recognized at cost and deducted from equity. Any gain or loss arising from a purchase, sale, issuance or cancellation of treasury shares is recognized directly in equity.
| F-18 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| l. | Provisions |
A provision in accordance with IAS 37 is recognized when the Group has a present obligation (legal or constructive) as a result of a past event, it is probable that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation and a reliable estimate can be made of the amount of the obligation. If the Group expects part or all of the expense to be reimbursed to the Company, such as in an insurance contract, the reimbursement is recognized as a separate asset only when it is virtually certain that it will be received by the Company. The expense is recognized in the income statement net of the reimbursed amount.
No provisions pursuant to IAS 37 have been identified.
.
| m. | Employee benefit liabilities |
The Group has several employee benefit plans:
| 1. | Short-term employee benefits: |
Short-term employee benefits include salaries and social security contributions are recognized as expenses as the services are rendered. A liability in respect of a cash bonus is recognized when the Group has a legal or constructive obligation to make such payment as a result of past service rendered by an employee and a reliable estimate of the amount can be made.
| 2. | Post-employment benefits: |
The post-employment benefit plans are normally financed by contributions to insurance companies and classified as defined benefit plans.
The Company operates a defined benefit plan in respect of severance pay pursuant to the Severance Pay Law. According to the Severance Pay Law, employees are entitled to severance pay upon dismissal or retirement. The liability for termination of employment is measured using the projected unit credit method. The actuarial assumptions include rates of employee turnover and future salary increases based on the estimated timing of payment. The amounts are presented based on discounted expected future cash flows using a discount rate determined by reference to yields on government bonds with a term that matches the estimated term of the benefit obligation.
In respect of its severance pay obligation to certain of its employees, the Company makes current deposits in pension funds and insurance companies ("the plan assets"). Plan assets comprise assets held by a long-term employee benefit fund or qualifying insurance policies. Plan assets are not available to the Company's own creditors and cannot be returned directly to the Company.
| F-19 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| m. | Employee benefit liabilities (Cont.) |
| 2. | Post-employment benefits (Cont.) |
The liability for employee benefits shown in the statement of financial position reflects the present value of the defined benefit obligation less the fair value of the plan assets, less past service costs.
Actuarial gains and losses are recognized in profit or loss in the period in which they occur.
| n. | Share-based payment transactions |
The Company's employees and other service providers are entitled to remuneration in the form of equity-settled share-based payment transactions and certain employee and other service providers are entitled to remuneration in the form of share-based payment transactions that are measured based on the increase in the Company's share price.
Equity-settled transactions:
The cost of equity-settled transactions with employees is measured at the fair value of the equity instruments granted at grant date. The fair value is determined using an acceptable option pricing model.
As for other service providers, the cost of the transactions is measured at the fair value of the goods or services received as consideration for equity instruments. In cases where the fair value of the goods or services received as consideration of equity instruments cannot be measured, they are measured by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments granted.
The cost of equity-settled transactions is recognized in profit or loss, together with a corresponding increase in equity, during the period which the performance and/or service conditions are to be satisfied, ending on the date on which the relevant employees become fully entitled to the award ("the vesting period"). The cumulative expense recognized for equity-settled transactions at the end of each reporting period until the vesting date reflects the extent to which the vesting period has expired and the Group's best estimate of the number of equity instruments that will ultimately vest. The expense or income recognized in profit or loss represents the change between the cumulative expense recognized at the end of the reporting period and the cumulative expense recognized at the end of the previous reporting period.
If the Company modifies the conditions on which equity-instruments were granted, an additional expense is recognized for any modification that increases the total fair value of the share-based payment arrangement or is otherwise beneficial to the employee/other service provider at the modification date.
| F-20 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 2:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Cont.) |
| o. | Loss per share |
Losses per share are calculated by dividing the net loss attributable to equity holders of the Company by the weighted number of ordinary shares outstanding during the period. Potential ordinary shares (convertible securities such as convertible debentures, warrants and employee options) are only included in the computation of diluted loss per share when their conversion increases loss per share from continuing operations. Potential ordinary shares that are converted during the period are included in diluted loss per share only until the conversion date and from that date in basic loss per share. The Company's share of loss of subsidiary is included based on the loss per share of the subsidiary multiplied by the number of shares held by the Company.
| NOTE 3:- | SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING JUDGMENTS, ESTIMATES AND ASSUPMTIONS USED IN THE PREPARATION OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
In the process of applying the significant accounting policies, the Group has made the following judgments which have the most significant effect on the amounts recognized in the financial statements:
| a. | Judgments |
Determining the fair value of share-based payment transactions
The fair value of share-based payment transactions is determined using an acceptable option-pricing model. The model includes data as to the share price and exercise price, and assumptions regarding expected volatility, expected life, expected dividend and risk-free interest rate.
| b. | Estimates and assumptions |
The preparation of the financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that have an effect on the application of the accounting policies and on the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses.
Changes in accounting estimates are reported in the period of the changes in estimates.
The key assumptions made in the financial statements concerning uncertainties at the end of the reporting period and the critical estimates computed by the Group that may result in a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year are discussed below.
Pensions and other post-employment benefits
The liability in respect of post-employment defined benefit plans is determined using actuarial valuations. The actuarial valuation involves making assumptions about, among others, discount rates, expected rates of return on assets, future salary increases and mortality rates. The carrying amount of the liability may be significantly affected by changes in such estimates.
| F-21 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 4:- | DISCLOSURE OF NEW STANDARDS IN THE PERIOD PRIOR TO THEIR ADOPTION |
IAS 19 (Revised) - Employee Benefits
The IASB made several changes to IAS 19, the principal of which are as follows:
| - | The remeasurement of the net defined benefit liability (formerly - actuarial gains and losses) are recognized in other comprehensive income and not in profit or loss. |
| - | The "corridor" approach which allowed the deferral of actuarial gains or losses has been eliminated. |
| - | Income from the plan assets is recognized in profit or loss based on the discount rate used to measure the employee benefit liabilities. The return on plan assets excluding the aforementioned income recognized in profit or loss is included in the remeasurement of the net defined benefit liability. |
| - | The distinction between short-term employee benefits and long-term employee benefits is based on the expected settlement date and not on the date on which the employee first becomes entitled to the benefits. |
| - | Past service cost arising from changes in the plan is recognized immediately. |
This standard is to be applied retrospectively in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013, or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted.
The Group estimates that this standard is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
IAS 32 - Financial Instruments: Presentation and IFRS 7 - Financial Instruments: Disclosure
The IASB issued certain amendments to IAS 32 ("the amendments to IAS 32") regarding the offsetting of financial assets and liabilities. The amendments to IAS 32 clarify, among others, the meaning of "currently has a legally enforceable right of set-off" ("the right of set-off").
The IASB also issued amendments to IFRS 7 ("the amendments to IFRS 7") regarding the offsetting of financial assets and liabilities.
The amendments to IAS 32 are to be applied retrospectively commencing from the financial statements for periods beginning on January 1, 2014, or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted, but disclosure of early adoption is required, as well as the disclosures required by the amendments to IFRS 7 as described above. The amendments to IFRS 7 are to be applied retrospectively commencing from the financial statements for periods beginning on January 1, 2013, or thereafter.
| F-22 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 4:- | DISCLOSURE OF NEW STANDARDS IN THE PERIOD PRIOR TO THEIR ADOPTION (Cont.) |
The Group estimates that the amendments to IAS 32 are not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements. The required disclosures pursuant to the amendments to IFRS 7 will be included in the Group's financial statements.
IFRS 9 - Financial Instruments
| 1. | The IASB issued IFRS 9, "Financial Instruments", the first part of Phase 1 of a project to replace IAS 39, "Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement". IFRS 9 ("the Standard") focuses mainly on the classification and measurement of financial assets and it applies to all financial assets within the scope of IAS 39. |
According to this standard, all financial assets (including hybrid contracts with financial asset hosts) should be measured at fair value upon initial recognition. In subsequent periods, debt instruments should be measured at amortized cost only if both of the following conditions are met:
| - | the asset is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets in order to collect the contractual cash flows. |
| - | the contractual terms of the financial asset give rise on specified dates to cash flows that are solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding. |
Notwithstanding the foregoing, upon initial recognition, the Company may designate a debt instrument that meets both of the abovementioned conditions as measured at fair value through profit or loss if this designation eliminates or significantly reduces a measurement or recognition inconsistency ("accounting mismatch") that would have otherwise arisen.
Subsequent measurement of all other debt instruments and financial assets should be at fair value.
Financial assets that are equity instruments should be measured in subsequent periods at fair value and the changes recognized in profit or loss or in other comprehensive income, in accordance with the election by the Company on an instrument-by-instrument basis (amounts recognized in other comprehensive income cannot be subsequently reclassified to profit or loss). If equity instruments are held for trading, they should be measured at fair value through profit or loss.
When an entity changes its business model for managing financial assets, it shall reclassify all affected financial assets. In all other circumstances, reclassification of financial instruments is not permitted.
This standard is effective commencing from January 1, 2015. Earlier application is permitted. Upon initial application, this standard should be applied retrospectively by providing the required disclosure or restating comparative figures, except as specified in the standard.
| F-23 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 4:- | DISCLOSURE OF NEW STANDARDS IN THE PERIOD PRIOR TO THEIR ADOPTION (Cont.) |
| 2. | The IASB issued certain amendments to the Standard regarding derecognition and financial liabilities. According to those amendments, the provisions of IAS 39 will continue to apply to derecognition and to financial liabilities for which the fair value option has not been elected (designated as measured at fair value through profit or loss); that is, the classification and measurement provisions of IAS 39 will continue to apply to financial liabilities held for trading and financial liabilities measured at amortized cost. |
Pursuant to the amendments, the amount of the adjustment to the liability's fair value that is attributable to changes in credit risk should be presented in other comprehensive income. All other fair value adjustments should be presented in profit or loss.
If presenting the fair value adjustment of the liability arising from changes in credit risk in other comprehensive income creates an accounting mismatch in profit or loss, then that adjustment should also be presented in profit or loss rather than in other comprehensive income.
The amendments are effective commencing from January 1, 2015. Earlier application is permitted provided that the Company also adopts the provisions of this standard regarding the classification and measurement of financial assets (the first part of Phase 1). Upon initial application, the amendments are to be applied retrospectively by providing the required disclosure or restating comparative figures, except as specified in the amendments.
The Group estimates that this standard is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
IFRS 10, IFRS 11, IFRS 12, IFRS 13 - Consolidated Financial Statements, Joint Arrangements, Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities, Fair Value Measurement
The IASB issued four new standards: IFRS 10, "Consolidated Financial Statements", IFRS 11, "Joint Arrangements", IFRS 12, "Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities" ("the new Standards") and IFRS 13, "Fair Value Measurement", and amended two existing standards, IAS 27R (Revised 2011), "Separate Financial Statements", and IAS 28R (Revised 2011), "Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures".
The new standards IFRS 10,IFRS 12 and IFRS 13 are to be applied retrospectively in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013 or thereafter. Earlier application is permitted. However, if the Company chooses earlier application, it must adopt all the new standards as a package (excluding the disclosure requirements of IFRS 12 which may be adopted separately). The standards prescribe transition provisions with certain modifications upon initial adoption.
The new IFRS 11"Joint Arrangements" standard is irrelevant to the Group.
The abovementioned standards that are expected to have an impact on the Group are as follows:
| F-24 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 4:- | DISCLOSURE OF NEW STANDARDS IN THE PERIOD PRIOR TO THEIR ADOPTION (Cont.) |
IFRS 10 - Consolidated Financial Statements:
IFRS 10 supersedes IAS 27 regarding the accounting treatment in respect of consolidated financial statements and includes the accounting treatment for the consolidation of structured entities previously accounted for under SIC 12, "Consolidation - Special Purpose Entities".
According to IFRS 10, in order for an investor to control an investee, the investor must have power over the investee and exposure, or rights, to variable returns from the investee. Power is defined as the ability to influence and direct the investee's activities that significantly affect the investor's return. According to IFRS 10, when assessing the existence of control, potential voting rights should be considered only if they are substantive.
IFRS 10 also prescribes that an investor may have control even if it holds less than a majority of the investee's voting rights (de facto control), as opposed to the provisions of the existing IAS 27 which permits a choice between two consolidation models - the de facto control model and the legal control model.
IFRS 10 is to be applied retrospectively in financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013, or thereafter.
The Group estimates that this standard is not expected to have a material impact on its financial statements.
IFRS 12 - Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities:
IFRS 12 prescribes disclosure requirements for the Company's investees, including subsidiaries, joint arrangements, associates and structured entities. IFRS 12 expands the disclosure requirements to include the judgments and assumptions used by management in determining the existence of control, joint control or significant influence over investees, and in determining the type of joint arrangement. IFRS 12 also provides disclosure requirements for material investees.
The required disclosures will be included in the Group's financial statements upon initial adoption of IFRS 12.
IFRS 13 - Fair Value Measurement:
IFRS 13 establishes guidance for the measurement of fair value, to the extent that such measurement is required according to IFRS. IFRS 13 defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. IFRS 13 also specifies the characteristics of market participants and determines that fair value is based on the assumptions that would have been used by market participants. According to IFRS 13, fair value measurement is based on the assumption that the transaction will take place in the asset's or the liability's principal market, or in the absence of a principal market, in the most advantageous market. The new disclosures are to be applied prospectively and they do not apply to comparative figures.
| F-25 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 4:- | DISCLOSURE OF NEW STANDARDS IN THE PERIOD PRIOR TO THEIR ADOPTION (Cont.) |
Amendments to IFRS 10, IFRS 11, IFRS 12 - Consolidated Financial Statements, Joint Arrangements, Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities
In July 2012, the IASB issued certain amendments to the above standards (“the Amendments”) which provide certain relief with respect to the transition provisions and allow restatement of comparative amounts for one year only. The restatement of comparative amounts for earlier periods is optional. The Amendments also eliminate the requirement to present comparative amounts for earlier periods regarding non-consolidated structured entities. The Amendments are effective starting from financial statements for annual periods commencing on January 1, 2013. Earlier adoption is permitted.
| NOTE 5:- | CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Cash for immediate withdrawal | 3,718 | 466 | ||||||
| Cash equivalents - short-term deposits | 560 | 14,156 | ||||||
| 4,278 | 14,622 | |||||||
| NOTE 6:- | ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Government authorities | 112 | 227 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses | 1,551 | 3,386 | ||||||
| Other receivables | 9 | 147 | ||||||
| 1,672 | 3,760 | |||||||
| F-26 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 7:- | OPHTHALIX SPIN OFF |
| a. | Purchase agreement |
On November 21, 2011, ("the effective date"), the Company consummated the acquisition of 82% of the issued and outstanding share capital of OphthaliX Inc. ("the subsidiary" or "OphthaliX") (formerly: Denali Concrete Management Inc.) a U.S. public company whose shares are traded on the OTCBB (Over the Counter Bulletin Board) (symbol OTC BB: OPLI) ("the acquisition transaction").
The acquisition transaction was consummated pursuant to an agreement dated June 5, 2011 to spin-off the Company's activity in the ophthalmology field to OphthaliX and, based on its conditions, the following agreements were signed:
| 1. | The spin-off agreement |
According to the spin-off agreement, the Company transferred to OphthaliX 100% of the issued and outstanding capital of Eye-Fite ("Eye-Fite"), the Company's former wholly-owned subsidiary, such that Eye-Fite became the wholly-owned subsidiary of OphthaliX in exchange for 36,000,000 shares of OphthaliX common stock, representing 86.7% of OphthaliX’s issued and outstanding capital. In addition, the Company received 2,097,626 shares of OphthaliX common stock in exchange for 714,922 ordinary shares pursuant to the terms of a material private placement that the Company effected on November 21, 2011 at a price of $1.144 per share, which reflected a value for OphthaliX of approximately $50 million before the transfer of the Company’s ordinary shares, described above, and before the material private placement fundraising for OphthaliX (the key elements of which are described below). The Company purchased 437,005 shares of OphthaliX common stock in the same private placement at the same price per share, or an aggregate purchase price of $1.144 per share.
Upon the closing of the transactions contemplated by the spin-off agreement, the Company appointed all of the members of OphthaliX’s board of directors (three members of which are also members of the Company’s board of directors). According to the spin-off agreement, OphthaliX will, among other things, continue the development processes, clinical trials and registration of the ophthalmic indications for CF101. The Company will provide certain services to OphthaliX under the services agreement detailed below.
The transaction was accounted for in the consolidated financial statements of Can-Fite as a continuation of the financial statements of Eye-Fite, together with a deemed issuance of shares to the pre-acquisition shareholders of OphthaliX. The deemed issuance of shares was in consideration for Eye-Fite becoming a wholly owned subsidiary of OphthaliX, a U.S. public company, and therefore it is in effect a share-based payment transaction.
The share-based payment transaction was accounted for in accordance with IFRS 2 "Share based payment". Consequently, the financial statements include a charge of NIS 11,060 thousand that represent the value of OphthaliX shares before the transaction. Additional issuance expenses in an amount of NIS 436 thousand were recorded in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income report.
Because OphthaliX was previously a shell company, the transaction has been accounted in OphthaliX financial statements as a reverse capitalization transaction in which the accounting acquiree is not a business.
| F-27 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 7:- | OPHTHALIX SPIN OFF(Cont.) |
| a. | Purchase agreement (Cont.) |
| 2. | License agreement |
A license agreement was entered into between the Company and Eye-Fite ("the license agreement") according to which the Company granted Eye-Fite a non-transferrable exclusive license, as set forth in the license agreement, for the use of the Company's know-how solely in the field of ophthalmic diseases for research, development, commercialization and marketing throughout the world. Eye-Fite is permitted to sublicense subject to the license agreement. As consideration for the grant of the license according to the license agreement, the Company received 1,000 ordinary shares of Eye-Fite, par value NIS 0.01 per share, representing 100% of the issued and outstanding share capital of Eye-Fite.
However, even if after such extensions the trial does not begin, due to circumstances that are not under Eye-Fite’s control, it shall be considered a material breach of the license agreement. According to the license agreement with the U.S. National Institute of Health, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ("NIH"), Eye-Fite is obligated to make royalty payments to NIH.
All inventions resulting from the indication that is licensed thereunder shall belong to the Company whether it was invented solely by it, solely by Eye-Fite or by both in cooperation. However, the Company granted Eye-Fite an exclusive license to use these inventions in the field of ophthalmic diseases around the world at no consideration. The license will remain in effect until the expiration of the last patent licensed thereunder unless it is terminated sooner by a mutual agreement in writing or by one of the parties according to the clauses of the license agreement.
| 3. | Services agreement |
In addition to the license agreement, the Company, OphthaliX and Eye-Fite (OphthaliX and Eye-Fite are collectively referred to as "the Group") entered into a services agreement ("the services agreement") pursuant to which the Company provides management services to the Group with respect to all pre-clinical and clinical research studies, production and supply of the compounds related to the license agreement and payment for consultants that are listed in the agreement for their involvement in the clinical trials and in all the activities leading up to, and including, the commercialization of CF101 for ophthalmic indications.
| F-28 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 7:- | OPHTHALIX SPIN OFF(Cont.) |
| a. | Purchase agreement (Cont.) |
As consideration for the rendering of services, as above, the Company will be paid only for its costs and expenses incurred in rendering the services plus 15%, as well as reimbursed for the expenses actually charged for the maintenance of patents underlying the license to Eye-Fite.
In February 2013, the Company's board of directors decided to defer the receipt of payments due to the Company according to the service agreement until Eye-Fite completed raising capital.
Further, the Company will be entitled to an additional payment of 2.5% of any revenues received by the Group for the rights to use the transferred know-how ("the additional payment").
The Company is entitled during a 5-year period from the date of the approval of the services agreement, to convert its right to the additional payment into 2,160,102 shares of OphthaliX (representing about 5% of OphthaliX shares on a fully diluted basis as of the date of closing the spin-off agreement) in consideration for the exercise price set forth in the services agreement. The services agreement shall remain in force for an unlimited period of time, however, following the first anniversary, each party is entitled to terminate the agreement upon six months' prior notice or, by special events, in an earlier notice as outlined in the services agreement.
| 4. | Pre-ruling from the Income Tax |
The Company received a pre-ruling decision from the Israeli Income Tax Authority which confirms (1) that the grant of the license to Eye-Fite is not liable for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 104a to the Income Tax Ordinance (New Version), 1961 ("the Ordinance"); (2) that OphthaliX is considered the receiving company pursuant to section 103c(7)(b) to the Ordinance; (3) that the sale of Eye-Fite shares to OphthaliX as consideration for OphthaliX shares does not create liability for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 103t to the Ordinance ("change in structure"); and (4) the date for the change in structure was determined. According to the tax pre-ruling, the date of change in structure shall also be the date of exchange of shares with respect to the spin-off and notification to the tax assessor. The Company and Eye-Fite presented to the tax assessor and the merger and spin-off department of the tax assessor the forms required by the Ordinance and the regulations thereunder. The tax pre-ruling further provides that the grant of a license to Eye-Fite as consideration for the issuance of Eye-Fite shares to the Company does not create liability for tax pursuant to the provisions of section 104a to the Ordinance.
| F-29 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 7:- | OPHTHALIX SPIN OFF(Cont.) |
| b. | Capital raising in OphthaliX |
With the completion of the spin-off transaction, as above, OphthaliX raised from a group of investors under a private placement ("the group of investors") approximately $3,330 thousand in exchange for the sale of 2,910,455 shares of OphthaliX common stock, representing about 6.20% of OphthaliX’s issued and outstanding share capital after the above purchase ("OphthaliX capital raise"). As part of the OphthaliX capital raise, the group of investors requested that the Company's board of directors approve the OphthaliX capital raise and also purchase shares from OphthaliX. Accordingly, the Company's CEO and director agreed to the request and invested $50 thousand after the audit committee and board of directors approved the transaction on November 21, 2011. In addition, another director in the Company purchased OphthaliX common stock from former OphthaliX shareholders for $75 thousand after the audit committee and board of directors approved the transaction on November 21, 2011.
The OphthaliX capital raise was made at share price of $1.144 per share, reflecting a value of approximately $50 million prior to closing. After the OphthaliX capital raise, the Company holds about 82.3% of OphthaliX’s issued and outstanding share capital on a fully-diluted basis and OphthaliX’s value was approximately $56.5 million. Under the OphthaliX capital raise, the Company agreed to carry out the following actions:
| 1. | The rights under the license agreement for the CF101 drug solely in the field of ophthalmic diseases ("the drug") will be transferred only against the allocation of OphthaliX shares to the Company and without any commitment to pay for the past for any reason whatsoever, except as detailed in the license agreement and the services agreement. OphthaliX will not be required to make to the Company any retroactive payments for the drug, except for the trials in dry eye syndrome (Phase III) and glaucoma (Phase II), which will be transferred to the Company at cost. |
| 2. | The Company has undertaken not to withdraw any money from Eye-Fite and/or OphthaliX, except the payment for the services agreement entered into between the Company and OphthaliX under which the Company is reimbursed for its cost plus 15% (see above description of the services agreement). |
| F-30 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 8:- | PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
Composition and movement
2012:
| Laboratory equipment | Computers, office furniture and equipment | Leasehold improvements | Total | |||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost: | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2012 | 1,115 | 1,129 | 1,210 | 3,454 | ||||||||||||
| Purchases during the year | - | 17 | - | 17 | ||||||||||||
| Disposals during the year | (185 | ) | (120 | ) | *) (564 | ) | (869 | ) | ||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | 930 | 1,026 | 646 | 2,602 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2012 | 1,056 | 926 | 1,194 | 3,176 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation during the year | 28 | 56 | 2 | 86 | ||||||||||||
| Disposals during the year | (182 | ) | (73 | ) | *) (564 | ) | (819 | ) | ||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | 902 | 909 | 632 | 2,443 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciated cost at December 31, 2012 | 28 | 117 | 14 | 159 | ||||||||||||
| *) | The Company minimized the lab activity on the leased space in the beginning of the reporting year. |
| F-31 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 8:- | PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET (Cont.) |
2011:
| Laboratory equipment | Computers, office furniture and equipment | Leasehold improvements | Total | |||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost: | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2011 | 2,333 | 1,049 | 1,210 | 4,592 | ||||||||||||
| Purchases during the year | 1 | 80 | - | 81 | ||||||||||||
| Disposals during the year | (1,219 | ) | - | - | (1,219 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | 1,115 | 1,129 | 1,210 | 3,454 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2011 | 2,053 | 857 | 1,192 | 4,102 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation during the year | 147 | 69 | 2 | 218 | ||||||||||||
| Disposals during the year | (1,144 | ) | - | - | (1,144 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | 1,056 | 926 | 1,194 | 3,176 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciated cost at December 31, 2011 | 59 | 203 | 16 | 278 | ||||||||||||
| NOTE 9:- | TRADE PAYABLES |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Open accounts | 2,595 | 1,864 | ||||||
| Checks payable | 226 | 66 | ||||||
| 2,821 | 1,930 | |||||||
| NOTE 10:- | OTHER ACCOUNTS PAYABLE |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Employees and payroll accruals | 582 | 599 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses | 4,004 | 2,087 | ||||||
| 4,586 | 2,686 | |||||||
| F-32 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 11:- | FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
| a. | Classification of financial assets and liabilities |
| The financial assets and financial liabilities in the statement of financial position are classified by groups of financial instruments pursuant to IAS 39: |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Financial assets: | ||||||||
| Receivables | 121 | 374 | ||||||
| Financial liabilities: | ||||||||
| Financial liabilities measured at amortized cost | 7,407 | 4,616 | ||||||
| Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss | 1,279 | 1,327 | ||||||
| b. | Financial risks factors |
The Group's activities expose it to foreign exchange risk. The Group's comprehensive risk management plan focuses on activities that reduce to a minimum any possible adverse effects on the Group's financial performance.
The Company's management identifies and manages financial risks.
Foreign exchange risk
The Group is exposed to foreign exchange risk resulting from the exposure to different currencies, mainly the U.S. dollar. Foreign exchange risk arises on recognized assets and liabilities that are denominated in a foreign currency other than the functional currency.
The Group acts to reduce the foreign exchange risk by managing an adequate part of the available liquid sources in or linked to the dollar.
| c. | Fair value |
The carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, trade payables and other accounts payable approximate their fair value.
Classification of financial instruments by fair value hierarchy
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss are classified in the statement of financial position in Level 1 (quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities).
| F-33 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 11:- | FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (Cont.) |
| d. | Linkage terms of financial instruments |
| December 31, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| In
or linked to dollar | In
or linked to Euro | Linked
to Israeli CPI | Unlinked | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 3,952 | 6 | - | 320 | 4,278 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | - | - | 30 | 91 | 121 | |||||||||||||||
| 3,952 | 6 | 30 | 411 | 4,399 | ||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Trade payables | 2,298 | 257 | - | 266 | 2,821 | |||||||||||||||
| Other accounts payable | 2,749 | - | - | 1,837 | 4,586 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 6) | - | - | 149 | - | 149 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 7) | - | - | 773 | - | 773 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 8) | - | 357 | - | 357 | ||||||||||||||||
| 5,047 | 257 | 1,279 | 2,103 | 8,686 | ||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| In or linked to dollar | In or linked to Euro | Linked to Israeli CPI | Unlinked | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | 14,089 | 65 | - | 468 | 14,622 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | - | - | - | 374 | 374 | |||||||||||||||
| 14,089 | 65 | - | 842 | 14,996 | ||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Trade payables | 1,029 | 570 | - | 331 | 1,930 | |||||||||||||||
| Other accounts payable | 1,725 | - | - | 961 | 2,686 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 5) | - | - | 138 | - | 138 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 6) | - | - | 396 | - | 396 | |||||||||||||||
| Warrants exercisable into shares (series 7) | - | - | 793 | - | 793 | |||||||||||||||
| 2,754 | 570 | 1,327 | 1,292 | 5,943 | ||||||||||||||||
| F-34 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 11:- | FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (Cont.) |
| e. | Sensitivity tests relating to changes in market factors |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Sensitivity test to changes in the U.S. dollar exchange rate: | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) from the change: | ||||||||
| Increase of 10% in exchange rate | (110 | ) | 1,134 | |||||
| Decrease of 10% in exchange rate | 110 | (1,134 | ) | |||||
| Sensitivity test to changes in the market price of listed securities: | ||||||||
| Gain (loss) from the change: | ||||||||
| Increase of 10% in market price | (128 | ) | (133 | ) | ||||
| Decrease of 10% in market price | 128 | 133 | ||||||
Sensitivity tests and the main work assumptions:
The selected changes in the relevant risk variables were determined based on management's estimate as to reasonable possible changes in these risk variables.
The Group has performed sensitivity tests of principal market risk factors that are liable to affect its reported operating results or financial position. The sensitivity tests present the profit or loss in respect of each financial instrument for the relevant risk variable chosen for that instrument as of each reporting date. The test of risk factors was determined based on the materiality of the exposure of the operating results or financial condition of each risk with reference to the functional currency and assuming that all the other variables are constant.
Based on the Group's policy, the Group generally mitigates the currency risk arising from recognized assets and recognized liabilities denominated in foreign currency other than the functional currency by maintaining part of the available liquid sources in deposits in foreign currency. Accordingly, the main currency exposures presented in the sensitivity tables are for those deposits.
| F-35 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 12:- | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT LIABILITIES, NET |
Employee benefits consist of short-term benefits and post-employment benefits.
Post-employment benefits
According to the labor laws and Severance Pay Law in Israel, the Company is required to pay compensation to an employee upon dismissal or retirement or to make current contributions in defined contribution plans pursuant to section 14 to the Severance Pay Law, as specified below. The Company's liability is accounted for as a post-employment benefit. The computation of the Company's employee benefit liability is made in accordance with a valid employment contract based on the employee's salary and employment term which establish the entitlement to receive the compensation.
In 2009, management accepted a decision according to which although section 14 applies, as above, the Company would pay all compensation upon dismissal of employees pursuant to the conditions of the Severance Pay Law.
In accordance with the abovementioned, since 2009, the Group does not contribute to defined contribution plans, but only to defined benefit plans.
The post-employment employee benefits are financed by contributions classified as a defined benefit plan as follows:
A defined benefit plan:
The Company accounts for the part of the compensation payments as a defined benefit plan for which an employee benefit liability is recognized and for which the Company deposits amounts in qualifying insurance policies.
| 1. | Expenses recognized in profit or loss: |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Current service cost | 149 | 161 | 132 | |||||||||
| Interest cost on benefit obligation | 36 | 47 | 44 | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (29 | ) | (32 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) recognized in the year | (42 | ) | 59 | 29 | ||||||||
| Total employee benefit expenses | 114 | 235 | 174 | |||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets | 98 | (28 | ) | 76 | ||||||||
| F-36 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 12:- | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT LIABILITIES, NET (Cont.) |
| 2. | The plan liabilities, net: |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Defined benefit obligation | (849 | ) | (1,067 | ) | ||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 781 | 877 | ||||||
| Total liabilities, net | (68 | ) | (190 | ) | ||||
| 3. | Changes in the present value of defined benefit obligation: |
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1, | (1,067 | ) | (1,004 | ) | ||||
| Interest cost | (36 | ) | (47 | ) | ||||
| Current service cost | (149 | ) | (161 | ) | ||||
| Benefits paid | 430 | 144 | ||||||
| Net actuarial gain (loss) | (27 | ) | 1 | |||||
| Balance at December 31, | (849 | ) | (1,067 | ) | ||||
| 4. | Plan assets: |
| a) | Plan assets comprise assets held by a long-term employee benefit fund and qualifying insurance policies. |
| b) | The movement in the fair value of the plan assets: |
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||
| Balance at January 1, | 877 | 873 | ||||||
| Expected return | 29 | 32 | ||||||
| Contributions by employer less withdrawals | 123 | 169 | ||||||
| Withdrawals from the plan | (317 | ) | (137 | ) | ||||
| Net actuarial gain (loss) | 69 | (60 | ) | |||||
| Balance at December 31, | 781 | 877 | ||||||
| F-37 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 12:- | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT LIABILITIES, NET (Cont.) |
| 5. | The principal assumptions underlying the defined benefit plan: |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| % | ||||||||
| Discount rate of the plan liability | 3.77 | 3.75 | ||||||
| Expected rate of return on plan assets | 4.28 | 4.03 | ||||||
| Future salary increases | 3.50 | 3.50 | ||||||
| NOTE 13:- | TAXES ON INCOME |
| a. | Tax laws applicable to the Company: |
Income Tax (Inflationary Adjustments) Law, 1985:
According to the law, until 2007, the results for tax purposes were adjusted for the changes in the Israeli CPI.
In February 2008, the "Knesset" (Israeli parliament) passed an amendment to the Income Tax (Inflationary Adjustments) Law, 1985, which limits the scope of the law starting in2008 and thereafter. Since 2008, the results for tax purposes are measured in nominal values, excluding certain adjustments for changes in the Israeli CPI carried out in the period up to December 31, 2007. Adjustments relating to capital gains, such as for sale of property (betterment) and securities, continue to apply until disposal. Since 2008, the amendment to the law includes, among other things, the cancellation of the inflationary additions and deductions.
| b. | Tax rates applicable to the Group companies: |
| 1. | The Israeli corporate tax rate was 25% in 2010 and 24% in 2011. |
A company is taxable on its real (non-inflationary) capital gains at the corporate tax rate in the year of sale. A temporary provision for 2006-2009 stipulates that the sale of an asset other than a quoted security (excluding goodwill that was not acquired) that had been purchased prior to January 1, 2003, and sold by December 31, 2009, is subject to corporate tax as follows: the part of the real capital gain that is linearly attributed to the period prior to December 31, 2002 is subject to the corporate tax rate in the year of sale as set forth in the Ordinance, and the part of the real capital gain that is linearly attributed to the period from January 1, 2003, through December 31, 2009, is subject to tax at a rate of 25%.
| F-38 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 13:- | TAXES ON INCOME (Cont.) |
| b. | Tax rates applicable to the Group companies (Cont.) |
| 1. | (Cont.) |
On December 5, 2011, the Israeli Parliament (the Knesset) passed the Law for Tax Burden Reform (Legislative Amendments), 2011 ("the Law") which, among others, cancels effective from 2012, the scheduled progressive reduction in the corporate tax rate. The Law also increases the corporate tax rate to 25% in 2012. In view of this increase in the corporate tax rate to 25% in 2012, the real capital gains tax rate and the real betterment tax rate were also increased accordingly.
The above change had no effect on the financial statements.
| 2. | The principal tax rate applicable to the subsidiary whose place of incorporation is the U.S. is a weighted tax at the rate of about 40% (Federal tax, State tax and City tax of the city where the subsidiary operates). |
| c. | Final tax assessments: |
The Company received final tax assessments through 2008.
The related companies, OphthaliX and Eye-Fite, have not received final tax assessments since its incorporation.
| d. | Carryforward losses for tax purposes and other temporary differences: |
Carryforward operating tax losses of the Company total approximately NIS 236,117 thousand as of December 31, 2012.
A deferred tax asset relating to carryforward operating losses of approximately NIS 59,029 thousand was not recognized because its utilization in the foreseeable future is not probable.
| e. | Theoretical tax: |
The reconciliation between the tax expense, assuming that all the income and expenses, gains and losses in the statement of income were taxed at the statutory tax rate and the taxes on income recorded in profit or loss arising from carryforward tax losses for which the Company did not create a deferred tax asset since its utilization in the foreseeable future is not expected.
| F-39 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 14:- | CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND COMMITMENTS |
| a. | Liabilities to pay royalties: |
| 1. | According to the license agreement signed on January 29, 2003 with the U.S. National Institute of Health ("NIH") (through the US Public Health Service, "PHS") ("the PHS agreement"), the Company is committed to pay royalties as follows: |
| a) | A minimum annual payment of $50 thousand, which is non-refundable. |
| b) | 4%-5.5% of the Company's total net revenues from sales of licensed products or from conducting tests, as defined in the PHS agreement, on a consolidated basis. |
| c) | Royalties in a total of up to $700 thousand, subject to meeting certain drug development milestones as defined in the PHS agreement as follows: (i) $25 thousand upon first Phase I initiation per indication; (ii) $75 thousand upon first Phase II initiation per indication; (iii) $100 thousand upon first Phase III initiation per indication; and (iv) $500 thousand upon approval by the FDA or any other regulatory authority. |
| d) | Additional payments totaling 20% of total payments received from any subcontractor. |
The agreement will remain in effect until the expiration of the last patent, unless it is terminated sooner by one of the parties, according to the PHS agreement.
On August 4, 2005, a revised agreement was signed with the NIH which extends the milestone dates. On February 4, 2013, a second revised agreement was signed for updating the milestone dates. These revised agreements have no effect on the original license terms. In addition, CF101 and CF102 are defined in the agreements.
| 2. | According to the research and license agreement signed with Aderis Pharmaceuticals Inc. ("Aderis") on May 6, 2002 (and its amendment of May 28, 2003), the Company is committed to pay royalties as follows: |
| a) | 1.75%-2.75% of total net sales (as this term is defined in the agreement). |
| b) | 2% of all payments received from the Company's subcontractors in connection with the agreement. |
The Company will be entitled to a reduction in the rate of royalties payable according to the PHS agreement in paragraph 2 above in an amount equivalent to the royalties payable under this agreement.
The agreement will remain in effect until the expiration of the last patent, unless it is terminated sooner by one of the parties, according to the agreement.
| F-40 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 14:- | CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND COMMITMENTS (Cont.) |
| a. | Liabilities to pay royalties (Cont.): |
| 3. | According to the patent license agreement signed on July 28, 2009 with the Leiden University in the Netherlands, which is affiliated with the NIH, the Company is committed to pay royalties as follows: |
| a) | A one-time concession commission of € 25 thousand; |
| b) | Annual royalties of € 10 thousand until the clinical trials commence; |
| c) | 2%-3% of net sales (as defined in the agreement) received by the Company; |
| d) | Royalties in a total of up to €850 thousand based on certain progress milestones in the license stages of the products, which are the subject of the patent under the agreement, as follows: (i) €50 thousand upon initiation of Phase I studies; (ii) €100 thousand upon initiation of Phase II studies; (iii) €200 thousand upon initiation of Phase III studies; and (iv) €500 thousand upon marketing approval by any regulatory authority. |
| e) | If the agreement is sublicensed to another company, the Company will provide the Leiden University royalties at a rate of 10%. |
A merger, consolidation or any other change in ownership will not be viewed as an assignment of the agreement as discussed in this paragraph.
| b. | Commitments: |
| 1. | As for engagements with the Company's directors and CEO, see Note 22(c). |
| 2. | On September 22, 2006, the Company signed an exclusive license agreement regarding inflammatory indicators, including rheumatoid arthritis indicators (excluding eye disease indicators) with a public Japanese company, Seikagaku Corporation ("the Japanese corporation"), for the use, development and marketing of the Company's CF101 drug in Japan only. |
According to the agreement, the Company is entitled to receive the following amounts:
| a) | A non-refundable amount of $ 3 million (gross) (NIS 12,909 thousand) paid immediately upon signing the agreement. This amount was included in the Company's revenues in its financial statements for 2006. |
| b) | An amount of $ 500 thousand (gross) on January 1 of each year starting from January 1, 2007, until the earlier of the date of filing an application for a new drug with the Japanese regulatory authorities and the beginning of the fifth year from the date of signing (until January 1, 2011). |
| c) | An amount equal to $12 million (gross) based on the Japanese corporation's progress milestones in the development of CF101 for treating rheumatoid arthritis in Japan as follows: (i) $1 million following the commencement of a Phase I clinical trial of the CF101 drug by the Japanese corporation (such amount was received and included in the Company's revenues in the year ended December 31, 2008); (ii) $5 million upon marketing authorization in Japan for the first indication; (iii) $1.5 million upon commencement of a Phase II clinical trial of the CF101 drug by the Japanese corporation for the first indication in Japan; (vi) $2.5 million upon submission of a new drug application to the appropriate regulatory authority in Japan for the first indication; and (v) $2 million if the Japanese corporation does not employ Bridging Strategy (as defined in the agreement) upon commencement of a Phase III clinical trial by the Japanese corporation for the first indication. |
| F-41 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 14:- | CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND COMMITMENTS (Cont.) |
| d) | An aggregate amount of $2 million (gross) received in 2006 and 2007 ($ 1 million each year) based on milestones underlying the Company's Phase IIb clinical trial in rheumatoid arthritis indicators. These amounts were included in the Company's financial statements for said years under participation in research and development expenses, based on the milestones met by the Company according to the agreement. |
| e) | If the Japanese corporation decides to develop CF101 for the treatment of indications other than rheumatoid arthritis, the Company will be entitled to at least an additional $1 million (gross) based on milestones met in the development of CF101 for such other indications as follow: (i) $3 million upon marketing authorization in Japan for the second indication; and (ii) $1 million upon the commencement of each Phase III clinical trial in Japan for each indication after the first indication. |
In addition to the amounts detailed above, the Company will be entitled to royalties of 7%-12% on sales of the CF101 marketed by the Japanese corporation according to the agreement and on additional revenues from sales of raw materials to the Japanese corporation for the purpose of the development, production and marketing of the CF101. If the Japanese corporation decides to produce the raw materials itself, the Company will be entitled to an additional $ 1 million (gross). Furthermore, according to the agreement, the Company will be entitled to receive additional amounts if the Japanese corporation requests information regarding the results of other clinical trials conducted by the Company in the future. The Company is committed to pay 5% of the above amounts as brokerage commission to a Japanese company which brokered the agreement. The agreement is for an indefinite period.
| 3. | On December 22, 2008, the Company signed an agreement regarding the provision of a license for its CF101 drug with a Korean pharmaceutical company, Kwang Dong Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. ("the license agreement" and "the Korean company", respectively). According to the license agreement, the Company granted the South Korean company a license to use, develop and market its CF101 drug for treating only rheumatoid arthritis only in Korea. |
According to the license agreement, the Company is entitled to receive the following amounts:
| a) | A non-refundable amount of $300 thousand that was received on the effective date of the license agreement in 2006, and up to $1.2 million (gross) based on the Company's achievement of certain milestones as follows: (i) $200 thousand upon the public announcement of the data from the Can-Fite Phase IIb clinical trial (such amount was received and included in the Company's revenue for the year ended December 31, 2010); (ii) $200 thousand upon commencement of the first clinical study by the Korean company in the Republic of Korea; (iii) $200 thousand upon submission by the Korean company of a new drug application in the Republic of Korea; (iv) $300 thousand upon all approvals, licenses or authorizations of any regulatory authority necessary for the commercial marketing, sale and use of the product in the United States, in the European Union as a whole or in any one of the followings countries: Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, France or Switzerland; and (v) $300 thousand upon commercial launch of the product in the Republic of Korea. |
| b) | The Company is entitled to annual royalties of 7% based on sales of CF101 in Korea as marketed by the Korean company according to the license agreement. |
| F-42 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 14:- | CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND COMMITMENTS (Cont.) |
| 4. | On January 19, 2010, the Company signed a memorandum of understanding with Morningside Asia Venture (HK) Limited from Hong Kong ("the memorandum of understanding" and "MAV", respectively). |
According to the memorandum of understanding, the Company and MAV will establish a joint venture in Hong Kong ("the joint venture"), which will receive commercialization rights to the CF102 treatment in China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan ("the territory") and will have exclusive responsibility to develop the CF102 for these markets. MAV will inject all the $ 7.5 million in financing necessary for the preclinical and clinical development of CF102 through the Phase II clinical trial. The Company will provide all pertinent information in its possession relevant for CF102 in order to obtain regulatory permits for it in the territory. The Company indicated that it will have access to all the clinical and pre-clinical results and data to be developed by the joint venture and will have the right to use all this information for purposes outside the territory.
The memorandum of understanding is not binding and the engagement is pending a final agreement. As of the date of the approval of the financial statements, a final agreement has not been signed.
| NOTE 15:- | EQUITY |
In May 2013, the Company’s authorized share capital and the issued and outstanding share capital were consolidated at the ratio of 1:25. All Ordinary Shares, warrants and options and per share amounts have been adjusted to give retroactive effect to these reverse splits for all periods presented (see Note 23.l.3).
| a. | Composition of share capital: |
| December 31, 2012 | December 31, 2011 | |||||||||||||||
| Authorized | Issued and outstanding | Authorized | Issued and outstanding | |||||||||||||
| NIS | ||||||||||||||||
| Ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each | 5,000,000 | 2,733,799 | 5,000,000 | 2,605,857 | ||||||||||||
| F-43 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 15:- | EQUITY (Cont.) |
| b. | Movement in share capital: |
Issued and outstanding capital:
| Number of shares | NIS par value | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2010 | 9,286,085 | 2,321,521 | ||||||
| Movement during 2011: | ||||||||
| Issue of share capital | 1,111,222 | 277,806 | ||||||
| Exercise of unlisted share options (Note 16) | 26,120 | 6,530 | ||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | 10,423,427 | 2,605,857 | ||||||
| Movement during 2012: | ||||||||
| Issue of share capital | 486,720 | 121,680 | ||||||
| Exercise of warrants (series 5) (Note 16) | 933 | 233 | ||||||
| Exercise of unlisted share options | 24,116 | 6,029 | ||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | 10,935,196 | 2,733,799 | ||||||
c. Rights attached to shares:
All ordinary shares have equal rights for all intent and purposes and each ordinary share confers its holder:
| 1. | The right to be invited and participate in all the Company's general meetings, both annual and regular, and the right to one vote per ordinary share owned in all votes and in all Company's general meeting participated. |
| 2. | The right to receive dividends if and when declared and the right to receive bonus shares if and when distributed. |
| 3. | The right to participate in the distribution of the Company's assets upon liquidation. |
| 4. | Quoted on the Tel-Aviv Stock Exchange. |
| d. | Capital management in the Company: |
The Company's capital management objectives are to preserve the Group's ability to ensure business continuity thereby creating a return for the shareholders, investors and other interested parties.
The Company is not under any minimal equity requirements nor is it required to attain a certain level of capital return.
| F-44 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 15:- | EQUITY (Cont.) |
| e. | Issue of shares and warrants and changes in equity: |
| 1. | On November 16, 2011, the Company offered the public securities according to a shelf proposal report which was published on the basis of a shelf prospectus which the Company had published on May 27, 2010. The securities were offered to the public in 3,963 units ("the units") by a tender in unit's price of NIS 1.61 thousand per unit. Each unit comprises 100 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each at NIS 0.5 per share, 1,250 warrants (series 6) and 2,500 warrants (series 7) (both series at no consideration; See note (f) below). The total net proceeds amounted to approximately NIS 5,976 thousand (net of issuance expenses of approximately NIS 406 thousand). The shares were approved for listing on November 16, 2011. The issuance proceeds were received on November 22, 2011. |
| 2. | On March 26, 2012, 23,333 warrants (series 5) were exercised into 933 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each in consideration of an exercise increment of approximately NIS 76 thousand. The remaining 13,226,667 warrants (series 5) which had not been exercised expired on March 31, 2012. |
| 3. | On May 1, 2012, the Company offered the public securities according to a shelf proposal report which was published on the basis of a shelf prospectus which the Company published on May 27, 2010. The securities were offered to the public in 4,000 units ("the units") by a tender on the unit's price where the minimum price was NIS 1,431 per unit. Each unit comprises 120 ordinary shares at NIS 0.477 per share, 2,000 warrants (series 8) and 3,000 warrants (series 9). Both series of warrants are at no consideration. |
Every 25 warrants (series 8) is exercisable into one ordinary share of NIS 0.25 par value in consideration of NIS 0.55, linked to the Israeli CPI with the base index being the CPI of March 2012. The exercise period of the warrants is until May 1, 2013.
In addition, every 25 warrants (series 9) is exercisable into one ordinary share of NIS 0.25 par value in consideration of NIS 0.85, unlinked. The exercise period of the warrants is until May 1, 2015.
There was overwriting in the issuance and 4,056 units at NIS 1,440 per unit were sold. Total net issuance proceeds amounted to approximately NIS 5,349 thousand (net of issue expenses of approximately NIS 491 thousand). The issuance consideration was received on May 2, 2012. Until the issuance consideration is used, the issuance proceeds are held in the Company's accounts and invested by it consistently with the Company's investment policy as it will be from time to time provided that any investment, as above, shall be in solid channels, including and without derogating from the generality of the above an interest-bearing NIS deposit or interest-bearing deposit in foreign currency.
The shares were admitted to trading on May 1, 2012.
| F-45 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 15:- | EQUITY (Cont.) |
| f. | Warrants classified as liability: |
The Company has 4,953,750 registered warrants (series 6) that are exercisable into 198,150 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each in every trading day except from the 12 to the 16 of each calendar month from their admission to trading through May 16, 2012 for the exercise price of NIS 0.63 per share, linked to the Israeli CPI published for October 2011.
On June 17, 2012, the Petach-Tikva District Court granted the Company's request to extend the exercise period of all the warrants (series 6) by December 31, 2012. On January 27, 2013, the Court granted the Company's additional request to extend the exercise period of all the warrants (series 6) by September 1, 2013. On August 18, 2013, the Company filed an urgent application to the Petah-Tikva District Court to approve the convening of a general meeting of the Company's shareholders and a general meeting of the holders of warrants (series 6) of the Company to extend the exercise period of the warrants (series 6) until September 1, 2014. On August 26, 2013, the District Court in Petah-Tikva, Israel approved the extension of the exercise period until October 30, 2013.
These warrants are classified as a liability in the financial statements.
The Company has 9,907,500 registered warrants (series 7) that are exercisable into 396,300 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each in every trading day except from the 12 to the 16 of each calendar month from their admission to trading through November 16, 2013 for the exercise price of NIS 0.80 per share, linked to the Israeli CPI for October 2011. Since exercise price is linked to the Israeli CPI, These warrants are classified as a liability in the financial statements which are measure at fair value through profit or loss.
The Company has 8,112,000 registered warrants (series 8) that are exercisable into 324,480 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value from their admission to trading through May 1, 2013 for the exercise price of NIS 0.55 per share, linked to the Israeli CPI for March 2012. Since exercise price is linked to the Israeli CPI, These warrants are classified as a liability in the financial statements which are measured at fair value through profit or loss.
| g. | Warrants classified as equity: |
The Company has 12,168,000 registered warrants (series 9) that are exercisable into 486,720 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value from their admission to trading through May 1, 2015 for the exercise price of NIS 0.85 per share unlinked.
These warrants are classified as equity in the financial statements.
| h. | Unlisted share options: |
On October 21, 2010 ("the Effective Date"), the Company entered into an investment with an investor ("the Investor"), according to which it granted the Company a put option that expired on October 28, 2010 as a result of the investor’s participation in a financing round of the Company involving ordinary shares to be registered on the TASE.
As part of the arrangement, the Company issued to the Investor 12,550,644 unlisted share options which are exercisable into 502,026 Ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company for an exercise price of NIS 0.6 per option. The share options are exercisable immediately for a period of 42 months from the effective date. The average fair value
| F-46 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 15:- | EQUITY (Cont.) |
| h. | Unlisted share options (Cont.): |
of the investor's share options as of the effective date was NIS 0.399 per option. The share options are classified as an equity component in the financial statements.
The shares issuable upon the exercise of the unlisted share options were admitted to trading on January 26, 2011
| i | Treasury shares: |
| 1. | The Company's shares held by the Company and/or subsidiaries are recognized at cost and deducted from equity. Any gain or loss arising from a purchase, sale, issue or cancellation of treasury shares is recognized directly in equity. |
| 2. | Treasury shares - Company's shares held by its subsidiary: |
| December 31, | January 1, | |||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2011 | ||||||||||
| % | ||||||||||||
| Percentage of issued capital | 6.54 | 6.86 | - | |||||||||
| NOTE 16:- | SHARE-BASED PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS |
| a. | Total share-based payment expenses recognized in 2012, 2011 and 2010: |
The total expense related to share-based payment, for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, was comprised as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Research and development expenses | $ | 144 | $ | 144 | $ | 253 | ||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 1,312 | 175 | 375 | |||||||||
| $ | 1,456 | $ | 319 | $ | 628 | |||||||
There have been no modifications or cancellations to the benefit plans granted during 2011 or 2010. During 2012, the modifications made were as described in Note 15f(4) and Note 16b(6).
| F-47 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 16:- | SHARE-BASED PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS (Cont.) |
| b. | Share-based payment transactions granted by the Company: |
| 1. | On May 27, 2010, the Company's board of directors approved a grant to a consultant of the Company of 145,464 unlisted share options that are exercisable into 5,819 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each. The exercise price is NIS 0.512 per each share option. These share options are exercisable in equal amounts each month over 12 months from the date of the grant. The contractual life of share options is 4 years from the grant date. |
The fair value of the options was determined at NIS 48 thousand at the grant date.
| 2. | On February 15, 2011, the Company's board of directors approved the employment contract of a senior officer, as well as an immaterial grant to the officer ("the optionee"), subject to the approval of the employment contract by the parties. On February 22, 2011, the parties signed the employment contract. |
| According to the agreement, the Company will grant to the optionee, at no consideration, 230,000 unlisted share options of the Company ("the options") that are exercisable into 9,200 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each ("the exercise shares"). The exercise price of the options is NIS 0.754 per option (the closing price of the Company's share on the day preceding the date of the approval of the Company's board of directors, namely February 14, 2011). The options vest quarterly over a period of four years (1/16 per quarter) from the date of grant. The contractual term of the options is ten years from the date of grant. The fair value on the grant date was approximately NIS 106 thousand. |
| 3. | As for the grant of additional share options to senior interested parties, see Note 22(c). |
| 4. | On January 2 2012, the subsidiary granted a member of the subsidiary's board of directors 235,000 options to purchase 235,000 shares of common stock of the subsidiary at the exercise price of $2 per share. The shares will vest at the earlier of a period of 36 months or until the termination of the director's service term in the subsidiary. The options will expire within ten years from the date of grant. |
The following inputs were used as a basis in determining the fair value of the share options using the binomial model: closing price of the subsidiary's shares, $ 2.11, average risk-free interest of 0.92%, life of the options of 10 years, volatility of 80%, and distribution of annual dividend of 0%. The expense recorded in the year totaled NIS 847 thousand.
| 5. | On April 2, 2012, the Company's board of directors approved a grant to employees and senior employees in the Company ("the optionees") of 600,000 unlisted options of the Company that are exercisable into 24,000 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each. The exercise price of the options is NIS 0.385 per option (the closing price for the Company's shares on the trading day which preceded the receipt of the approval from the Company's board of directors). | |
| Nevertheless, the Company granted only 500,000 unlisted options based on the other terms above. |
| F-48 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 16:- | SHARE-BASED PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS (Cont.) |
| b. | Share-based payment transactions granted by the Company (Cont.) |
| 5. | (Cont.) |
According to the binomial model, the fair value of the options for each of the employees on the date when the Company's board of directors accepted the decision was NIS 0.198 per option and a total of NIS 17,785 for all options, this based on the following inputs: closing price of the Company's shares, as above, ranges of risk-free interest of 2.61%-6.65%, life of options of 10 years, volatility range of 51.62%-74.12%, annual employee turnover of 5%, early exercise factor of 2 and distribution of annual dividend of 0%.
According to the binomial model, the fair value of the options for each of the senior employees on the date when the Company's board of directors accepted the decision was NIS 0.215 per option and a total of NIS 77,259 for all options, this based on the following inputs: closing price of the Company's share, as above, ranges of risk-free interest of 2.61%-6.65%, life of options of 10 years, annual standard deviation range of 51.62%-74.12%, annual employee turnover of 5%, early exercise factor of 2.5 and distribution of annual dividend of 0%.
The optionees are entitled to exercise the options over 48 months from the allocation date such that 1/16 of the number of options granted to each optionee, as above, is exercisable every quarter. The term of the options is 10 years from the grant date.
Assuming that the optionees exercise all options, the underlying shares will constitute 0.193% of the issued and outstanding share capital and 0.15% on a fully diluted basis. The shares were admitted to trading on May 2, 2012.
The fair value of the options was determined at NIS 95 thousand at the grant date.
| 6. | On May 8, 2012, the general meeting approved the extension of the exercise period for 2,032,136 unlisted options of the Company originally granted in 2007 to a director in the Company for a period of five years at an exercise price of NIS 1.25 by another five years to a total exercise period of ten years from the date of grant (until May 9, 2017), similarly to the exercise period defined in the Company's option plan. Since the director is entitled to exercise all the options held by him, the Company recognized an immediate expense of approximately NIS 248 thousand in the financial statements. |
| F-49 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 16:- | SHARE-BASED PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS (Cont.) |
| b. | Share-based payment transactions granted by the Company (Cont.) |
| 7. | On July 30, 2012, according to the board of directors’ decision of June 7, 2012, the Company's general meeting approved the grant to directors in the Company of 450,000 unlisted options which are exercisable into 18,000 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company for an exercise price of NIS 0.6 per option. |
According to the binomial model, the economic value of the options for each of the directors as of the date of the board of directors’ decision was NIS 0.17 per option and a total of NIS 72,831 for all the options based on the following assumptions: a closing price of the Company's share of NIS 0.365, a range of risk-free interests of 2.23%-6.95%, an option term of ten years, volatility of 55.13%-73.45%, annual turnover rate of 5%, early exercise factor of 2.5 and annual dividend distribution rate of 0%.
Each of the optionees will be entitled to exercise one half of the options granted to it immediately upon grant and the other half once a quarter over a period of two years. The 450,000 shares deriving from the exercise of the options represent about 0.1% of share capital on a fully diluted basis.
On August 20, 2012, the general director of the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange approved the listing of the options for trading. The fair value was NIS 73 thousand at the grant date.
In 2012, 602,889 unlisted options were exercised by employees into 24,116 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company for total proceeds of approximately NIS 176 thousand.
| F-50 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 16:- | SHARE-BASED PAYMENT TRANSACTIONS (Cont.) |
| c. | Movement during the year: |
The following table lists the number of share options, their weighted average exercise prices and modification in option plans of employees, directors and consultants during the current year:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number
of options | Weighted average exercise price | Number
of options | Weighted average exercise price | Number
of options | Weighted average exercise price | |||||||||||||||||||
| NIS | NIS | NIS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share options at beginning of year | 25,541,892 | 0.44 | 26,060,079 | 0.44 | 23,490,171 | 0.41 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share options granted during the year | 950,000 | 0.49 | 230,000 | 0.75 | 2,825,464 | 0.64 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share options exercised during the year | (602,889 | ) | 0.29 | (653,000 | ) | 0.45 | (70,000 | ) | 0.31 | |||||||||||||||
| Share options expired during the year | (384,208 | ) | 0.46 | (95,187 | ) | 0.31 | (185,556 | ) | 0.50 | |||||||||||||||
| Share options at end of year | 25,504,796 | 0.45 | 25,541,892 | 0.44 | 26,060,079 | 0.44 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share options exercisable at end of year | 24,741,045 | 0.45 | 24,268,077 | 0.44 | 23,477,696 | 0.43 | ||||||||||||||||||
| d. | The weighted average remaining contractual life for the share options outstanding as of December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was 4.01 years, 3.71 years and 4.72 years, respectively. |
| e. | The range of exercise prices for share options outstanding as of December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was between NIS 0.01 and NIS 1.247. |
| f. | The weighted average fair value for the share options outstanding as of December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was NIS 0.18, NIS 0.54 and NIS 0.39, respectively. |
| g. | Measurement of the fair value of equity-settled share options: |
The Company uses the binomial model when estimating the fair value of equity-settled share options with the assistance of an external valuer. The measurement was made at the grant date of equity-settled share options since the options were granted to employees.
For options granted to service providers, the fair value is remeasured as the services are received.
The expected life of the share options is based on historical data of the Company and is not necessarily indicative of the exercise patterns of share options that may occur in the future.
The expected volatility of the share price reflects the assumption that the historical volatility of the share price is reasonably indicative of expected future trend.
| F-51 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 17:- | RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT EXPENSES |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Professional consulting - clinical trials | 8,509 | 6,007 | 2,554 | |||||||||
| Salary and related expenses | 877 | 1,972 | 1,749 | |||||||||
| Royalties | 240 | 590 | 235 | |||||||||
| Patents | 1,130 | 677 | 635 | |||||||||
| Professional consulting - research and development | 652 | 650 | 724 | |||||||||
| Subcontractors | 1,114 | 1,786 | 2,761 | |||||||||
| Materials | 146 | 468 | 506 | |||||||||
| Rent | 216 | 383 | 382 | |||||||||
| Depreciation | 30 | 149 | 199 | |||||||||
| Miscellaneous | 246 | 287 | 248 | |||||||||
| 13,160 | 12,969 | 9,993 | ||||||||||
| NOTE 18:- | GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Professional consulting - management | 901 | 715 | 980 | |||||||||
| Professional services | 3,356 | 2,023 | 1,505 | |||||||||
| Salary and related expenses | 1,410 | 1,861 | 1,196 | |||||||||
| Directors' fee | 1,290 | 410 | 426 | |||||||||
| Rent | 165 | 108 | 110 | |||||||||
| Travel abroad | 381 | 360 | 311 | |||||||||
| Office and computer maintenance | 393 | 317 | 314 | |||||||||
| Vehicle maintenance | 110 | 300 | 262 | |||||||||
| Insurance | 410 | 154 | 153 | |||||||||
| Depreciation | 56 | 69 | 80 | |||||||||
| Brokerage commissions | - | - | 80 | |||||||||
| Other | 800 | 764 | 588 | |||||||||
| 9,272 | 7,081 | 6,005 | ||||||||||
| F-52 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 19:- | OTHER INCOME |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Gain from sale of property, plant and equipment, net | 42 | 88 | - | |||||||||
| 42 | 88 | - | ||||||||||
| NOTE 20:- | FINANCE EXPENSES (INCOME) |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Finance expenses: | ||||||||||||
| Bank commissions | 27 | 50 | 26 | |||||||||
| Net loss from exchange rate fluctuations | - | - | 330 | |||||||||
| Issue expenses attributed to liabilities | - | 182 | - | |||||||||
| 27 | 232 | 356 | ||||||||||
| Finance income: | ||||||||||||
| Interest income on bank deposits | (50 | ) | (89 | ) | (110 | ) | ||||||
| Net gain from exchange rate fluctuations | (62 | ) | (10 | ) | - | |||||||
| Net change in fair value of financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss | (429 | ) | (1,570 | ) | (787 | ) | ||||||
| (541 | ) | (1,669 | ) | (897 | ) | |||||||
| NOTE 21:- | LOSS PER SHARE |
| a. | Details of the number of shares and loss used in the computation of loss per share: |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted
number of shares | Loss | Weighted number of shares | Loss | Weighted
number of shares | Loss | |||||||||||||||||||
| In thousands | NIS in thousands | In thousands | NIS in thousands | In thousands | NIS in thousands | |||||||||||||||||||
| Number of shares and loss used in the computation of basic and diluted loss per share | 10,051 | 20,820 | 9,353 | 25,499 | 8,687 | 13,048 | ||||||||||||||||||
| F-53 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 21:- | LOSS PER SHARE (Cont.) |
| b. | To compute diluted loss per share, the securities, detailed below, have not been taken into account since their conversion decreases the basic loss per share (anti-dilutive effect): |
13,250,000 warrants exercisable into 530,000 shares (series 5). Expired during 2012.
4,953,750 warrants exercisable into 198,150 shares (series 6).
9,907,500 warrants exercisable into 396,300 shares (series 7).
8,112,000 warrants exercisable into 324,480 shares (series 8).
12,168,000 warrants exercisable into 486,720 shares (series 9).
25,504,795 unlisted share options exercisable into 1,020,192 shares - share-based payment.
12,550,644 unlisted share options exercisable into 502,026 shares.
| NOTE 22:- | BALANCES AND TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PARTIES AND INTERESTED PARTIES |
| a. | Benefits to related parties and interested parties: |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Management and consulting fees to interested parties (including bonuses) (1) | 1,050 | 1,109 | 1,265 | |||||||||
| Other expenses relating to an interested party | 63 | 78 | 95 | |||||||||
| Directors' fee (2) | 398 | 400 | 406 | |||||||||
| (1) Number of interested parties | 1 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| (2) Number of directors | 5 | 4 | 4 | |||||||||
| F-54 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 22:- | BALANCES AND TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PARTIES AND INTERESTED PARTIES (Cont.) |
| b. | Benefits to key management personnel: |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| NIS in thousands | ||||||||||||
| Share-based payment (1) | 503 | 255 | 459 | |||||||||
| (1) Number of directors | 2 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
| c. | Commitments: |
| 1. | Through September 21, 2005, the total outstanding share options granted to Dr. Ilan Cohen is 292,357 share options that are exercisable into 11,694 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each. |
On September 21, 2005, the meeting of the Company's shareholders approved another grant of 2,260,729 share options to Dr. Ilan Cohen as to compensate him for the ongoing provision of services. All of such granted share options are exercisable
On March 21, 2007, the meeting of the Company's shareholders approved the Company's Board decision from November 29, 2006 regarding the grant with no consideration of 2,032,136 share options to Dr. Ilan Cohen ("the optionee") to purchase 81,285 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each. All of such granted share options are exercisable.
On May 8, 2012, the general meeting approved the extension of the exercise period for 2,032,136 unlisted options of the Company. (For any farther information see Note 16b(6))
On August 17, 2010, the general meeting of the Company's shareholders approved the Company's engagement with Dr. Ilan Cohen in an agreement for providing business consulting services to the Company ("the consulting services") for a monthly fee in NIS calculated according to Dr. Cohen's actual work hours relating to the consulting services in a specific month multiplied by NIS 1,000 per hour. Dr. Cohen will also be entitled to reimbursement of travel expenses in connection with the consulting services in an amount of $2,000 for the first day and another $1,000 for each travel day.
| F-55 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 22:- | BALANCES AND TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PARTIES AND INTERESTED PARTIES (Cont.) |
| c. | Commitments: (Cont.) |
| 2. | On September 27, 2002, an agreement was signed between F.D. Consulting International and Marketing Ltd. ("FD"), a company wholly owned by Prof. Pnina Fishman, the Company's founder and its director at that time, according to which FD will render management services to the Company. On June 30, 2005, Prof. Pnina Fishman was appointed as the Company's CEO. |
Through September 22, 2005, a total of 6,040,332 share options that are exercisable into 241,613 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each were granted to Prof. Pnina Fishman. The share options were exercisable after the reporting date (see also Note 23).
On July 4, 2006, the Company's board of directors accepted a decision which was later approved by the annual general meeting of the Company's shareholders which was convened on August 24, 2006, to grant to Prof. Pnina Fishman:
| a) | 4,890,760 share options to purchase for no consideration 195,630 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each. |
The exercise price of these share options is equivalent to NIS 0.5 per option (subject to adjustments in cases of share dividend (bonus shares), share split and etc.). The Company's CEO is entitled to exercise the share options based on a vesting period of 1/48 each month starting in October 2005. The last date on which these share options may be exercised under the plan is 10 years from the date of their allocation.
| b) | Increase in the monthly salary from $13 thousand to NIS 75 thousand linked to the changes in the Israeli CPI. |
| F-56 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 22:- | BALANCES AND TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PARTIES AND INTERESTED PARTIES (Cont.) |
| c. | Commitments (Cont.) |
| 2. | (Cont.) |
| On January 13, 2011, after the Company's board of directors decision from December 7, 2010 and after the approval of the Company's audit committee from November 23, 2010, the general meeting of shareholders approved the allocation for no consideration of 2,680,000 share options to the Company's CEO, a director and a shareholder to purchase 107,200 ordinary shares of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value each ("the optionee"). |
The exercise price of the share options granted to the optionee is NIS 0.644 per each share option, representing the average share price in the 60 trading days which preceded the date of the board of directors’ decision.
The optionee shall be entitled to receive the share options and to exercise them over a maximum period of 120 months from the date of their allocation, subject to the conditions outlined in this report and based on the periods detailed below:
| a) | 1,240,000 share options may be exercised by the optionee immediately after their grant. |
| b) | 1,440,000 share options may be exercised by the optionee in 24 equal portions, namely 60,000 share options every month over a period of 24 months which started on the date of approval by the meeting. |
The fair value of all the share options as of the date of the board of directors’ decision is NIS 0.337 per option.
The shares deriving from the exercise of the unlisted share options were admitted to trading on January 6, 2011.
The fair value of the options was determined at NIS 854 thousand at the grant date.
| 3. | On September 21, 2005, the Company's general meeting approved the employment conditions of the chairman of the Board Mr. Avigdor Kaplan as well as the grant of 2,000,000 share options to purchase 80,000 shares of the Company. |
The exercise price of said share options is NIS 1.125 per option. All such share options have vested.
The last date on which these share options may be exercised under the plan is 10 years from the date of their allocation.
| F-57 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 23:- | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS |
| a. | On January 27, 2013, the Petach-Tikva District Court granted the Company's request to extend the exercise period of all the warrants (series 6) by September 1, 2013 according to the general meeting's decision of January 10, 2013. |
| b. | On January 29, 2013, the subsidiary's board of directors approved the addendum to the 2012 option plan. On February 7, 2013, it was approved by the Israeli Tax Authority and on March 8, 2013 the plan came into effect and will be effective with respect to new grants under the 2012 option plan. |
| c. | On February 4, 2013, the Company signed a revised agreement with the NIH for updating the milestone dates. The revised agreement has no effect on the original license terms agreed with the NIH. |
| d. | On February 5, 2013, the Company offered securities to the public on the TASE based on a shelf offering report issued on July 26, 2012. 69,270,000 ordinary shares of NIS 1 par value each of the Company, representing 20.22% of the Company's issued and outstanding share capital and 14.21% on a fully-diluted basis, were offered to the public. In addition, 34,635,000 warrants (series 10) were offered ("warrants (series 10)"), representing 7.11% of the Company's issued and outstanding share capital on a fully-diluted basis, which are exercisable on each trading day, excluding on the 12 and 16 of each calendar month, starting from the date of their listing for trading through October 31, 2015, inclusive. Every 25 warrants (series 10) is exercisable into one ordinary share of NIS 0.25 par value each, subject to certain adjustments for a cash exercise price of NIS 0.394, linked to the Israeli CPI published on January 15, 2013 for December 2012. Any warrants (series 10) that are not exercised by October 31, 2015, inclusive, will expire and become null and void. In June 2013, the Company’s Board of Directors decided that the exercise price of the warrants (series 10) will no longer be linked to the Israeli consumer price index. Such settlement was approved on August 20, 2013 (See note 23.v.). |
In addition, 34,635,000 warrants (series 11) were offered ("warrants (series 11)"), representing 7.11% of the Company's issued and outstanding share capital on a fully-diluted basis, which are exercisable on each trading day, excluding on the 12 and 16 of each calendar month, starting from the date of their listing for trading through April 30, 2016, inclusive. Every 25 warrants (series 11) is exercisable into one ordinary share of NIS 0.25 par value each, subject to certain adjustments for a cash exercise price of NIS 0.392, linked to the Israeli CPI published on January 15, 2013 for December 2012. Any warrants (series 11) that are not exercised by April 30, 2016, inclusive, will expire and become null and void. In June 2013, the Company’s Board of Directors decided that the exercise price of the warrants (series 11) will no longer be linked to the Israeli consumer price index. Such settlement was approved on August 20, 2013 (See note 23.v.). The shares, warrants (series 10) and warrants (series 11) were all offered to the public in 6,927 units by way of unit price bid with the minimum price being NIS 3,144 per unit.
The Company responded to the bid results by issuing 7,477 units at a price of NIS 3,544 per unit for total proceeds of NIS 23,959 thousand (net of issuance expenses of approximately NIS 2,539 thousand. The Company's issuance expenses include the grant of warrants to underwriters as a commission for handling the capital raising rounds. The issuance proceeds were received on February 5, 2013. The issuance proceeds are held in the Company's accounts and will be invested by it in accordance with its investment policy, as it will be from time to time, until they are used and provided that each investment thereof will be in solid channels, including and without derogating from the general nature of the aforementioned, an interest-bearing NIS deposit or an interest-bearing foreign currency deposit.
The shares were listed for trading on February 5, 2013.
| F-58 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 23:- | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS (Cont.) |
| e. | On February 21, 2013, the Company's board of directors approved the grant of 1,682,000 warrants (series 10) of the Company which are exercisable into 67,280 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company to the Company's external advisors. The grant was part of the issuance expenses accumulated in the Company in said capital raising round. The exercise price of the warrants is NIS 0.394 per warrant. The last exercise date of the warrants is October 31, 2015, inclusive. Assuming full exercise of all the warrants, they will represent about 0.47% of the Company's issued and outstanding share capital and about 0.34% on a fully-diluted basis. The total fair value of the warrants is approximately NIS 124 thousand. |
| f. | In addition to the foregoing, on February 5, 2013, 6,040,332 unlisted options were exercised into 241,613 shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company by an interested party in the Company in consideration of approximately NIS 60 thousand. |
| g. | On February 28, 2013, the subsidiary's board of directors approved the appointment of the new CEO who had been appointed with such board of directors’ approval in the meeting of December 12, 2012, in accordance with its decision to terminate the former CEO's service. Because the new CEO also acts as the Company's CBDO, his salary related expenses will be equally allocated between the Company and the subsidiary. The new CEO's appointment is effective from March 1, 2013. |
| h. | On March 5, 2013, 143,187 unlisted options were exercised into 5,727 shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company by an external advisor of the Company. The exercise proceeds are immaterial. |
| i. | On March 21, 2013, the Company's board of directors approved a grant of 740,000 unlisted options which are exercisable into 29,600 ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company to two employees of the Company, three senior officers and three advisors. The exercise price of the options is NIS 0.326 per option. The options can be exercised for a period of 48 months from the date of grant over eight quarters. The term of the options is ten years from the date of grant. Assuming full exercise of all the options, they will represent about 0.21% of the Company's issued and outstanding share capital and about 15% on a fully-diluted basis. The total fair value of the unlisted options is NIS 141 thousand. |
| F-59 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 23:- | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS (Cont.) |
| j. | On March 28, 2013, 2,472,107 unlisted options were exercised into 98,884 shares of NIS 0.25 par value each of the Company by an interested party in the Company in consideration of approximately NIS 25 thousand. |
| k. | On April 9, 2013, the Petach-Tikva District Court granted the Company's request to extend the exercise period of all share options (series 8) by June 30, 2013. |
| l. | On May 2, 2013, the general meeting of the Company's shareholders was convened and accepted the following decisions: |
| 1 | To reappoint Pnina Fishman, Ilan Cohn, Avraham Sartani, Liora Lev and Guy Regev as directors of the Company until the next annual general meeting of the Company; | |
| 2. | Grant of 250,000 options (unlisted) which are exercisable into 10,000 Ordinary Shares of NIS 0.25 par value each to one of the Company's directors. The exercise price of the options is NIS 0.6 per option. |
| F-60 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 23:- | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS (Cont.) |
The director is entitled to exercise half of the number of options granted to him immediately upon their grant and the other half is exercisable every quarter over a period of two years.
The 10,000 Ordinary Shares issuable upon the exercise of the options will represent approximately 0.28% of the Company on a fully-diluted basis.
On May 6, 2013, the general director of the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange approved to list the underlying shares for trading.
| 3. | In May 2013, the Company's authorized capital was increased by 500,000,000 Ordinary Shares of NIS 0.01 par value each such that the Company's authorized capital became 1,000,000,000 Ordinary Shares of NIS 0.01 par value each. The Company's authorized share capital and the issued and outstanding share capital were then consolidated at the ratio of 1:25. The Company's authorized share capital after the consolidation is NIS 10 million divided into 40 million Ordinary shares of NIS 0.25 par value each. |
According to the terms of the warrants (series 6 to 11) and according to the terms of the Company's unlisted options issued under private placements to directors, employees, advisors and officers pursuant to the option plan which the Company had adopted on June 30, 2003, the number of shares deriving from exercise of any option will be proportionately adjusted to account for the capital consolidation such that each 25 options may be exercised into one Ordinary share of the Company of NIS 0.25 par value. The exercise price of each option will not undergo any change. However, the exercise price paid per one share will be multiplied by 25.
All Ordinary Shares, warrants and options and per share amounts have been adjusted to give retroactive effect to these reverse splits for all periods presented.
| m. | On May 20, 2013, one of the Company’s advisors informed the Company that he waives the 80,000 unlisted options that he was awarded on March 21, 2013 (see Note 23i). |
| F-61 |
CAN-FITE BIOPHARMA LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| NOTE 23:- | SUBSEQUENT EVENTS (Cont.) |
| n. | On May 9, 2013, OphthaliX granted options that were modified on May 29, 2013 to purchase 58,750 shares of its common stock to its chief financial officer. These options have an exercise price of $2.00 per share and expire on May 29, 2023. 29,375 of these options vest immediately and the remaining 29,375 will vest over a period of three years on a quarterly basis for 12 consecutive quarters from the date of the grant. Also on May 9, 2013 (as modified on May 29, 2013), the OphthaliX board of directors approved the grant of options, with the same terms as the options granted to its chief financial officer, to certain members of its board of directors, its secretary and a director of Eye-Fite. The options granted to its secretary and the Eye-Fite director were rescinded on June 13, 2013 and the respective grantees waived any rights in and to such options. The options to the members of its board of directors were never granted due to the failure to obtain the approval of its stockholders for such grants. |
| o. | On May 30, 2013, the Company's board of directors appointed Ilan Cohn to be the chairman of the board of directors. |
| p. | On June 11, 2013, the Shareholders Assembly and the Series 8 Warrants holders assembly approved a settlement according to which the exercise price was changed to 0.75 NIS per ordinary share (which may fluctuate as it is based on the Israeli consumer price index) and the exercise period was extended until December 31, 2013 (the "Settlement"). On June 24, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel approved the Settlement. |
| q. | On June 17, 2013, OphthaliX sold 268,095 ordinary shares of the Company on the TASE, for aggregate consideration of $511 thousand. After such sale, OphthaliX owns 446,827 ordinary shares of the Company. |
| r. | On June 23, 2013, 6,000 registered warrants (series 8) were exercised to purchase 240 ordinary shares of the Company, par value NIS 0.25 per share. |
| s. | On July 1, 2013, the board of directors of OphthaliX approved the grant of 235,000 options to purchase 52,222 shares of its common stock to one of its directors, at an exercise price of $6.638 per share. The options vest as follows: 1/12th will vest on September 30, 2013 and 1/12th of the total options on the last day of each 11 quarters thereafter so long as he remains a director, until fully vested. |
| t. | On July 2, 2013, OphthaliX publicly filed a registration statement on Form S-1 with the SEC with respect to a potential underwritten primary public offering of its common stock. |
| u. | On July 18, 2013, 15,348 unlisted options were exercised into 613 ordinary shares of the Company, NIS 0.25 par value per share, by a director of the Company. The proceeds of such exercise are immaterial. Also on July 18, 2013, the Company provided its written consent to OphthaliX approving a reverse split of issued and outstanding common stock of OphthaliX at a ratio of 1-for-4.5. |
| v. | On August 1, 2013 and August 4, 2013, the Shareholders Assembly and the holders of series 10 warrants and series 11 warrants assembly, respectively, approved a settlement according to which the exercise price of such warrants (series 10 and series 11) will no longer be linked to the Israeli consumer price index. On August 20, 2013, the District Court in Lod, Israel approved such settlement. The settlement changes the classification of the warrants (series 10 and series 11) from liabilities to equity instruments, thereby increasing the Company’s shareholders’ equity, which in turn may be needed to meet certain listing standards of certain U.S. national securities exchanges. |
| w. | On August 4, 2013, 2,000,000 options exercisable for 80,000 ordinary shares of the Company, held by a former director of the Company, expired. |
| x. | On August 18, 2013, the Company filed an urgent application to the Petah-Tikva District Court to approve the convening of a general meeting of the Company's shareholders and a general meeting of the holders of warrants (series 6) of the Company to extend the exercise period of the warrants (series 6) until September 1, 2014. On August 26, 2013, the District Court in Petah-Tikva, Israel approved the extension of the exercise period until October 30, 2013. |
- - - - - - - - - - -
| F-62 |